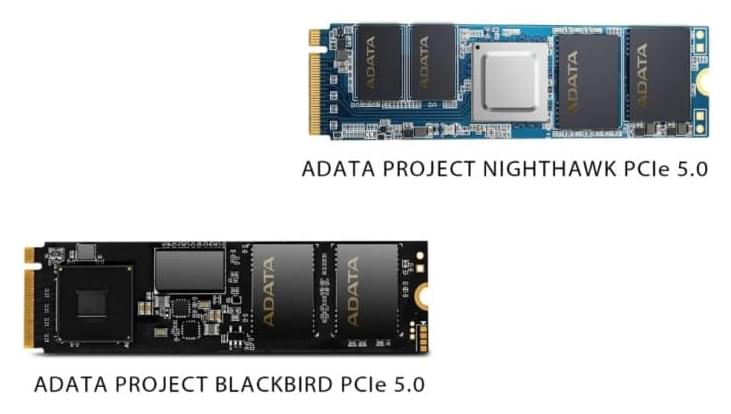
Memory and storage maker ADATA will show off a couple of sample PCIe 5.0-based NVMe SSDs at the upcoming CES 2022 event. These drives, the company claims, could read at speeds of up to 14GB/s.


=O-O=.
Moscow — President Vladimir Putin used some of his most direct language to date on Tuesday in his escalating standoff with the U.S. and its European allies. The Russian leader warned that if the U.S. and NATO do not halt what Moscow considers aggressive actions along the country’s border with Ukraine 0, Russia would respond in a “retaliatory military” manner.
“If the obviously aggressive line of our Western colleagues continues, we will take adequate, retaliatory military-technical measures [and] react toughly to unfriendly steps,” Putin told senior military officials during a meeting in remarks carried by Russian state TV. “I want to emphasize that we have every right to do so.”




Thieves are getting their hands on some quick and easy cash thanks to a new piece of equipment in town. Kiosks called EcoATM buy used phones. The company touts itself as reducing electronic waste and finding a way to reuse electronics through a simpler and safer way to sell devices. There are 5,000 machines located across the country, including several in northern Nevada. They’re located inside places like Walmart, grocery stores and malls.
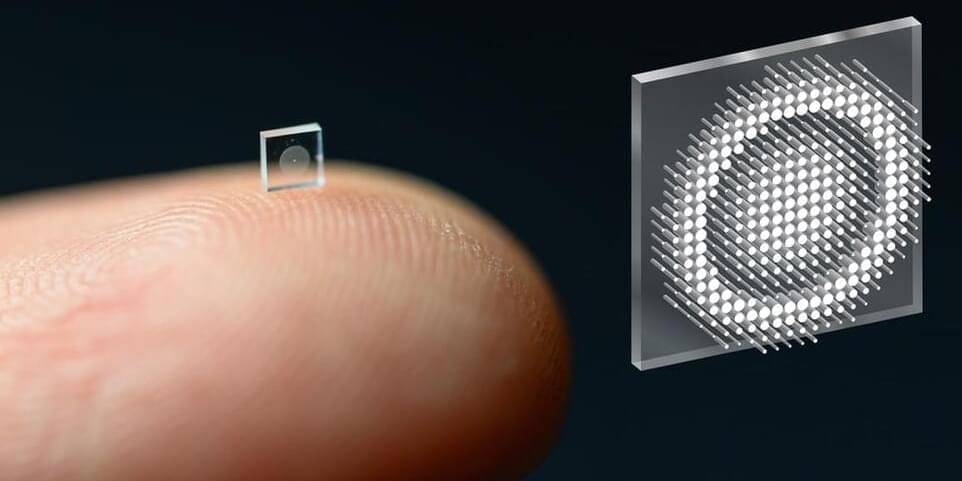
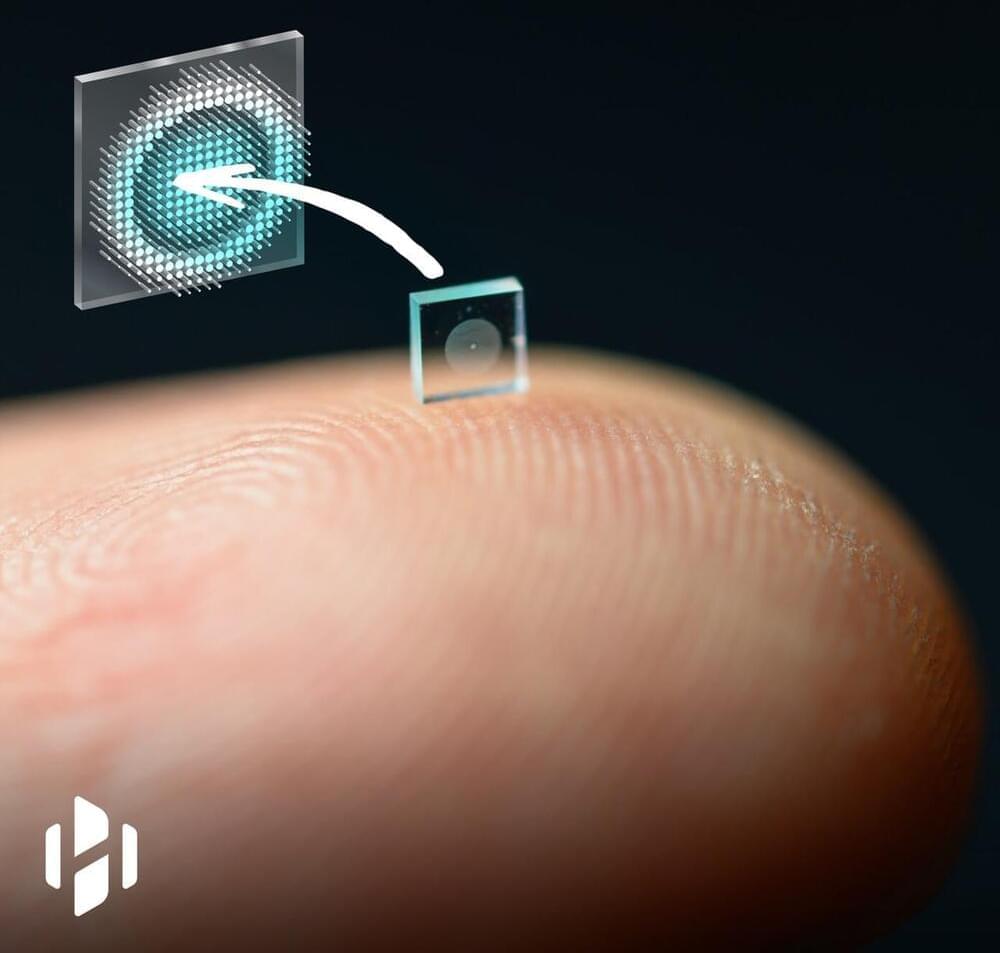
It is the highest resolution sensor of its type ever made.
