The future of floating additive manufacturing.
Category: 3D printing – Page 139
Australian surgeon inserts 3D-printed vertebrae in world-first
An Australian neurosurgeon has completed a world-first marathon surgery removing cancer-riddled vertebrae and successfully replacing them with a 3D-printed body part.
Doctors implant 3D-printed vertebrae in ‘world’s first’ surgery
Just Amazing
Ralph Mobbs, a neurosurgeon at the Prince of Wales Hospital in Sydney, made medical history in late 2015 when he successfully replaced two vertebrae with custom made prosthesis. The patient, in his 60s, suffered from Chordoma, a particularly nasty form of cancer that had formed on his top two vertebrae and threatened to cinch off his spinal cord as it grew. That would have left him a quadriplegic. Complicating matters, those top two vertebrae are what allow you to turn and tilt your head, so it’s not like doctors can easily fashion a replacement out of bone grafted from another part of the patient’s body. They have to fit perfectly and that’s where the 3D printers come in.
Mobbs worked with Anatomics, an Australian medical device manufacturer, to craft perfect replicas of the patient’s top two vertebrae out of titanium. This is the first time that these two particular neck bones have been printed and installed. “To be able to get the printed implant that you know will fit perfectly because you’ve already done the operation on a model … It was just a pure delight,” Mobbs told Mashable Australia. “It was as if someone had switched on a light and said ‘crikey, if this isn’t the future, well then I don’t know what is’.”
The surgery itself was no small feat. The 15-hour procedure is fraught with peril as the medical team operates within inches of the top of the spinal cord as well as the brainstem and numerous major arteries. “The surgery that we’re doing today is a particularly complicated and long and difficult