O.o circa 2016.
Dandelion root is being studied for possible anti-cancer properties, but there’s absolutely no proof it kills “98 percent of cancer cells in 48 hours.”



A drug molecule invented entirely by artificial intelligence is set to enter human clinical trials for the first time, marking a critical milestone for the role of machine learning in medicine.
The new compound, which has been designed to treat patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder, was developed by Oxford-based AI start-up Exscientia in collaboration with the Japanese pharmaceutical firm Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma.
In a sharp acceleration of the typical path to drug development, which can take about four and a half years, the AI-designed compound reached the point of entering clinical trials within just 12 months.

People without ANY symptoms can spread Wuhan Coronavirus.
The nation’s top infectious disease doctor says a new study published Thursday night shows people can spread the Wuhan coronavirus before symptoms set in.
German researchers found that the virus was transmitted by people without symptoms in five instances in one cluster of people: from a parent to a daughter; from that daughter to two colleagues; and from one of those colleagues to two other coworkers.
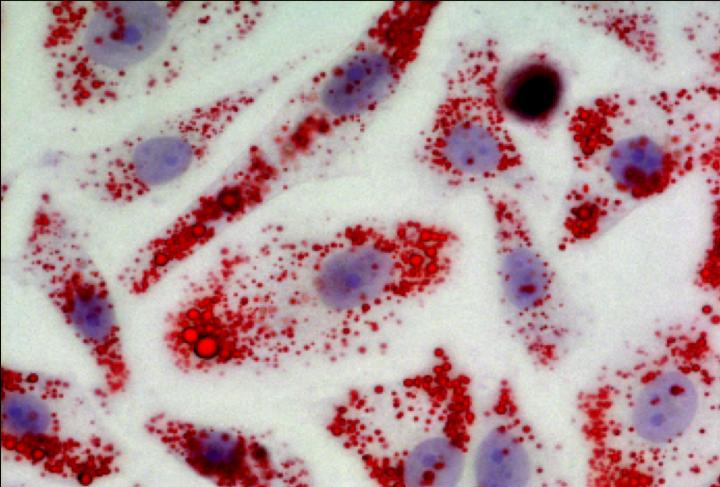
Olivier Feron, a University of Louvain researcher, studies how cancer spreads through the body via metastasis. His major discovery was that cancer cells multiply by using lipids as food. His latest discovery, published in the scientific journal Nature Communications, is that lipid storage promotes cancer invasiveness. A new drug currently being tested to treat obesity may also help fight metastasis.

VANCOUVER — Researchers at the University of British Columbia have confirmed that a rare clay used as medicine by aboriginals in B.C. contains antibacterial properties that could be used to to treat antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Some 400 kilometres north of Vancouver, on the Heiltsuk First Nation’s traditional territory, sits a 400-million kilogram deposit of glacial clay in Kisameet Bay that scientists believe was formed near the end of the last Ice Age, approximately 10,000 years ago.
The grey-green clay, known as Kisolite, has been used for centuries by the Heiltsuk First Nations to treat a range of ailments including ulcerative colitis, arthritis, neuritis, phlebitis, skin irritation, and burns. Locals also use the clay for eczema, acne and psoriasis.

From Blood to Bone (and back)! — Dr. Rhonda Prisby, from University of Texas at Arlington, joins me on ideaXme (http://radioideaxme.com/) to discuss her fascinating research in the Bone Vascular and Micro-Circulation Laboratory, focusing on the unique interaction between vascular and skeletal systems, and novel disease states where vessels become bone-like “dead space”! — https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PsK-pPjW020&t=1s #Ideaxme #Bone #Microcirculation #Vasculature #Ossification #Atherosclerosis #Parathyroid #Osteoblast #Osteoclast #Health #Wellness #Regeneration #Longevity #Aging #IraPastor #Bioquark #Regenerage
Ira Pastor, ideaXme exponential health ambassador, interviews Dr. Rhonda Prisby, Associate Professor in the Department of Kinesiology, at The University of Texas at Arlington.
Ira Pastor comments:
We have a fascinating show today focusing on the intersection of the cardiovascular system and the skeletal system.
We will be discussing interesting recent evidence that suggests a unique link between cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis, a disease in which both the density and quality of bone are reduced, where bones become more porous and fragile, and the risk of fracture is greatly increased.