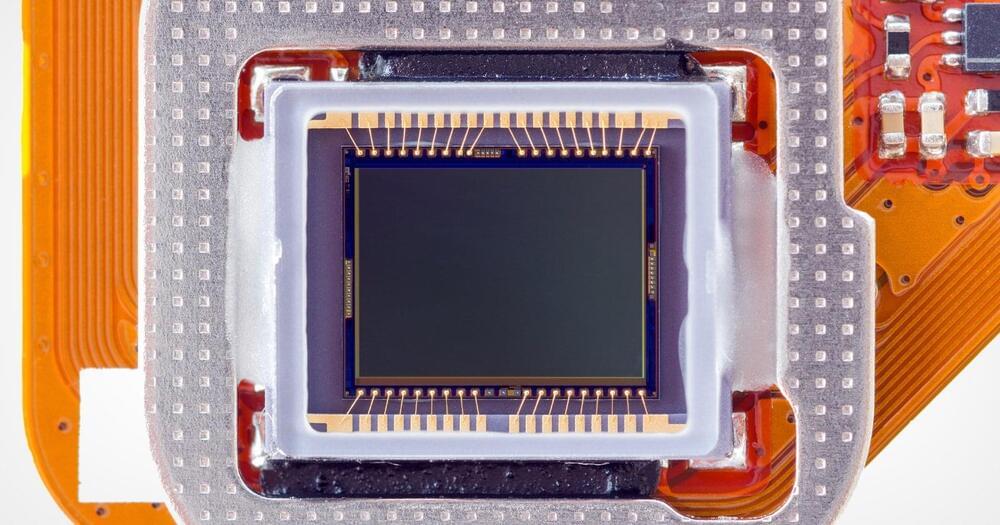
Canon has developed an image sensor that is capable of capturing high-quality color photography even in the dark. The company says that it will be able to shoot clear photos even in situations where nothing is visible to the naked eye.
In a report from Nikkei, Canon says that it has developed a new type of light-receiving element called a single photon avalanche diode (SPAD) and is implementing it on a CMOS sensor. SPAD photodetector technology on its own isn’t new, and has been in use since the 1970s. However, Canon has managed to create a sensor with 3.2 million pixels, which it says is more than three times the resolution of conventional SPADs and makes it the highest-resolution sensor of its type ever made.
The sensor is designed to replace, or at least provide an alternative to, infrared night vision cameras. Infrared is useful for recognizing shapes and providing sight in the dark, but is not capable of recognizing colors. On the flipside, cameras that can see color in the dark only do so by leveraging high ISOs, which can work to a certain point but eventually lead to extremely noisy images in levels of extreme darkness.
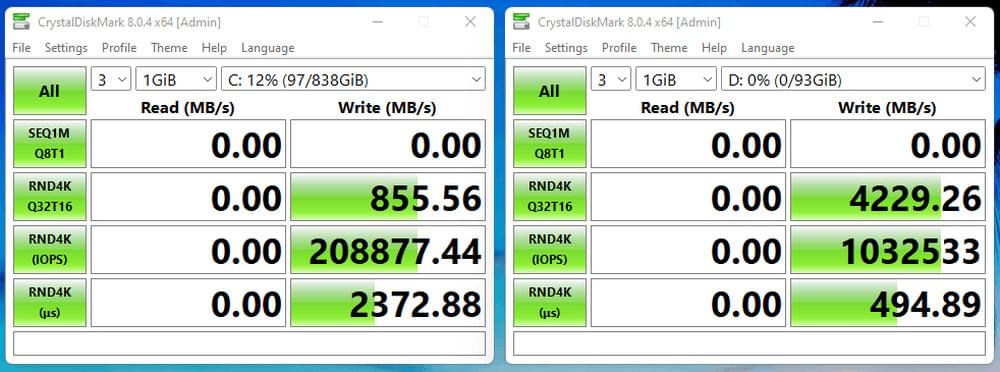
Months ago, before Windows 11 even shipped, beta users were complaining that Windows 11 was slowing their random write speeds on NVMe SSD by more than half.
Now, three months later and two months after the launch of the OS, it appears the issue is persisting.
Recent CrystalDiskMark benchmarks of the Samsung 980 Pro SSD performed by PleasedPen25317 show a massive reduction in random write speeds for any partition with Windows 11 installed.