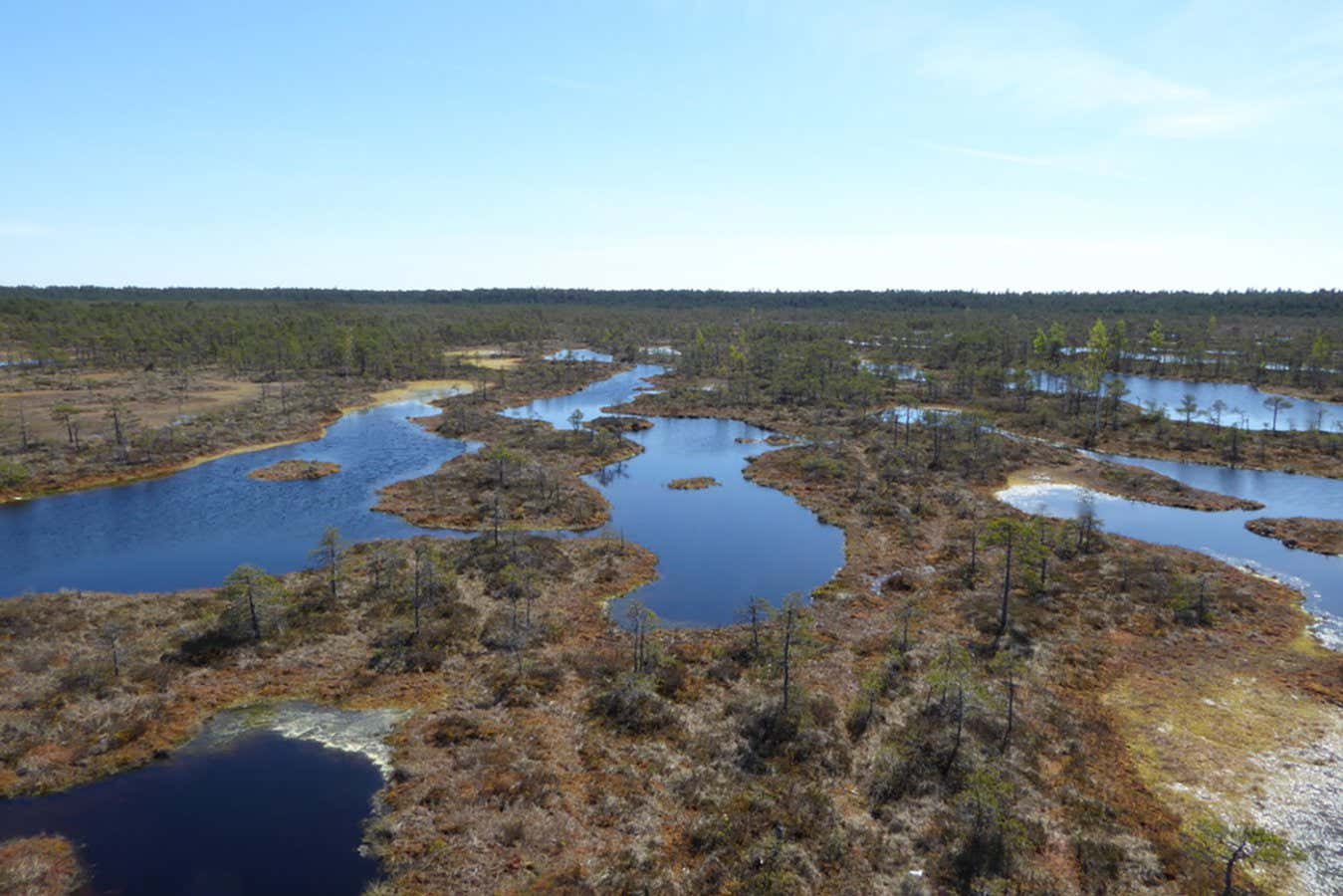
Photosynthesising microbes in soil may increase their activity as temperatures rise, offsetting some of the carbon emissions expected to be released from peatland and permafrost


