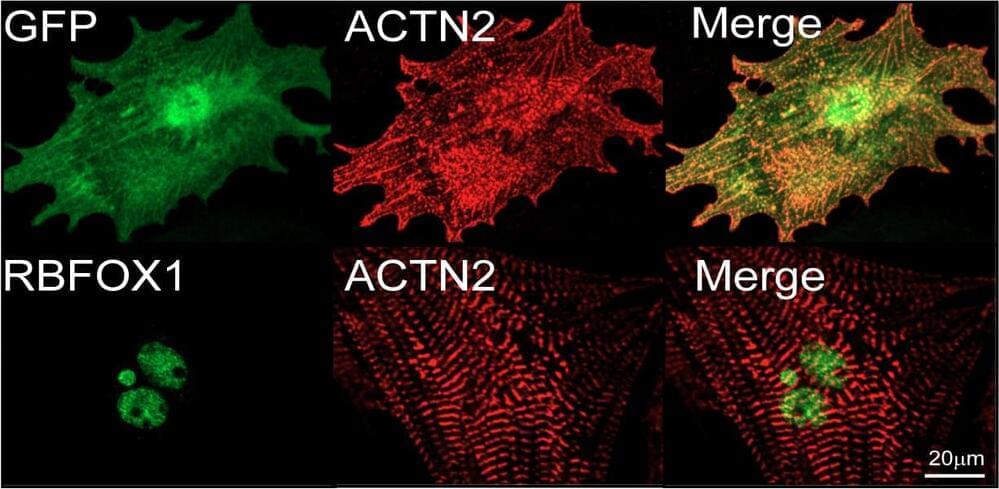
Researchers identify RBFox1 as a key intrinsic regulator of heart muscle cell maturation, overcoming a major limitation in cardiac regenerative therapy and disease modelling and demonstrating for the first time that RNA splicing control can significantly impact this process.
Scientists led by Duke-NUS Medical School in Singapore and the University of California, Los Angeles, (UCLA) in the United States have discovered a new control mechanism that can drive the maturation of human stem cell-derived heart muscle cells, providing fresh insight into the maturation process of heart muscle cells from fetal to adult form.
After birth, heart muscle cells undergo extensive changes to become fully mature adult cells, altering their form, function and physiology.