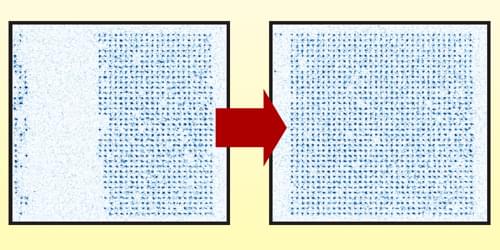
In most neutral-atom quantum computers, atoms are held in arrays of optical tweezers. Researchers typically populate the arrays stochastically, meaning that whether a given site receives an atom is down to chance. Atoms can later be rearranged individually, but the total number of atoms depends on the success of the initial loading.
The Atom Computing team developed an iterative process to fill an array to capacity. Instead of filling the array directly, the researchers first stochastically populated a second “reservoir” array. They then transferred atoms one by one from this reservoir to the target array using an optical tweezer. Between each loading step, the researchers imaged both arrays to determine which sites in each array were occupied. This step required temporarily switching off the tweezers and holding the atoms in an optical lattice formed from interfering laser beams.
The researchers showed that this sequence could be repeated as many times as necessary without losing atoms from the target array. They also showed that they could limit atom loss during the imaging step by enhancing the lattice strength using optical cavities. This enhancement allowed the atoms to be more strongly confined without increasing the optical lattice’s laser-power requirements.