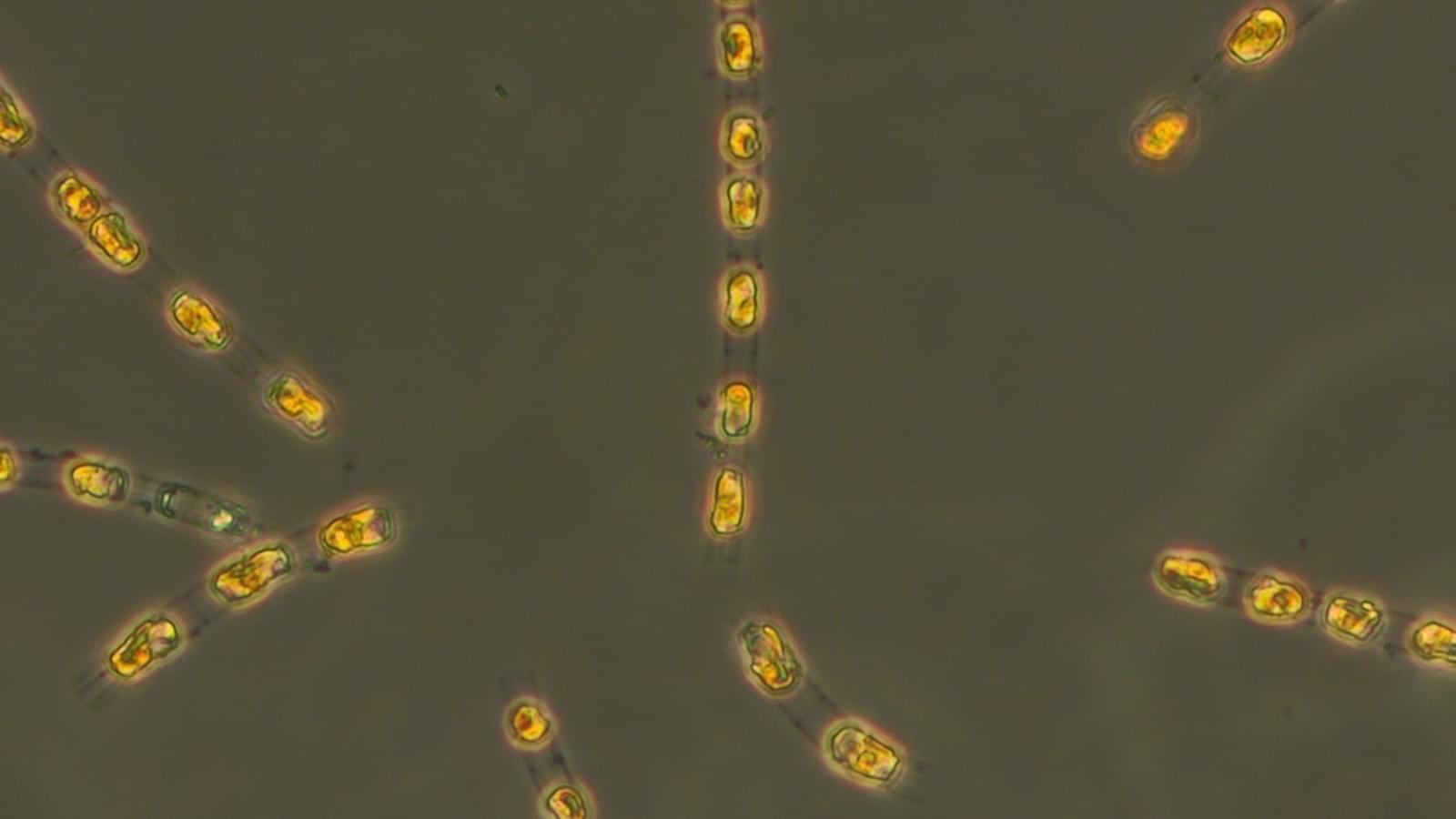

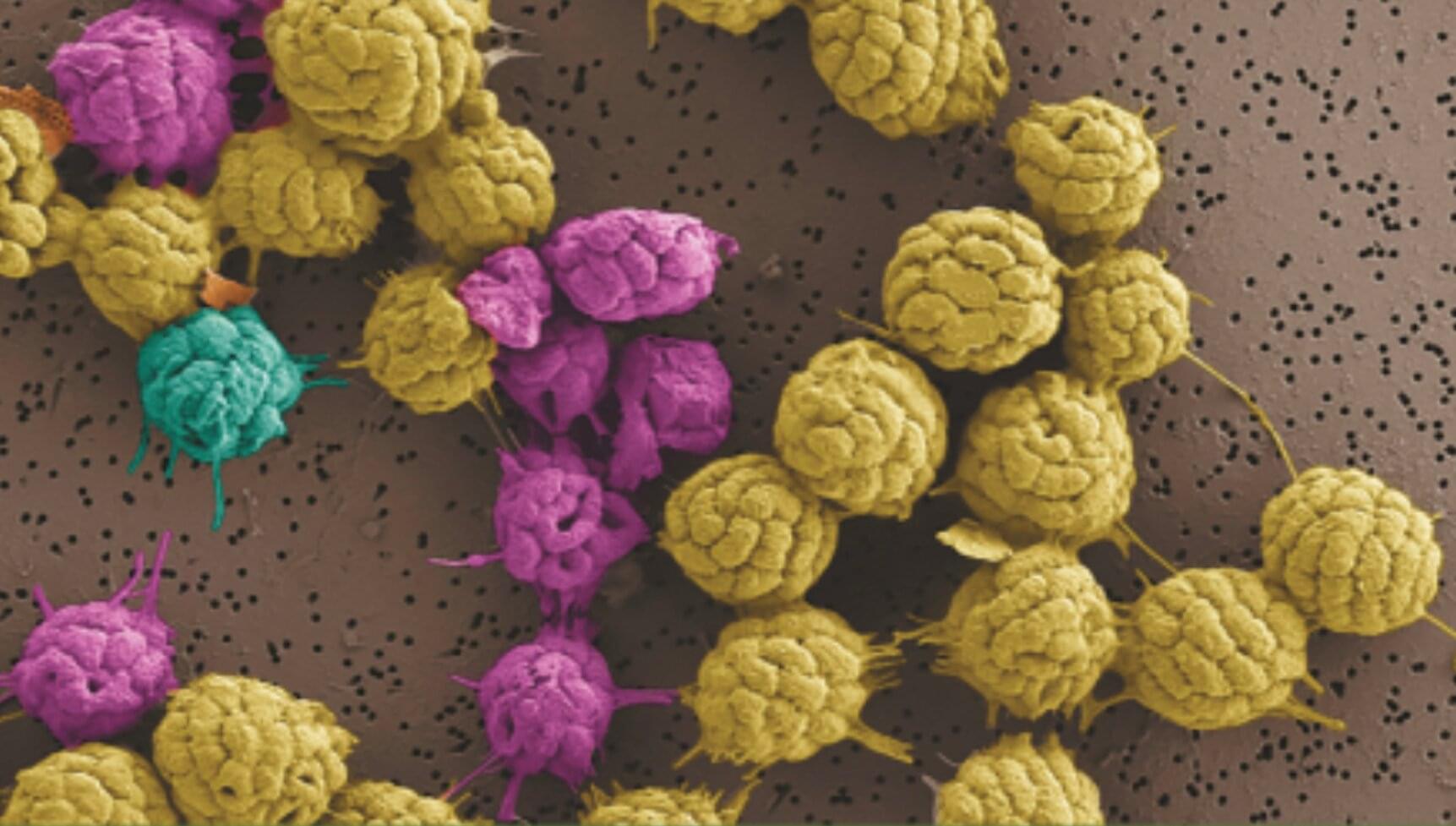
In a recent study, researchers gained new insight into the lives of bacteria that survive by grouping together as if they were a multicellular organism. The organisms in the study are the only bacteria known to do this in this way, and studying them could help astrobiologists explain important steps in the evolution of life on Earth.
