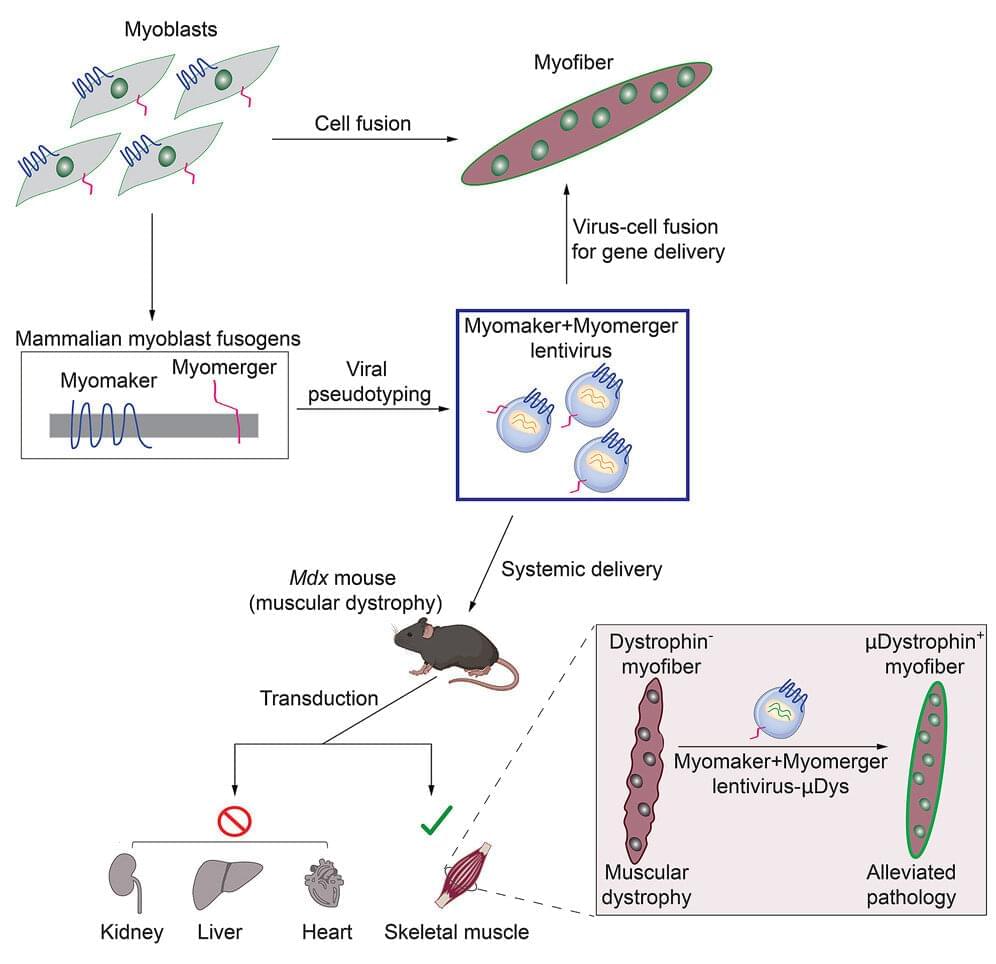
Doug Millay, Ph.D., a scientist with the Division of Molecular Cardiovascular Biology at Cincinnati Children’s has dedicated his career to revealing the most fundamental mechanisms of skeletal muscle development. He has been a leader in characterizing how two “fusogens” called Myomaker and Myomerger mediate the entry of stem cells into mature muscle cells to build the tissue that humans depend upon for movement, breathing, and survival.
Now, some of the basic discoveries made by Millay and colleagues are translating into a potential treatment for people living with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). Their latest research, published April 12, 2023, in the journal Cell, reveals that in mice, modified viruses, engineered with Myomaker and Myomerger, result in specific fusion with muscle cells. These viruses can therefore be used as a vector to deliver a vital gene needed for muscle function that is mutated in people with DMD.
A key unknown prior to this work was whether proteins like Myomaker and Myomerger, which mainly function on cells, could even work on viruses. First author Sajedah Hindi, Ph.D., also with the Division of Molecular Cardiovascular Biology at Cincinnati Children’s and a leading member of the research team, took on the challenge to test this idea.