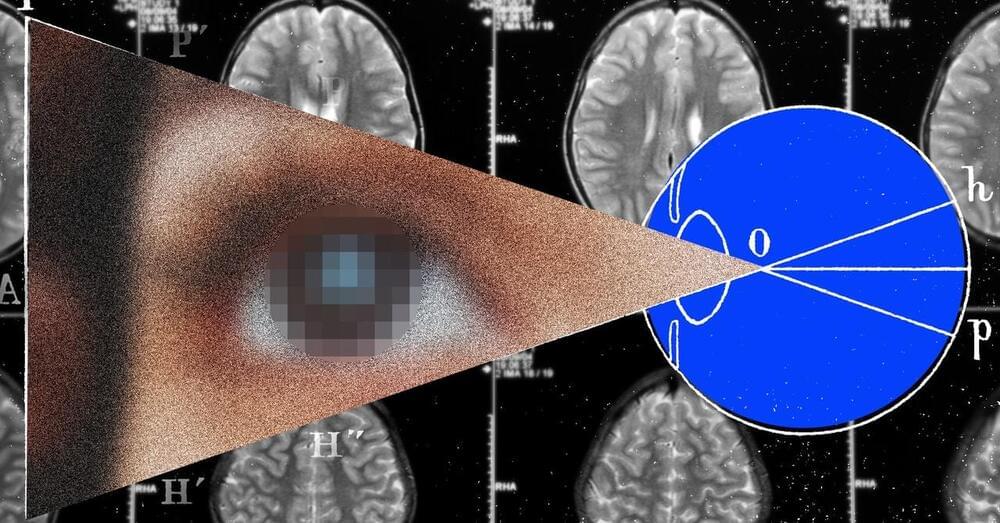
In 2021, he heard about a trial of a visual prosthesis at Illinois Institute of Technology in Chicago. Researchers cautioned that the device was experimental and he shouldn’t expect to regain the level of vision he had before. Still, he was intrigued enough to sign up. Thanks to the chips in his brain, Bussard now has very limited artificial vision—what he describes as “blips on a radar screen.” With the implant, he can perceive people and objects represented in white and iridescent dots.
Bussard is one of a small number of blind individuals around the world who have risked brain surgery to get a visual prosthesis. In Spain, researchers at Miguel Hernández University have implanted four people with a similar system. The trials are the culmination of decades of research.
There’s interest from industry, too. California-based Cortigent is developing the Orion, which has been implanted in six volunteers. Elon Musk’s Neuralink is also working on a brain implant for vision. In an X post in March, Musk said Neuralink’s device, called Blindsight, is “already working in monkeys.” He added: “Resolution will be low at first, like early Nintendo graphics, but ultimately may exceed normal human vision.”