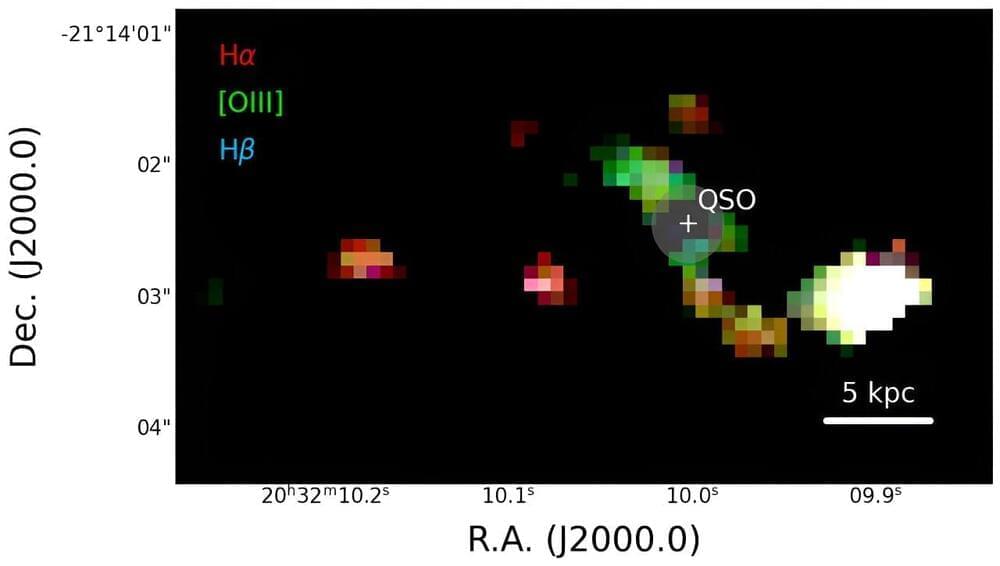
An international research group led by the Italian National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF) and comprising 34 research institutes and universities worldwide utilized the Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) on board the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to witness the dramatic interaction between a quasar inside the PJ308–21 system and two massive satellite galaxies in the distant universe.
The observations, made in September 2022, unveiled unprecedented and awe-inspiring details, providing new insights into the growth of galaxies in the early universe. The results, presented July 5 during the European Astronomical Society (EAS 2024) meeting in Padua (Italy), will be published soon in Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Observations of this quasar (already described by the same authors in another study published last May), one of the first studied with NIRSpec when the universe was less than a billion years old (redshift z = 6.2342), have revealed data of sensational quality: the instrument “captured” the quasar’s spectrum with an uncertainty of less than 1% per pixel.