The work is published in the journal PLOS Biology.
The organisms in the study are known as multicellular magnetotactic bacteria (MMB). Being magnetotactic means that MMB are part of a select group of bacteria that orient their movement based on Earth’s magnetic field using tiny “compass needles” in their cells. As if that weren’t special enough, MMB also live bunched up in collections of cells that are considered by some scientists to exhibit “obligate” multicellularity, the trait on which the new study is focused.
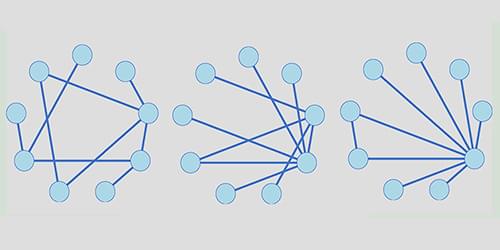
Network models provide a flexible way of representing objects and their multifaceted relationships. Deriving a network entails mapping hidden structures in inevitably noisy data—a critical task known as reconstruction. Now Gang Yan and Jia-Jie Qin of Tongji University in China have provided a mathematical proof showing what makes some networks easier to reconstruct than others [1].
Complex systems in biology, physics, and social sciences tend to involve a vast number of interacting entities. In a network model, these entities are represented by nodes, linked by connections weighted to describe the strength of each interaction. Yan and Qin took an empirical dataset and used a statistical inference method to calculate the likelihood that any pair of nodes is directly linked. Then, based on the true positive and false positive rates of these inferred connections, they analyzed the fidelity of the reconstructed networks. They found that the most faithful reconstructions are obtained with systems for which the number of connections per node varies most widely across the network. Yan and Qin saw the same tendency when they tested their model on synthetic and real networks, including metabolic networks, plant-pollinator webs, and power grids.
With the rapid increase in available data across research areas, network reconstruction has become an important tool for studying complex systems. Yan and Qin say their new result both solves the problem of what complex systems can be easily mapped into a network and provides a solid foundation for developing methods of doing so.