surgery. It involves exposure at the top of the neck where the neck and the head meets,” Mobbs told ABC 7.30. “It’s essentially disattaching the patient’s head from his neck and taking the tumour out and reattaching his head back onto his neck.” Thankfully, the surgery was a success. Mobbs was able to remove the tumor and implant the prosthetic.
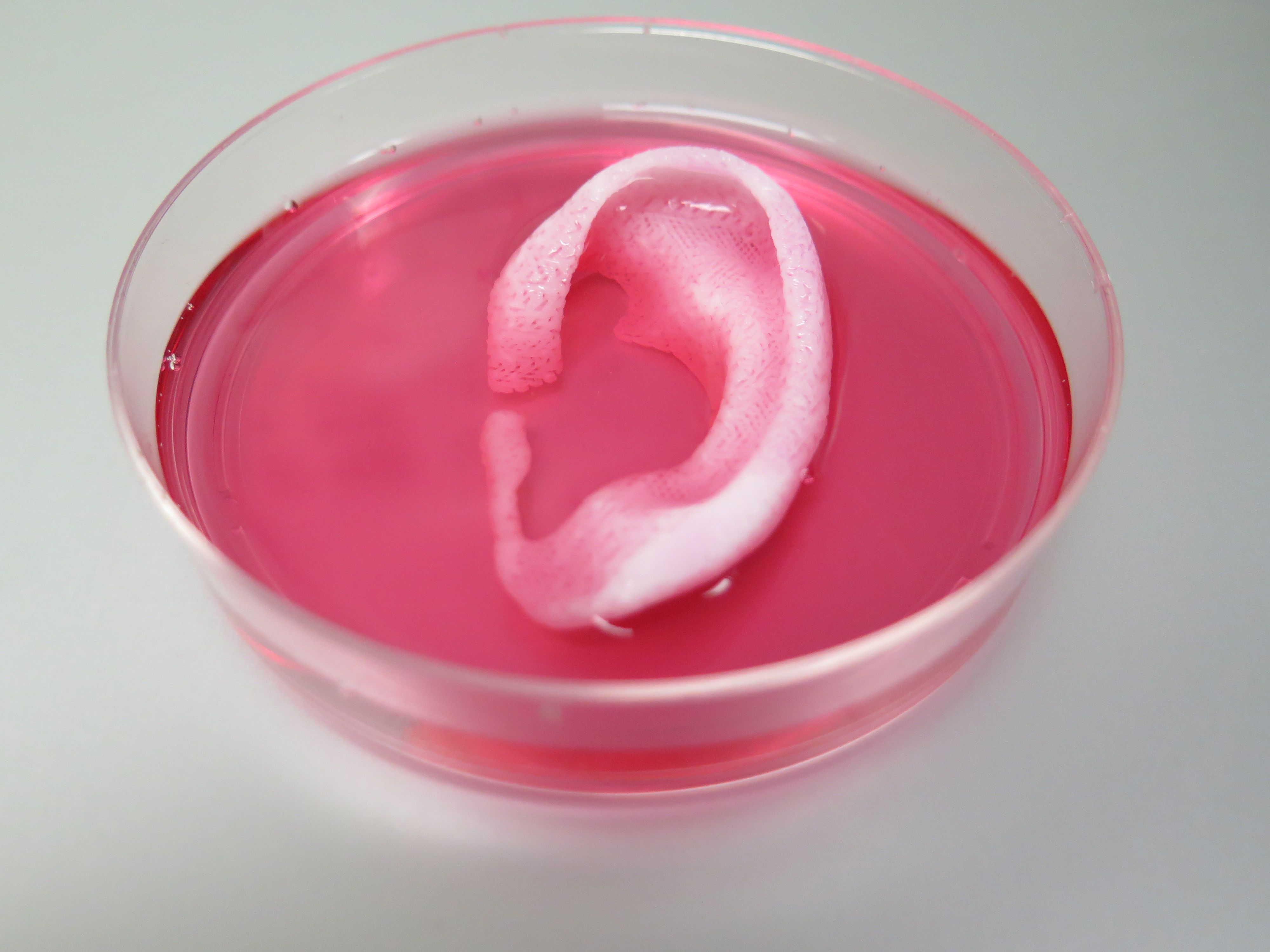
Regenerative medicine scientists ‘print’ replacement tissue
Using a sophisticated, custom-designed 3D printer, regenerative medicine scientists at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center have proved that it is feasible to print living tissue structures to replace injured or diseased tissue in patients.
Reporting in Nature Biotechnology, the scientists said they printed ear, bone and muscle structures. When implanted in animals, the structures matured into functional tissue and developed a system of blood vessels. Most importantly, these early results indicate that the structures have the right size, strength and function for use in humans.
“This novel tissue and organ printer is an important advance in our quest to make replacement tissue for patients,” said Anthony Atala, M.D., director of the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) and senior author on the study. “It can fabricate stable, human-scale tissue of any shape. With further development, this technology could potentially be used to print living tissue and organ structures for surgical implantation.”
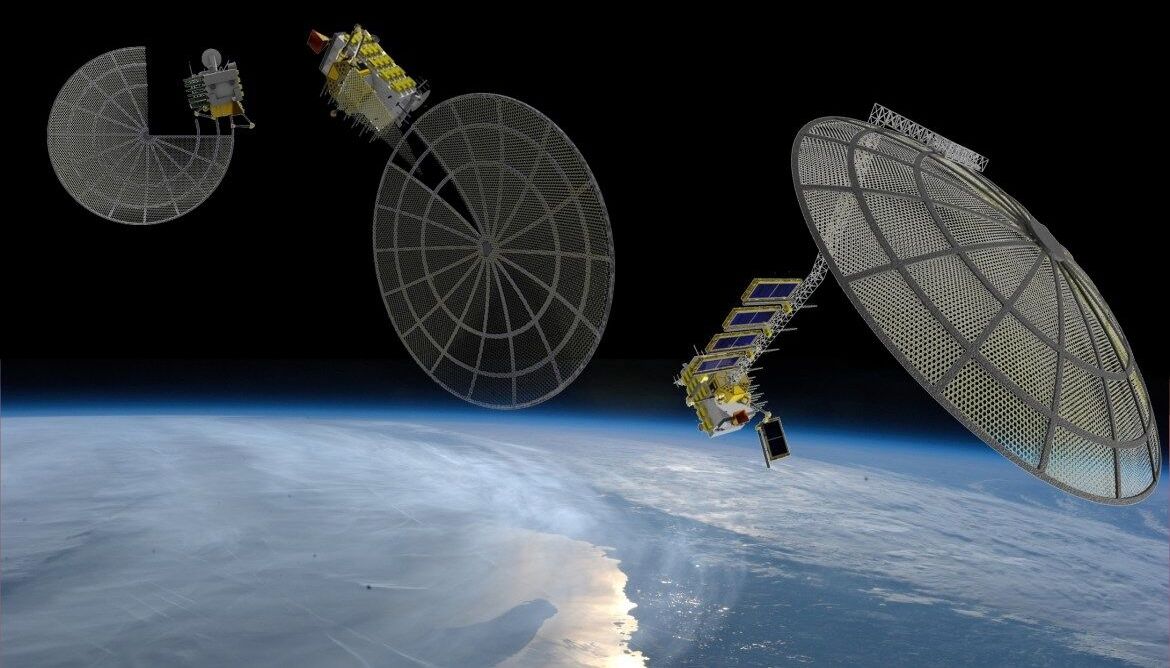

NASA, Made in Space think big with Archinaut, a robotic 3D printing demo bound for ISS
MOFFETT FIELD, California — Within five years, companies could begin in-orbit manufacturing and assembly of communications satellite reflectors or other large structures, according to Made in Space, the Silicon Valley startup that sent the first 3D printer to the International Space Station in 2014.
