Big scientific breakthroughs often require inventions at the smallest scale. Advances in tissue engineering that can replace hearts and lungs will require the fabrication of artificial tissues that allow for the flow of blood through passages that are no thicker than a strand of hair. Similarly, miniature softbotic (soft-robot) devices that physically interact with humans safely and comfortably will demand the manufacture of components with complex networks of small liquid and airflow channels.
Advances in 3D printing are making it possible to produce such tiny structures. But for those applications that require very small, smooth, internal channels in specific complex geometries, challenges remain. 3D printing of these geometries using traditional processes requires the use of support structures that are difficult to remove after printing. Printing these models using layer-based methods at a high resolution takes a long time and compromises geometric accuracy.
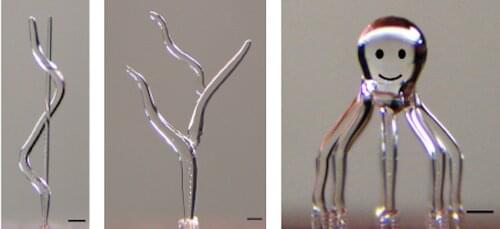
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University have developed a high-speed, reproducible fabrication method that turns the 3D printing process “inside out.” They developed an approach to 3D print ice structures that can be used to create sacrificial templates that later form the conduits and other open features inside fabricated parts.