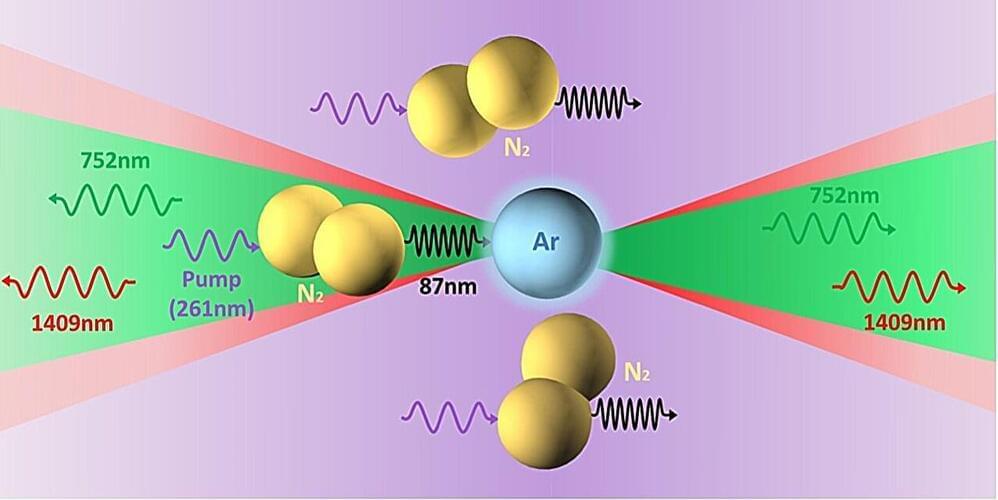
To produce light, lasers typically rely on optical cavities, pairs of mirrors facing each other that amplify light by bouncing it back and forth. Recently, some physicists have been investigating the generation of “laser light” in open air without the use of optical cavities, a phenomenon known as cavity-free lasing in atmospheric air.