As Made in Space prepares to send a second 3D printer into orbit, the company is beginning work with Northrop Grumman and Oceaneering Space Systems on Archinaut, an ambitious effort to build a 3D printer equipped with a robotic arm that the team plans to install in an external space station pod, under a two-year, $20 million NASA contract. The project will culminate in 2018 with an on-orbit demonstration of Archinaut’s ability to additively manufacture and assemble a large, complex structure, said Andrew Rush, Made in Space president.
NASA’s selected the Archinaut project, officially known as Versatile In-Space Robotic Precision Manufacturing and Assembly System, as part of its Tipping Points campaign, which funds demonstrations of space-related technologies on the verge of offering significant payoffs for government and commercial applications. Archinaut was one of three projects NASA selected in November that focus on robotic manufacturing and assembly of spacecraft and structures in orbit.
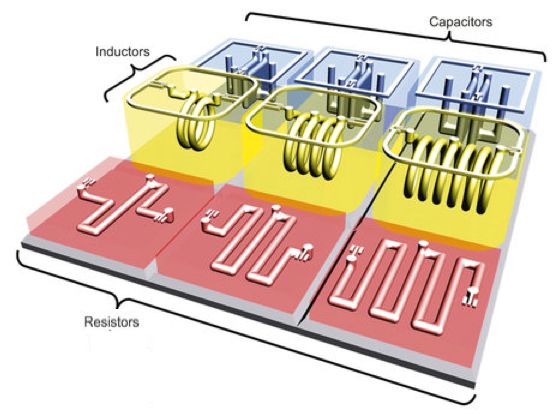
3D-printing basic electronic components
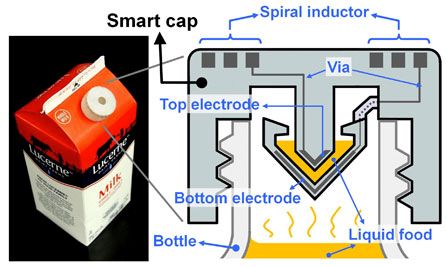
UC Berkeley engineers, in collaboration with colleagues at Taiwan’s National Chiao Tung University, have developed a 3D printing process for creating basic electronic components, such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, and integrated wireless electrical sensing systems.
As a test, they printed a wireless “smart cap” for a milk carton that detected signs of spoilage using embedded sensors.
The audacious plan to end hunger with 3D printed food
Anjan Contractor’s 3D food printer might evoke visions of the “replicator” popularized in Star Trek, from which Captain Picard was constantly interrupting himself to order tea. And indeed Contractor’s company, Systems & Materials Research Corporation, just got a six month, $125,000 grant from NASA to create a prototype of his universal food synthesizer.
But Contractor, a mechanical engineer with a background in 3D printing, envisions a much more mundane—and ultimately more important—use for the technology. He sees a day when every kitchen has a 3D printer, and the earth’s 12 billion people feed themselves customized, nutritionally-appropriate meals synthesized one layer at a time, from cartridges of powder and oils they buy at the corner grocery store. Contractor’s vision would mean the end of food waste, because the powder his system will use is shelf-stable for up to 30 years, so that each cartridge, whether it contains sugars, complex carbohydrates, protein or some other basic building block, would be fully exhausted before being returned to the store.
Ubiquitous food synthesizers would also create new ways of producing the basic calories on which we all rely. Since a powder is a powder, the inputs could be anything that contain the right organic molecules. We already know that eating meat is environmentally unsustainable, so why not get all our protein from insects?

Army selects 3D printed unmanned aircraft systems concept for future experiment
ABERDEEN PROVING GROUND, Md. (Feb. 5, 2016) — Each year, the U.S. Army conducts a series of technology demonstrations known as the Army Expeditionary Warrior Experiments, or AEWE. The event is the U.S. Army Training and Doctrine Command’s live, force-on-force experiment.
AEWE places technologies under development by industry and Army researchers into the hands of Soldiers for early and credible feedback from the end-user.
In January, the AEWE 2017 team selected a project submitted by the U.S. Army Research Laboratory for inclusion in its next round of experimentation: On-Demand Small Unmanned Aircraft Systems, or UAS. It is one of 50 technologies slotted to participate in the experiment with 14 from government researchers and 36 from industry.