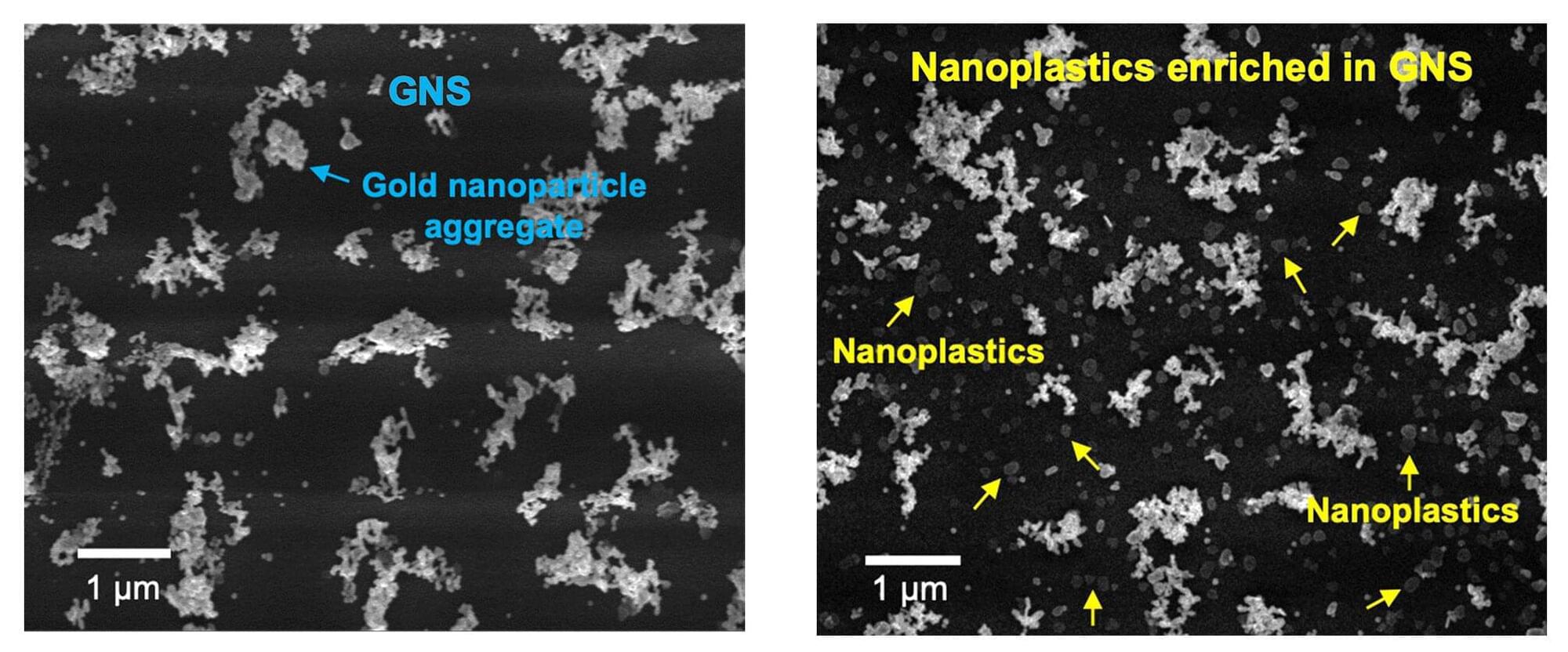
While the threat that microplastics pose to human and ecological health has been richly documented and is well known, nanoplastics, which are smaller than one micrometer (1/50th the thickness of an average human hair), are far more reactive, far more mobile and vastly more capable of crossing biological membranes. Yet, because they are so tiny and so mobile, researchers don’t yet have an accurate understanding of just how toxic these particles are.
The first step to understanding the toxicology of nanoplastics is to build a reliable, efficient and flexible tool that can not only quantify their concentration in a given sample, but also analyze which specific plastics that sample contains.
An international team of scientists led by the University of Massachusetts Amherst reports in Nature Water on the development of a new tool, known as the OM-SERS setup, which can do all of these things and can furthermore be used to detect particular nanoplastic concentrations and polymer types in solid samples, such as soils, body tissues and plants.

Why do certain plants flourish in some regions but not in others? A study led by researchers at the University of Göttingen sheds light on the factors that determine where plants grow and how these patterns have evolved over millions of years.
The team analyzed data from nearly 270,000 seed plant species.
A species is a group of living organisms that share a set of common characteristics and are able to breed and produce fertile offspring. The concept of a species is important in biology as it is used to classify and organize the diversity of life. There are different ways to define a species, but the most widely accepted one is the biological species concept, which defines a species as a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce viable offspring in nature. This definition is widely used in evolutionary biology and ecology to identify and classify living organisms.
