(THE CONVERSATION) Racism steals time from people’s lives – possibly because of the space it occupies in the mind.
Question Is racial discrimination associated with brain connectivity, and are alterations in deep brain functional connectivity associated with accelerated epigenetic aging?
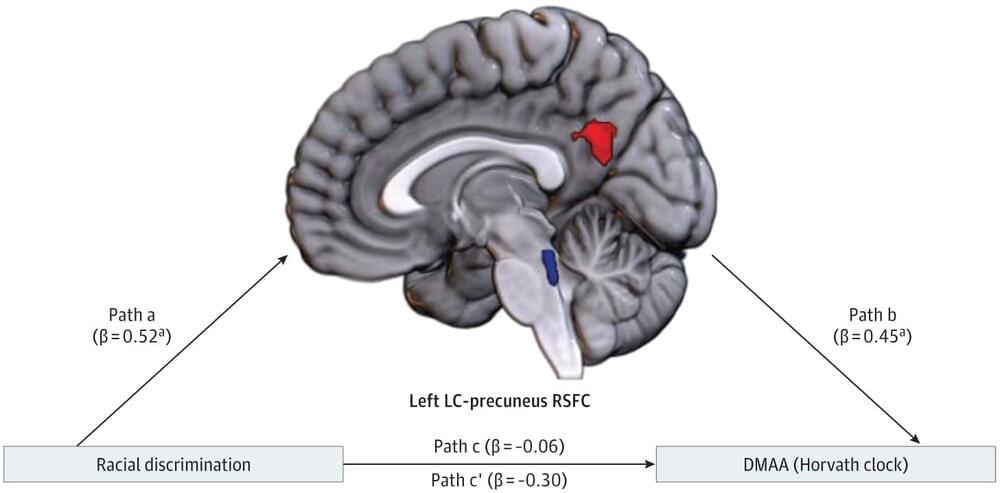
Findings In this cohort study of 90 Black women in the US, higher self-reported racial discrimination was associated with greater resting-state functional connectivity (RSFC) between the locus coeruleus (LC) and precuneus. Significant indirect effects were observed for the association between racial discrimination frequency and DNA methylation age acceleration.
Meaning These findings suggest that racial discrimination is associated with greater connectivity in pathways involved with rumination, which may increase vulnerability to stress-related disorders and neurodegenerative disease via epigenetic age acceleration.