Industrial yeasts are a powerhouse of protein production, used to manufacture vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, and other useful compounds. In a new study, MIT chemical engineers have harnessed artificial intelligence to optimize the development of new protein manufacturing processes, which could reduce the overall costs of developing and manufacturing these drugs.
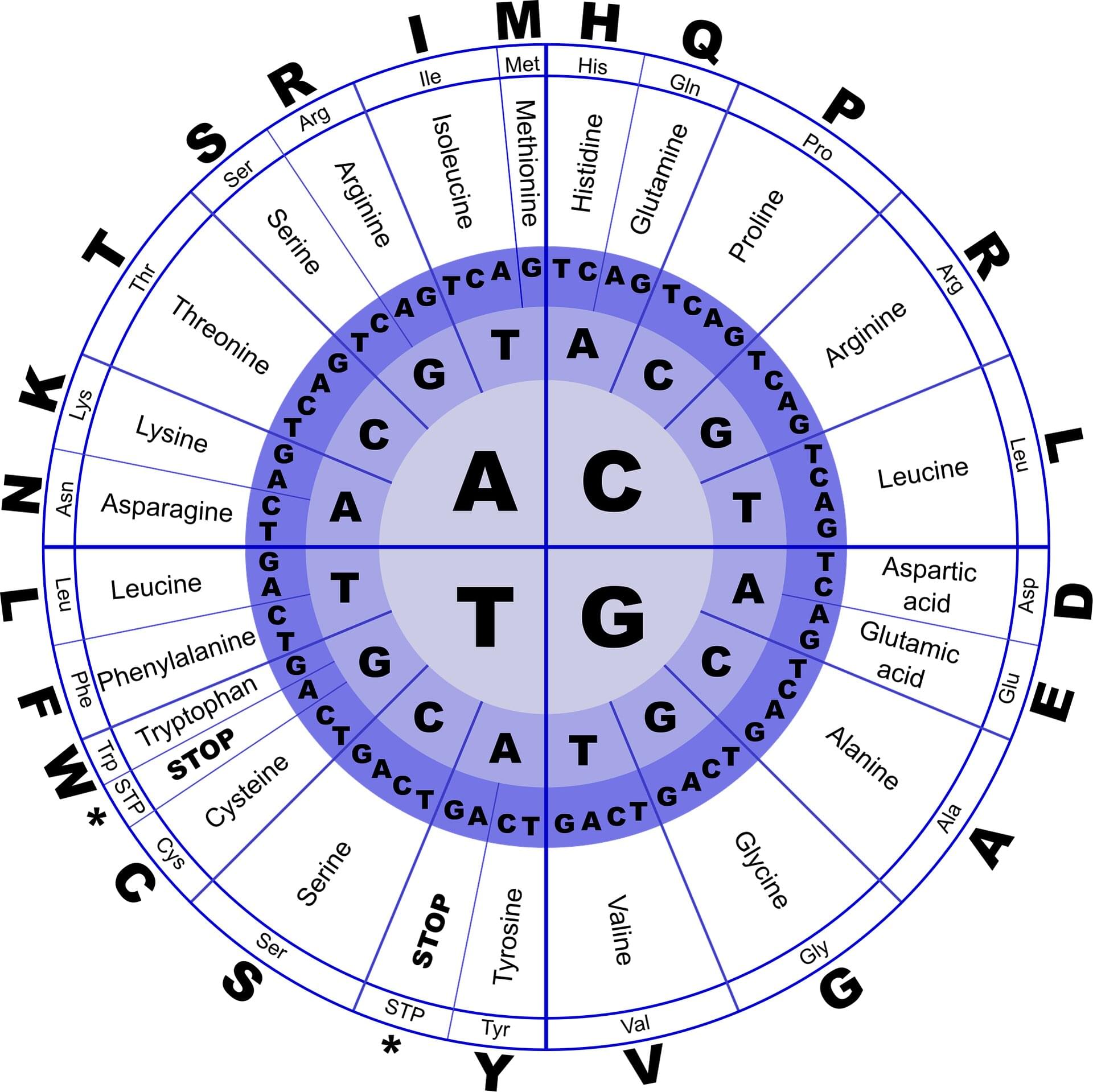
Using a large language model (LLM), the MIT team analyzed the genetic code of the industrial yeast Komagataella phaffii — specifically, the codons that it uses. There are multiple possible codons, or three-letter DNA sequences, that can be used to encode a particular amino acid, and the patterns of codon usage are different for every organism.
The new MIT model learned those patterns for K. phaffii and then used them to predict which codons would work best for manufacturing a given protein. This allowed the researchers to boost the efficiency of the yeast’s production of six different proteins, including human growth hormone and a monoclonal antibody used to treat cancer.