Does the enormous computing power of neurons mean consciousness can be explained within a purely neurobiological framework, or is there scope for quantum computation in the brain?


Are you ready?
“if you were the type of geek, growing up, who enjoyed taking apart mechanical things and putting them back together again, who had your own corner of the garage or the basement filled with electronics and parts of electronics that you endlessly reconfigured, who learned to solder before you could ride a bike, your dream job would be at the Intelligent Systems Center of the Applied Physics Laboratory at Johns Hopkins University. Housed in an indistinct, cream-colored building in a part of Maryland where you can still keep a horse in your back yard, the ISC so elevates geekdom that the first thing you see past the receptionist’s desk is a paradise for the kind of person who isn’t just thrilled by gadgets, but who is compelled to understand how they work.”
Then there are the legal questions: Can the cops make you wear one? What if they have a warrant to connect your brain to a computer? How about a judge? Your commanding officer? How do you keep your Google Nest from sending light bulb ads to your brain every time you think the room is too dark?
A wearable device that can decode the voice in your head is a way’s off yet, said Jack Gallant, professor of psychology at University of California, Berkeley and a leading expert in cognitive neuroscience. But he also said, “Science marches on. There’s no fundamental physics reason that someday we’re not going to have a non-invasive brain-machine interface. It’s just a matter of time.
”And we have to manage that eventuality.”
Returning to the theme of what might be dubbed “UFO Realism” I would like to address a topic that exercises the minds of a lot of UFO conspiracy theorists, namely, reverse engineered alien technologies.
First, is there any evidence at all that any technology we currently have has any extraterrestrial element? For example, one famous claim by Colonel Corso is that much modern technology was derived from the Roswell Incident. To quote the Wikipedia entry the list includes “…particle beam devices, fiber optics, lasers, integrated circuit chips and Kevlar material”, not to mention the transistor itself.
The initial problem with these claims is twofold.
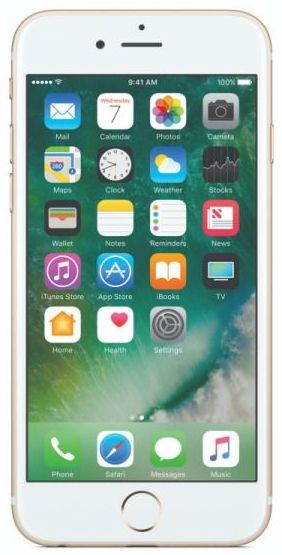
Modern construction is a precision endeavor. Builders must use components manufactured to meet specific standards — such as beams of a desired composition or rivets of a specific size. The building industry relies on manufacturers to create these components reliably and reproducibly in order to construct secure bridges and sound skyscrapers.
Now imagine construction at a smaller scale — less than 1/100th the thickness of a piece of paper. This is the nanoscale. It is the scale at which scientists are working to develop potentially groundbreaking technologies in fields like quantum computing. It is also a scale where traditional fabrication methods simply will not work. Our standard tools, even miniaturized, are too bulky and too corrosive to reproducibly manufacture components at the nanoscale.
Researchers at the University of Washington have developed a method that could make reproducible manufacturing at the nanoscale possible. The team adapted a light-based technology employed widely in biology — known as optical traps or optical tweezers — to operate in a water-free liquid environment of carbon-rich organic solvents, thereby enabling new potential applications.
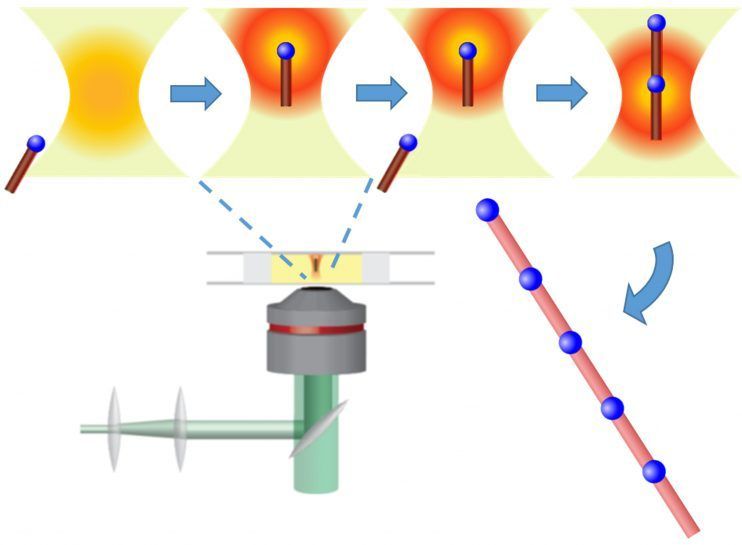
When a virus invades your cells, it changes your body. But in the process, the pathogen changes its shape, too. A new mathematical model predicts the points on the virus that allow this shape-shifting to occur, revealing a new way to find potential drug and vaccine targets. The unique math-based approach has already identified potential targets in the coronavirus that causes COVID-19.
Outlined in April in the Journal of Computational Biology, the strategy predicts protein sites on viruses that stash energy—important spots that drugs could disable. In a rare feat, the work proceeds from pure mathematics, says study author and mathematician Robert Penner of the Institute of Advanced Scientific Studies in France. “There’s precious little pure math in biology,” he adds. The paper’s predictions face a long road before they can be verified experimentally, says John Yin, who studies viruses at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and was not involved in the research. But he agrees that Penner’s approach has potential. “He’s coming at this from a mathematician’s point of view—but a very scientifically informed mathematician,” Yin says. “So that’s highly rare.”
Penner’s method takes advantage of the fact that certain viral proteins alter their shape dramatically when viruses breach cells, and this transformation depends on unstable features. (A stable protein site, by definition, resists change.) By identifying “high free energy sites”—areas on a viral protein that store lots of energy—Penner realized he could spot likely “spring” points that mediate this change in shape. He calls such high-energy spots exotic sites. Finding them required some complex math.

Tucked in the back of a laboratory at the IBM Research facility less than an hour north of New York City is a hulking mass of stainless steel and aluminum that looks like a sci-fi teleportation machine.
IBM promises a super-powerful quantum computer by decade’s end as it races against Google, Honeywell, and other rivals.

IBM today, for the first time, published its road map for the future of its quantum computing hardware. There is a lot to digest here, but the most important news in the short term is that the company believes it is on its way to building a quantum processor with more than 1,000 qubits — and somewhere between 10 and 50 logical qubits — by the end of 2023.
Currently, the company’s quantum processors top out at 65 qubits. It plans to launch a 127-qubit processor next year and a 433-qubit machine in 2022. To get to this point, IBM is also building a completely new dilution refrigerator to house these larger chips, as well as the technology to connect multiple of these units to build a system akin to today’s multi-core architectures in classical chips.


Today at TechCrunch Disrupt 2020, leaders from three quantum computing startups joined TechCrunch editor Frederic Lardinois to discuss the future of the technology. IonQ CEO and president Peter Chapman suggested we could be as little as five years away from a desktop quantum computer, but not everyone agreed on that optimistic timeline.
“I think within the next several years, five years or so, you’ll start to see [desktop quantum machines]. Our goal is to get to a rack-mounted quantum computer,” Chapman said.
But that seemed a tad optimistic to Alan Baratz, CEO at D-Wave Systems. He says that when it comes to developing the super-conducting technology that his company is building, it requires a special kind of rather large quantum refrigeration unit called a dilution fridge, and that unit would make a five-year goal of having a desktop quantum PC highly unlikely.

Electricity and magnetism are closely related: Power lines generate a magnetic field, rotating magnets in a generator produce electricity. However, the phenomenon is much more complicated: electrical and magnetic properties of certain materials are also coupled with each other. Electrical properties of some crystals can be influenced by magnetic fields—and vice versa. In this case one speaks of a “magnetoelectric effect.” It plays an important technological role, for example in certain types of sensors or in the search for new concepts of data storage.
A special material was investigated for which, at first glance, no magnetoelectric effect would be expected at all. But careful experiments have now shown that the effect can be observed in this material, it only works completely differently than usual. It can be controlled in a highly sensitive way: Even small changes in the direction of the magnetic field can switch the electrical properties of the material to a completely different state.