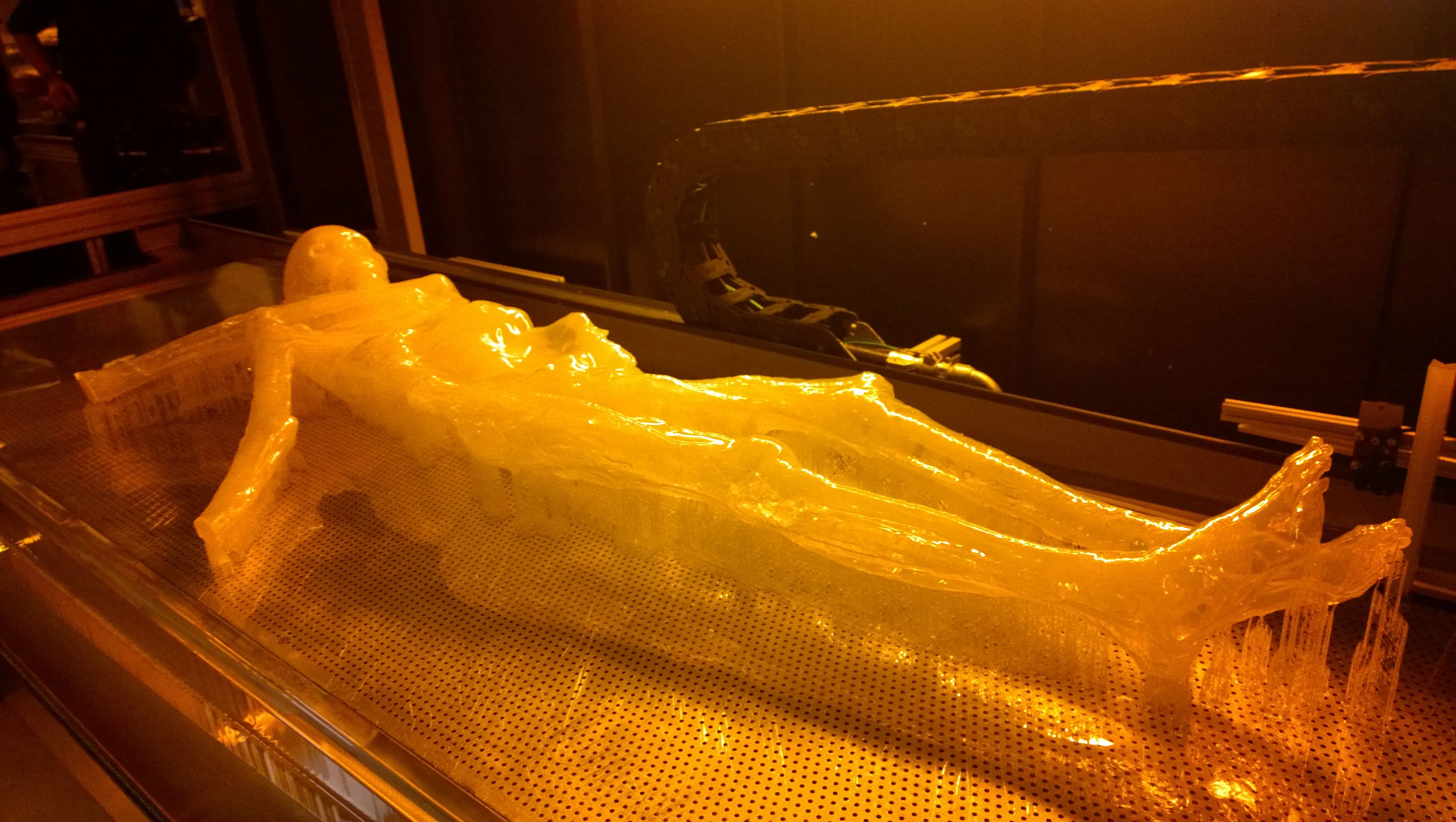

Scientists Can Now 3D Print Otzi The Mummified Ice Man
Re-creating the Ice Man — 3D Printer Style.
Otzi, for those not up on their 5,300-year-old mummified men, died and was frozen in the Alps near Hauslabjoch on the border between Austria and Italy. His body is one of the best preserved human mummies in Europe and now he’s getting a 3D-printed makeover.
Researchers and engineers have worked together with 3D-printing firm Materialise to perfectly scan Otzi. This allows researchers to 3D print his tortured frame over and over again and, in an interesting episode of Nova, an artist will create a perfect replica of the mummy for study by researchers and potential museum-goers. Otzi, for his part, his hanging out in a climate-controlled vault in Italy so he doesn’t degenerate.
The engineers had to recreate some of Otzi’s parts from scratch, a feat possible thanks to 3D modeling techniques. From the release: