Booyah, fellow interneters. In this episode Tesla Optimus gets an upgrade to generation 2. Droids get used to voice commands, robot dogs go sprinting, and of course where would we be without the neuromorphic cyborg supercomputer with human brain cells. This and more right here, right now! I’m Nick, let’s kick it!\
\
It is with the warmest feeling in our hearts that we thank you for staying with us. Your support and loyalty light up our path like Christmas lights. We also wish you ringing laughter, sincere gettogethers, warm embraces, unexpected surprises and bright, unforgettable moments. And to kick off these moments we are announcing a contest which will be held on December 26\
🎄✨ https://youtube.com/live/8rRhlyyfrSI?…\
\
0:00 beginning\
0:32 Merry Christmas\
1:24 Tesla news: new robot and Cybertruck\
4:09 The Digit robot understands humans\
5:07 The H1 humanoid robot is already on sale\
6:11 Robots work, not humans\
6:38 Four-legged robot mule\
7:39 The fastest four-legged robot\
8:34 The world’s first neuromorphic supercomputer\
9:51 Сyborg computer with a living organoid brain\
11:20 3D printing organs inside the body\
12:25 Robots conduct experiments and create medicines \
13:11 OpenAI creates a defense against superintelligent AI\
14:35 ESA’s mission to Mars\
\
🚀 Dive into the latest Tesla breakthroughs as we explore the new Optimus robot’s unique features and the eagerly awaited Cybertruck updates. Discover what sets Optimus apart from its counterparts, and join us as we analyze Morgan Stanley’s market predictions. Is it all just media hype, or is Tesla truly reshaping the future of technology? Let’s find out!\
\
Optimus Unleashed: Get the lowdown on how Tesla’s robot is becoming more human-like with improved agility, sensitivity, and design, mimicking the sleek style of a Model S.\
Cybertruck’s Debut: From its industrial aesthetics to Elon Musk’s quirky sense of humor, learn how the Cybertruck is more than just a vehicle—it’s a statement!\
Market Movements: Delve into Morgan Stanley’s explosive predictions for Tesla’s stock and discuss how AI and robotics could revolutionize the global labor market.\
Digit Speaks: Discover how the humanoid robot from Agility Robotics understands natural language, and ponder over the future of human-robot interaction.\
Unitree’s H1 Bot: A deep dive into the capabilities of this humanoid robot, set to revolutionize various industries with its advanced features and modularity.\
ANYmal in Action: Explore how this autonomous robot is taking over industrial inspections and what it means for the future of human labor.\
Barry the Robot Mule: Uncover the versatility of this pack robot and how it’s set to assist in construction, rescue missions, and more.\
Speedy HOUND: Meet the fastest four-legged robot that’s breaking records and setting new standards in robotics.\
DeepSouth — The Supercomputer: Learn about the world’s first neuromorphic supercomputer and its potential to unlock new horizons in AI.\
Ethical Tech Frontiers: From organ printing to cyborg computers, join us as we discuss the latest advancements and the ethical dilemmas they bring.\
Automating Science: Find out how XtalPi and ABB Robotics are transforming biochemistry labs with GoFa cobots.\
OpenAI’s Vigilance: Understand OpenAI’s strategy in defending against superintelligent AI threats and what it means for the future of technology.\
ESA’s Mars Mission: Gear up for the European Space Agency’s ambitious mission to Mars with the Rosalind Franklin rover and its quest to uncover signs of life.\
\
In this video, we’ll be discussing the evolution of ChatGPT to GPT5 | A new era of AI or the end of humanity? | Tech News | Pro Robots.\
\
chatGPT has long been a popular chatbot platform for businesses and organizations. Recently, the company has released a new platform called GPT5 which is claimed to be more advanced and robust than previous versions of the chatbot platform. In this video, we’ll be discussing the pros and cons of GPT5 and how it may change the future of AI. So whether you’re a robot lover or fearing for the future of humanity, be sure to check out this video and let us know what you think!\
\
#prorobots #ai #artificialintelligence #technology2021 #technologyfuture #Tesla, #OptimusRobot, #Cybertruck, #AI, #Robotics, #TechnologyUpdates
Category: cyborgs – Page 24

Humans as Cyborgs
Cyborgs are often misunderstood as mere humans with metallic skin or head-up displays in their visions. However, the true essence ofs lies in embedding tools within oneself, thereby augmenting and influencing personal skills. Surprisingly enough, humans have been unknowingly embracinganization for millennia through basic inventions such as clothing, serving as individual shelters against harsh weather conditions. Let’s delve deeper into understanding the fascinating history and how we are closer to the machine than man.
