The Microsoft founder noted that the virus spreads faster than Ebola and warned the situation could lead to a pandemic, killing 10 million worldwide.



More than 2000 Australian suffering from advanced melanoma will soon receive financial relief with an expansion of treatments on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, federal Health Minister Greg Hunt says.
From March 1 the PBS listed Opdivo (nivolumab) will be expanded, assisting 1500 patients who might otherwise pay more than $100,000 per course of treatment without the PBS subsidy.
“Opdivo is a breakthrough immunotherapy which works by blocking proteins and helping the body’s own immune system to find, attack and destroy cancer cells,” Mr Hunt said in a statement on Sunday.


Regeneron will work with the U.S. government to develop antibody treatments for the new coronavirus from China, disclosing Tuesday an expansion of a partnership that previously yielded an experimental drug cocktail for the Ebola virus.
The Tarrytown, New York-based biotech is one of roughly a dozen drugmakers now working on treatments for the coronavirus that emerged late last year in Wuhan, China. Most are smaller companies unlikely to possess sufficient funds to run large-scale tests, although Johnson & Johnson and Gilead have announced initial efforts in recent weeks.
The biotech hopes to replicate its past success in quickly advancing a treatment for Ebola. But, as that experience showed, proving a new antiviral isn’t easy.

Since the new coronavirus was first identified in Wuhan, China, on Jan. 7, companies and academic groups around the world have been working at breakneck pace to develop new therapies for the virus, now called SARS-CoV-2. This week, two US biotech firms, Moderna and Gilead Sciences, positioned themselves as frontrunners.
The world’s first clinical trial of a vaccine for the novel coronavirus will soon begin in the US. On Feb. 25, Moderna announced that it has shipped its experimental vaccine to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which will conduct the trial. The entire process—from vaccine design to manufacturing to shipment—took only 7 weeks.
Gilead has a head start on an antiviral, while Moderna is pursuing a novel mRNA vaccine.
The treatment could hold real promise as coronavirus infections and deaths outside of China continue to swell. “There is only one drug right now that we think may have real efficacy and that’s remdesivir,” said WHO assistant director-general Bruce Aylward during a press conference in Beijing on Monday. The drug is already being enlisted in clinical trials in China.
Gilead’s antiviral remdesivir is being used in the first U.S. clinical trial to treat COVID-19, the disease caused by the new coronavirus.

Wuhan Coronavirus Pandemic — Washington state: 1 death and 1 community spread case and 1 travel case.
“One case involves a teenager in Everett with no travel history. He is a presumptive positive, meaning tests have come back positive for the virus, while pending confirmation from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. He is currently in home isolation. Health officials don’t know how or where the teenager was infected, and are working on identifying anyone the teen may have come into contact with. The student attends Jackson High School in the Everett School District.
The second case involves a King County woman in her 50s who recently traveled to Daegu, South Korea. Her status is also presumptive positive and she is in home isolation.”
The first U.S. coronavirus-related death was reported in King County on Saturday, according to the Washington Department of Health.
Public Health – Seattle & King County will hold a news conference at 1 p.m. with more details. KIRO Radio will stream the news conference LIVE.
Person connected to Bothell H.S. tests negative for coronavirus

Removal of an essential gene was a major contributor to preterm labor, according to recent research.
Researchers from Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center started with a pathway linked to the tumor suppressor gene known as transformation-related protein 53 (Trp53), which encodes another protein: p53. Mutations of Trp53 are found in a variety of cancers, but the gene’s function in female reproduction and other normal physiological processes is not well understood. The role of p53, sometimes referred to as the “guardian angel gene,” is to help preserve genetic stability and prevent mutation.
The researchers targeted certain signaling pathways that function both in pregnancy and during the formation of cancerous tumors. During pregnancy, the pathways are usually tightly regulated. In tumor development, however, they can become dysfunctional.

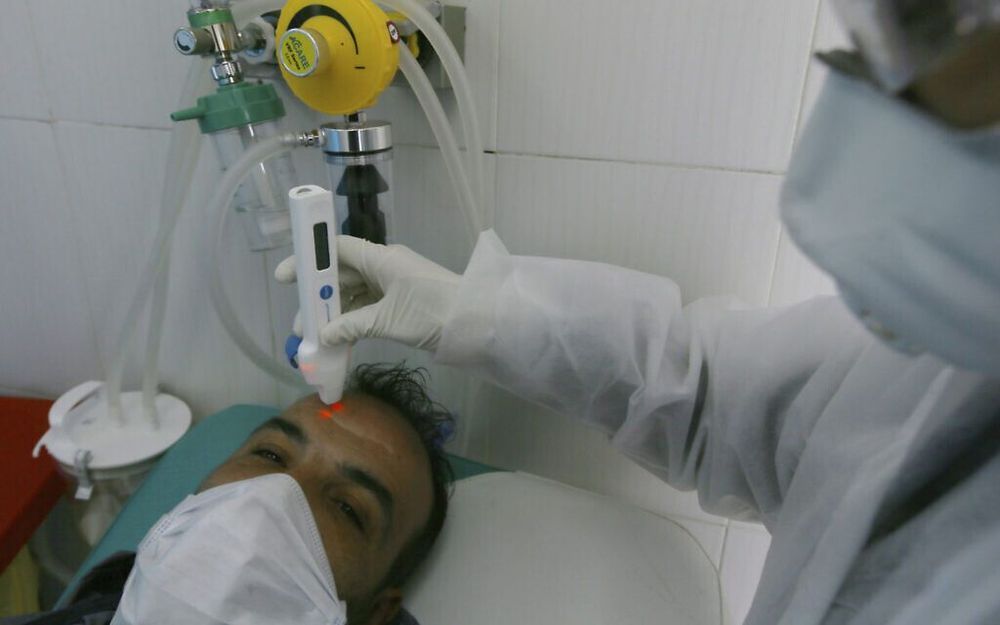
A dog in Hong Kong has tested positive for the COVID-19 virus that’s killed at least 2,859 humans across the world over the last two months, World Health Organization officials said Friday.
Dr. Maria Van Kerkhove, the technical lead of WHO’s emergencies program, said the canine tested “weakly positive,” meaning low levels of the virus were found.
Hong Kong scientists aren’t sure if the dog is actually infected or if it picked up the virus from a contaminated surface, she said.