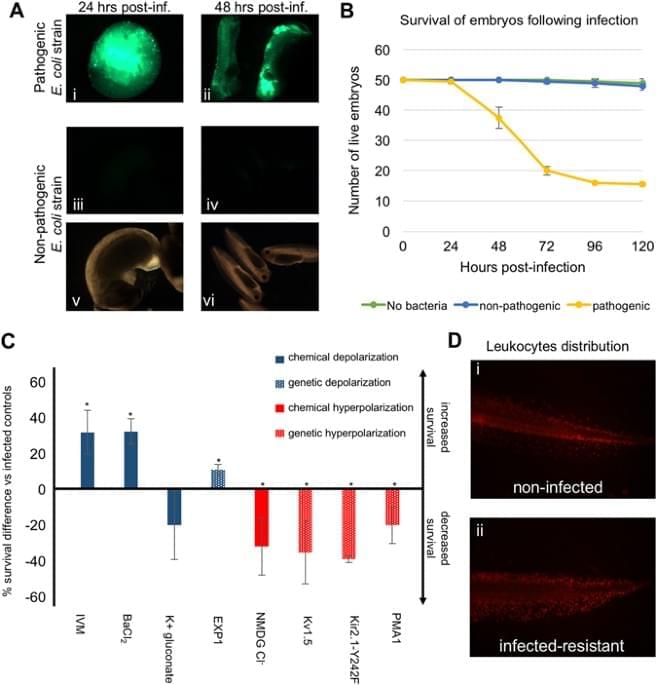
Bioelectrical signaling in the African clawed frog modulates both resistance to infection and tail regeneration. Michael Levin at Tufts University in Massachusetts, USA, and colleagues have used genetic technologies and drug treatments to manipulate the bioelectrical properties of tissues in frog embryos. Reducing the electric gradient between the inside and outside of cells (depolarization) increased the embryos’ survival rate to bacterial infection, whereas increasing the resting potential (hyperpolarization) had the opposite effect. The authors found that serotonergic signaling and an increase in the number of myeloid cells underpin depolarization-induced immunity. Interestingly, embryos undergoing tail regeneration, which triggers depolarization, also showed increased resistance to infection.