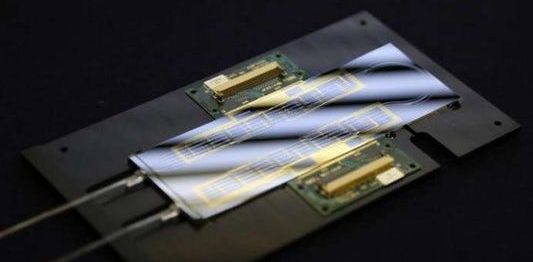
Physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and partners have demonstrated an experimental, next-generation atomic clock — ticking at high “optical” frequencies — that is much smaller than usual, made of just three small chips plus supporting electronics and optics.
Described in Optica, the chip-scale clock is based on the vibrations, or “ticks,” of rubidium atoms confined in a tiny glass container, called a vapor cell, on a chip. Two frequency combs on chips act like gears to link the atoms’ high-frequency optical ticks to a lower, widely used microwave frequency that can be used in applications.
The chip-based heart of the new clock requires very little power (just 275 milliwatts) and, with additional technology advances, could potentially be made small enough to be handheld. Chip-scale optical clocks like this could eventually replace traditional oscillators in applications such as navigation systems and telecommunications networks and serve as backup clocks on satellites.
Read more