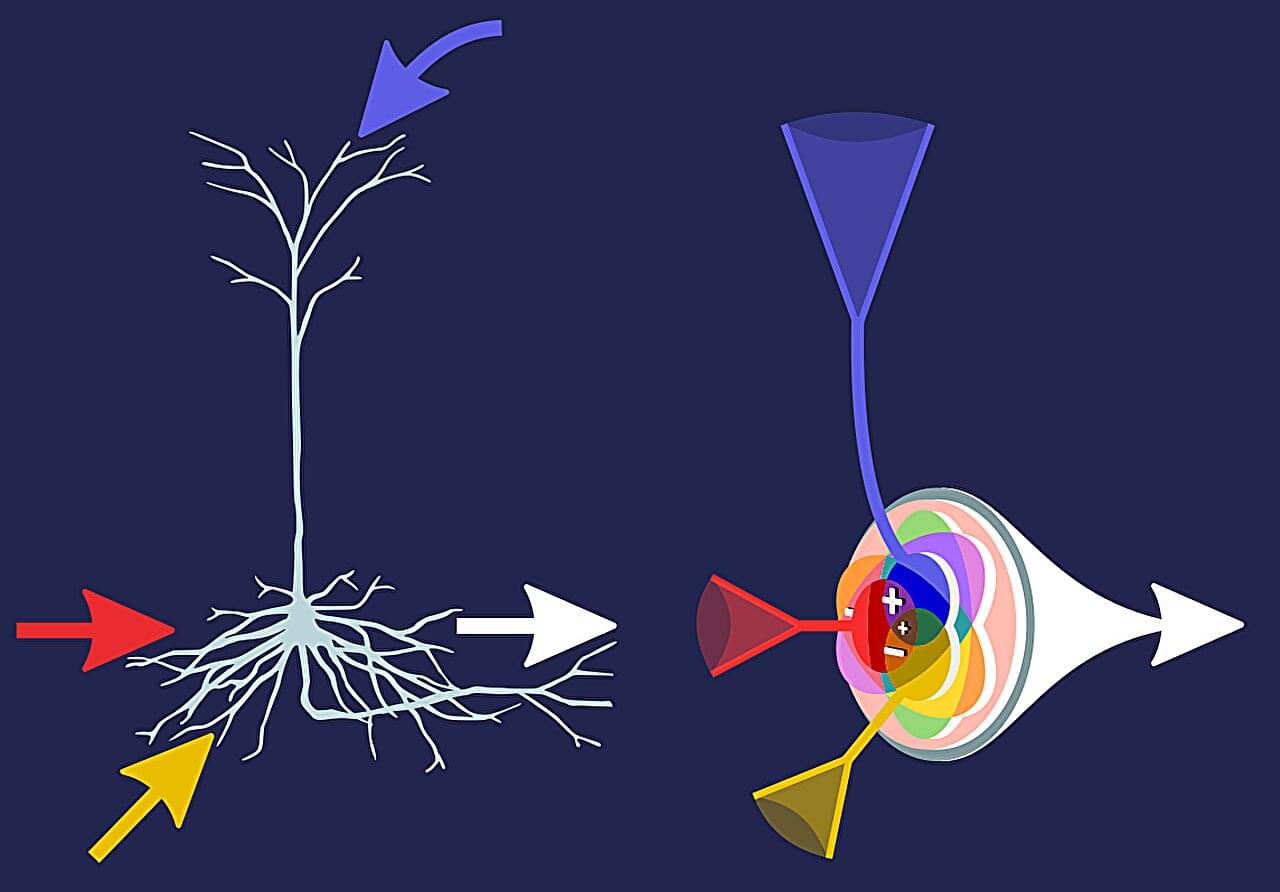
Researchers have developed “infomorphic neurons” that learn independently, mimicking their biological counterparts more accurately than previous artificial neurons. A team of researchers from the Göttingen Campus Institute for Dynamics of Biological Networks (CIDBN) at the University of Göttingen and the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPI-DS) has programmed these infomorphic neurons and constructed artificial neural networks from them.
The special feature is that the individual artificial neurons learn in a self-organized way and draw the necessary information from their immediate environment in the network. Their findings are published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Both the human brain and modern artificial neural networks are extremely powerful. At the lowest level, the neurons work together as rather simple computing units.
Humans like to think that being multicellular (and bigger) is a definite advantage, even though 80% of life on Earth consists of single-celled organisms—some thriving in conditions lethal to any beast.
In fact, why and how multicellular life evolved has long puzzled biologists. The first known instance of multicellularity was about 2.5 billion years ago, when marine cells (cyanobacteria) hooked up to form filamentous colonies. How this transition occurred and the benefits it accrued to the cells, though, is less than clear.