How Mind-Controlled Bionic Arms Fuse To The Body
A game-changer in prosthetics has been introduced to the world, and for the first time, amputees are regaining sensation through an electrical signal from their prosthetic arm. Max Ortiz-Catalan, a professor of bionics, explains the process of implanting these mind-controlled bionic arms through direct skeletal attachment. The researcher takes us through every step of this groundbreaking advancement in bionic medicine, from surgically implanting electrodes to fitting the prosthesis and training for everyday use.\r\
\r\
Director: Lisandro Perez-Rey\r\
Editor: Jordan Calig\r\
Expert: Prof. Max Ortiz Catalan\r\
Line Producer: Joseph Buscemi\r\
Associate Producer: Kameryn Hamilton\r\
Production Manager: D. Eric Martinez\r\
Production Coordinator: Fernando Davila\r\
Post Production Supervisor: Alexa Deutsch\r\
Post Production Coordinator: Ian Bryant\r\
Supervising Editor: Doug Larsen\r\
Assistant Editor: Justin Symonds\
\
Still haven’t subscribed to WIRED on YouTube? ►► http://wrd.cm/15fP7B7 \r\
Listen to the Get WIRED podcast ►► https://link.chtbl.com/wired-ytc-desc\r\
Want more WIRED? Get the magazine ►► https://subscribe.wired.com/subscribe…\r\
\r\
Follow WIRED:\r\
Instagram ►► / wired \r\
Twitter ►► / wired \r\
Facebook ►► / wired \r\
Tik Tok ►► / wired \r\
\r\
Get more incredible stories on science and tech with our daily newsletter: https://wrd.cm/DailyYT\r\
\r\
Also, check out the free WIRED channel on Roku, Apple TV, Amazon Fire TV, and Android TV. \r\
\r\
ABOUT WIRED\r\
WIRED is where tomorrow is realized. Through thought-provoking stories and videos, WIRED explores the future of business, innovation, and culture.
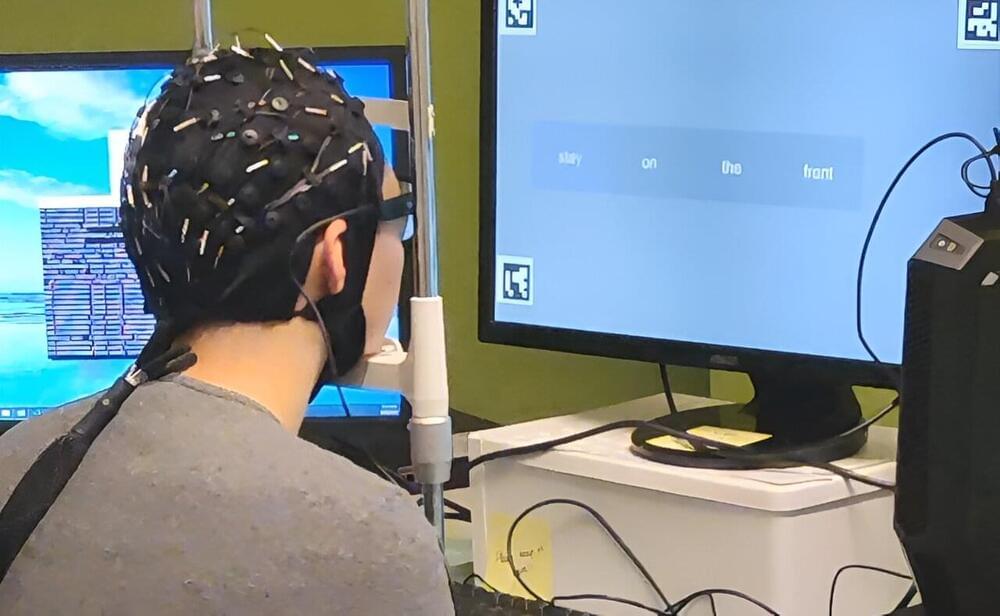

Portable, Non-invasive, Mindreading AI turns Thoughts into Text
In a world-first, researchers from the GrapheneX-UTS Human-centric Artificial Intelligence Centre at the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) have developed a portable, non-invasive system that can decode silent thoughts and turn them into text.
The technology could aid communication for people who are unable to speak due to illness or injury, including stroke or paralysis. It could also enable seamless communication between humans and machines, such as the operation of a bionic arm or robot.
The study has been selected as the spotlight paper at the NeurIPS conference, an annual meeting that showcases world-leading research on artificial intelligence and machine learning, held in New Orleans on 12 December 2023.
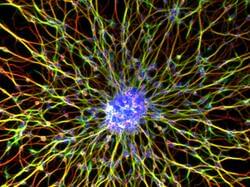
Hybrid Biocomputer Fuses Human Brain Tissue With Computer Chips
Scientists have fused human brain tissue to a computer chip, creating a mini cyborg in a petri dish that can perform math equations and recognize speech.
Dubbed Brainoware, the system consists of brain cells artificially grown from human stem cells, which have been fostered to develop into a brain-like tissue. This mini-brain organoid is then hooked up to traditional hardware where it acts as a physical reservoir that can capture and remember the information it receives from the computer inputs.
The researchers wanted to explore the idea of exploiting the efficiency of the human brain’s architecture to supercharge computational hardware. The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) has massively increased the demand for computing power, but it’s somewhat limited by the energy efficiency and performance of the standard silicon chips.

Revolutionary Mind-Reading AI System
This post is also available in:  עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)
Researchers from the Human-centric Artificial Intelligence Centre at the University of Technology Sydney have developed a portable, non-invasive system that can turn silent thoughts into text.
The technology is expected to aid communication for people who are unable to speak due to illness or injury, as well as enable seamless communication between humans and machines (like operating a bionic arm or a robot).

Scientists built a Cyborg computer with living brain tissue
📸 Look at this post on Facebook https://www.facebook.com/share/U5sBEHBUhndiJJDz/?mibextid=xfxF2i
In the realm of computing technology, there is nothing quite as powerful and complex as the human brain. With its 86 billion neurons and up to a quadrillion synapses, the brain has unparalleled capabilities for processing information. Unlike traditional computing devices with physically separated units, the brain’s efficiency lies in its ability to serve as both a processor and memory device. Recognizing the potential of harnessing the brain’s power, researchers have been striving to create more brain-like computing systems.
Efforts to mimic the brain’s activity in artificial systems have been ongoing, but progress has been limited. Even one of the most powerful supercomputers in the world, Riken’s K Computer, struggled to simulate just a fraction of the brain’s activity. With its 82,944 processors and a petabyte of main memory, it took 40 minutes to simulate just one second of the activity of 1.73 billion neurons connected by 10.4 trillion synapses. This represented only one to two percent of the brain’s capacity.
In recent years, scientists and engineers have delved into the realm of neuromorphic computing, which aims to replicate the brain’s structure and functionality. By designing hardware and algorithms that mimic the brain, researchers hope to overcome the limitations of traditional computing and improve energy efficiency. However, despite significant progress, neuromorphic computing still poses challenges, such as high energy consumption and time-consuming training of artificial neural networks.
New brain-computer interface allows people to play a game using their thoughts
😀 Amazing breakthrough face_with_colon_three
A group of Spanish researchers have developed a brain-computer interface based on electroencephalograms that allowed a group of 22 users to play a simple multiplayer game. The interface was 94% accurate in translating players’ thoughts into game moves, with each move taking just over 5 seconds. The study was published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
A brain-computer interface is a technology that enables direct communication between the human brain and external devices, such as computers or prosthetic limbs. Brain-computer interfaces work by detecting and interpreting neural signals, typically through electrodes placed on the user’s head. These signals are then translated into actionable commands, allowing individuals to control computers, devices, or applications using their thoughts.
Brain-computer interfaces offer significant potential in medicine, from helping paralyzed individuals regain environmental control to treating neurological disorders. However, their broader adoption is hindered by challenges in accuracy and the extended time required to interpret brain signals.
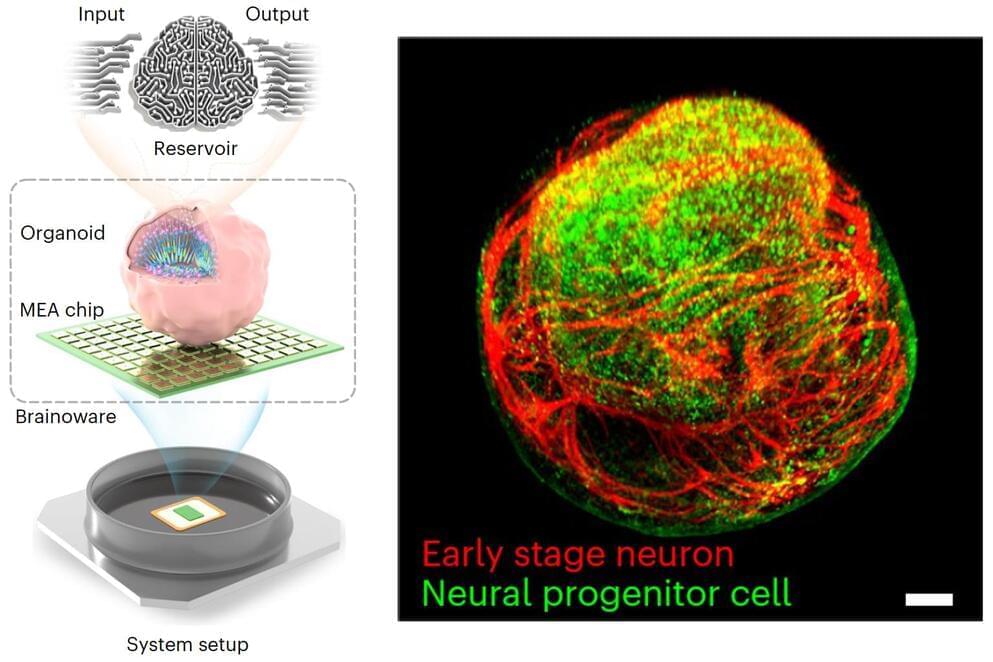
Cyborg computer with living brain organoid aces machine learning tests
Scientists have grown a tiny brain-like organoid out of human stem cells, hooked it up to a computer, and demonstrated its potential as a kind of organic machine learning chip, showing it can quickly pick up speech recognition and math predictions.
As incredible as recent advances have been in machine learning, artificial intelligence still lags way behind the human brain in some important ways. For example, the brain happily learns and adapts all day long on an energy budget of about 20 watts, where a comparably powerful artificial neural network needs about 8 million watts to achieve anything remotely comparable.
What’s more, the human brain’s neural plasticity, its ability to grow new nervous tissue and expand existing connective channels, has granted it an ability to learn from noisy, low-quality data streams, with minimal training and energy expenditure. What AI systems accomplish with brute force and massive energy, the brain achieves with an effortless elegance. It’s a credit to the billions of years of high-stakes trial and error that delivered the human brain to the state it’s in today, in which it’s chiefly used to watch vast numbers of other people dancing while we’re on the toilet.