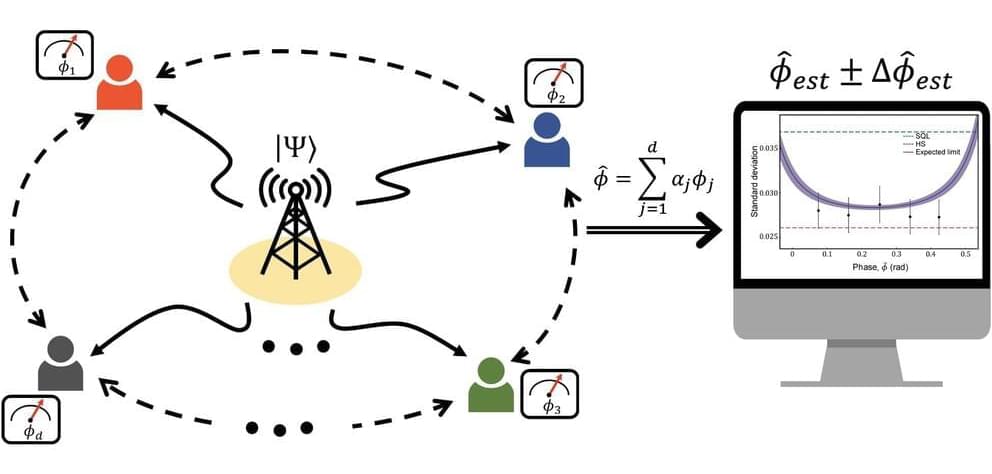
A research team has succeeded in implementing a distributed quantum sensor that can measure multiple spatially distributed physical quantities with high precision beyond the standard quantum limit with few resources. Their findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.
Sharing the exact time between distant locations is becoming increasingly important in all areas of our lives, including finance, telecommunications, security, and other fields that require improved accuracy and precision in sending and receiving data.
Quantum phenomena such as superposition and entanglement can be used to more precisely measure the time of different clocks in two distant spaces. Similarly, if you have two physical quantities, one in Seoul and one in Busan, you can share the entanglement state in Seoul and Busan and then measure the two physical quantities simultaneously with greater precision than if you measure the physical quantities in Seoul and Busan separately.