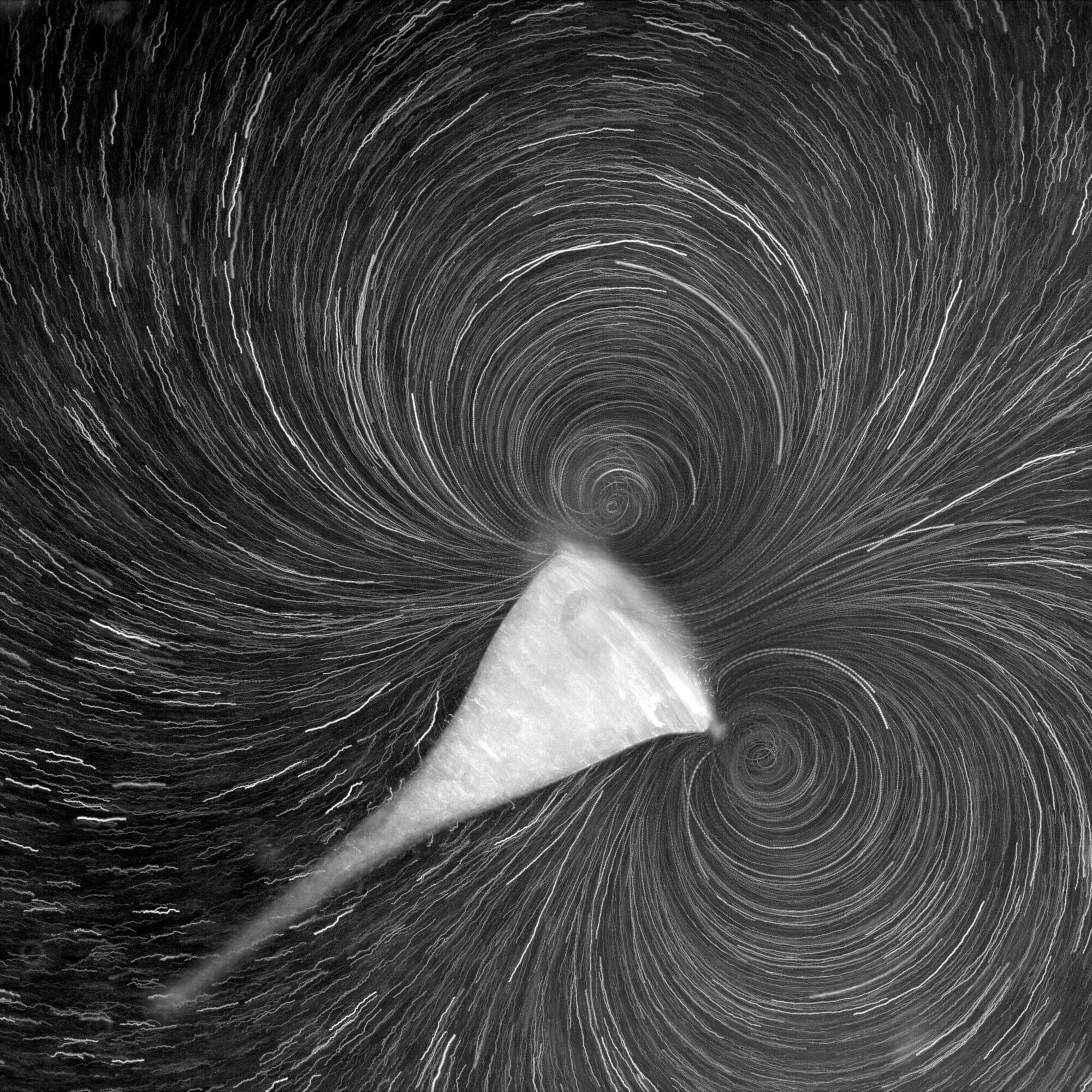
A study originating from the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) presents a striking example of cooperative organization among cells as a potential force in the evolution of multicellular life. Based on the fluid dynamics of cooperative feeding by Stentor, a relatively giant unicellular organism, the report is published in Nature Physics.
Biological systems, once thought too chaotic for quantum effects, may be quietly leveraging quantum mechanics to process information faster than anything man-made.
New research suggests this isn’t just happening in brains, but across all life, including bacteria and plants.
Schrödinger’s legacy inspires a quantum leap.