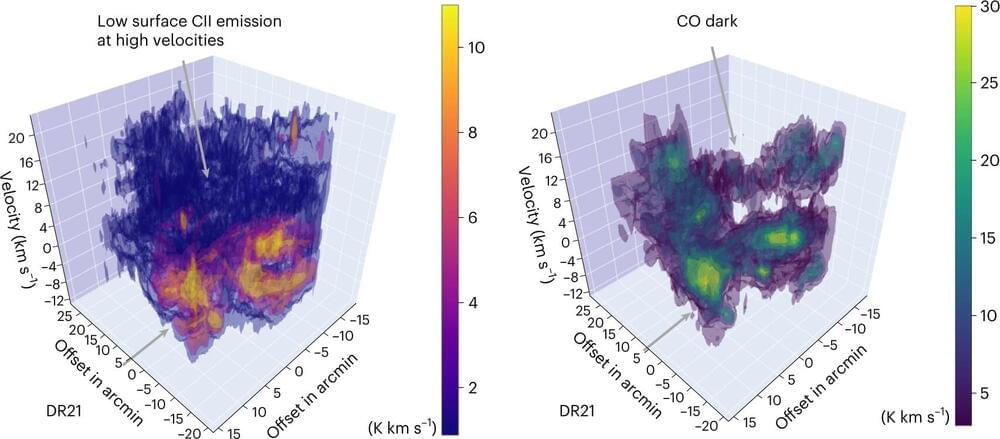
Gas clouds in the Cygnus X Region, a region where stars form, are composed of a dense core of molecular hydrogen (H2) and an atomic shell. These ensembles of clouds interact with each other dynamically in order to quickly form new stars. That is the result of observations conducted by an international team led by scientists at the University of Cologne’s Institute of Astrophysics and at the University of Maryland.
Until now, it was unclear how this process precisely unfolds. The Cygnus X region is a vast luminous cloud of gas and dust approximately 5,000 light years from Earth. Using observations of spectral lines of ionized carbon (CII), the scientists showed that the clouds have formed there over several million years, which is a fast process by astronomical standards. The results of the study, “Ionized carbon as a tracer for the assembly of interstellar clouds,” will appear in the next issue of Nature Astronomy.
The observations were carried out in an international project led by Dr. Nicola Schneider at the University of Cologne and Prof Alexander Tielens at the University of Maryland as part of the FEEDBACK program on board the flying observatory SOFIA (Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy). The new findings modify previous perceptions that this specific process of star formation is quasi-static and quite slow. The dynamic formation process now observed would also explain the formation of particularly massive stars.