Identifying individuals who are at a high risk of age-related morbidities may aid in personalized medicine. Circulating proteins can discriminate disease cases from controls and delineate the risk of incident diagnoses1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8. While singular protein markers offer insight into the mediators of disease5,9,10,11, simultaneously harnessing multiple proteins may improve clinical utility12. Clinically available non-omics scores such as QRISK typically profile the 10-year onset risk of a disease13. Proteomic scores have recently been trained on diabetes, cardiovascular and lifestyle traits as outcomes in 16,894 individuals14. Proteomic and metabolomic scores have also been developed for time-to-event outcomes, including all-cause mortality6,15,16,17,18,19,20,21.
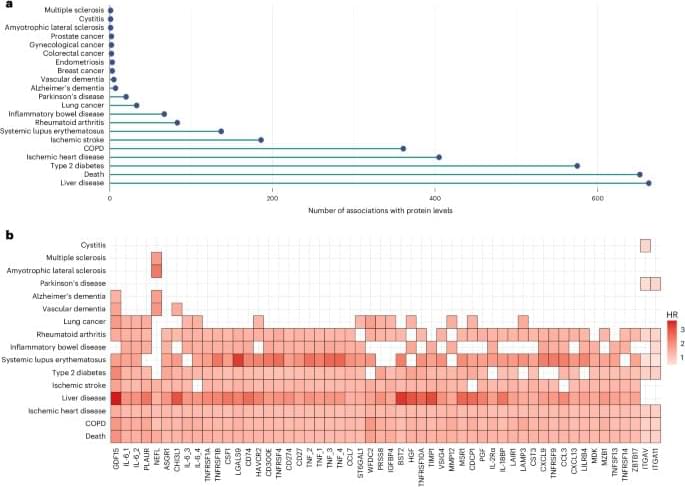
Here, we demonstrate how large-scale proteomic sampling can identify candidate protein targets and facilitate the prediction of leading age-related incident outcomes in mid to later life (see the study design summary in Extended Data Fig. 1). We used 1,468 Olink plasma protein measurements in 47,600 individuals (aged 40–70 years) available as part of the UK Biobank Pharma Proteomics Project (UKB-PPP)22. Cox proportional hazards (PH) models were used to characterize associations between each protein and 24 incident outcomes, ascertained through electronic health data linkage. Next, the dataset was randomly split into training and testing subsets to train proteomic scores (ProteinScores) and assess their utility for modeling either the 5-or 10-year onset of the 19 incident outcomes that had a minimum of 150 cases available. We modeled ProteinScores alongside clinical biomarkers, polygenic risk scores (PRS) and metabolomics measures to investigate how these markers may be used to augment risk stratification.