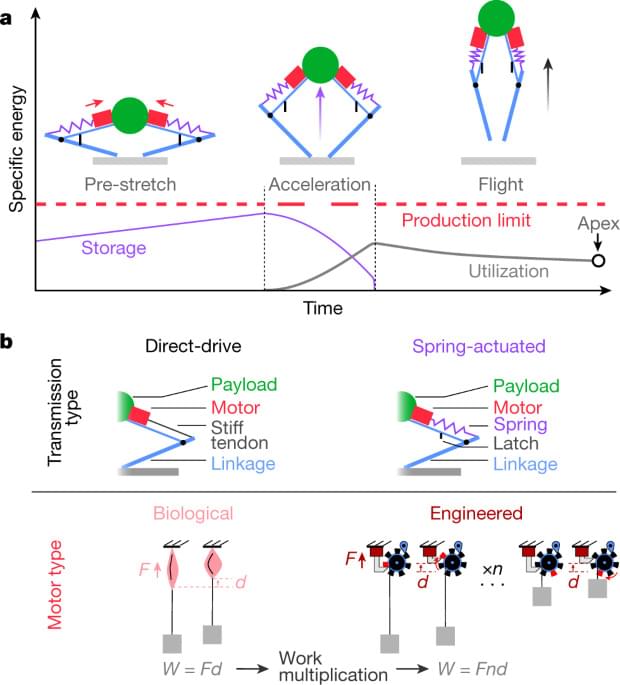
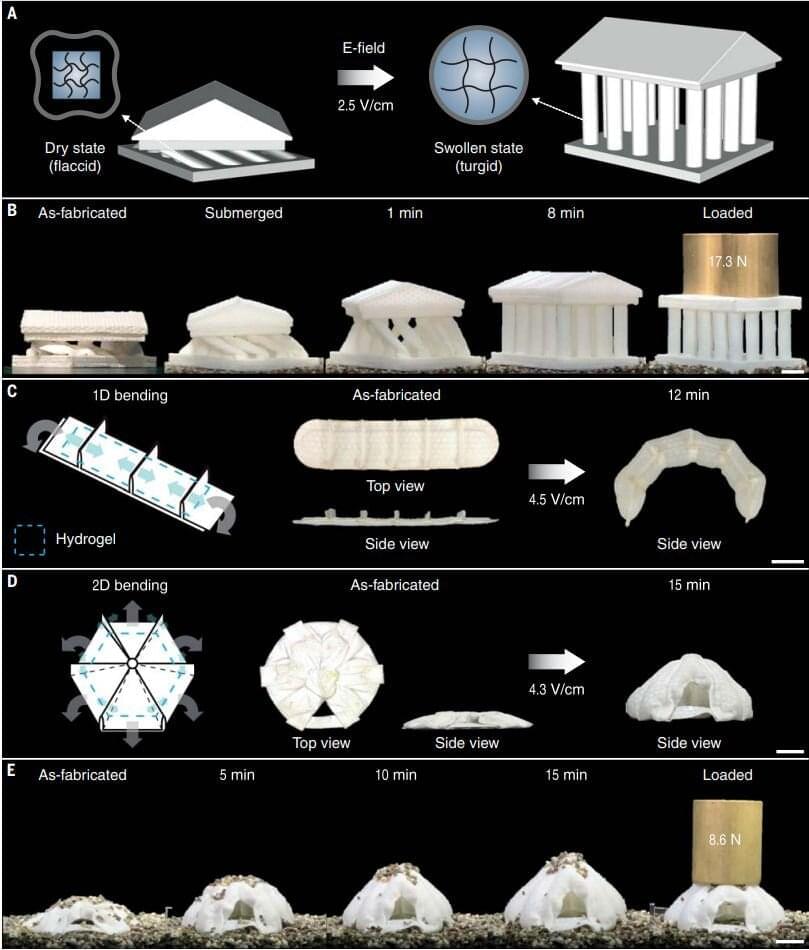
Would start with scanning and reverse engineering brains of rats, crows, pigs, chimps, and end on the human brain. Aim for completion by 12/31/2025. Set up teams to run brain scans 24÷7÷365 if we need to, and partner w/ every major neuroscience lab in the world.
If artificial intelligence is intended to resemble a brain, with networks of artificial neurons substituting for real cells, then what would happen if you compared the activities in deep learning algorithms to those in a human brain? Last week, researchers from Meta AI announced that they would be partnering with neuroimaging center Neurospin (CEA) and INRIA to try to do just that.
Through this collaboration, they’re planning to analyze human brain activity and deep learning algorithms trained on language or speech tasks in response to the same written or spoken texts. In theory, it could decode both how human brains —and artificial brains—find meaning in language.
By comparing scans of human brains while a person is actively reading, speaking, or listening with deep learning algorithms given the same set of words and sentences to decipher, researchers hope to find similarities as well as key structural and behavioral differences between brain biology and artificial networks. The research could help explain why humans process language much more efficiently than machines.