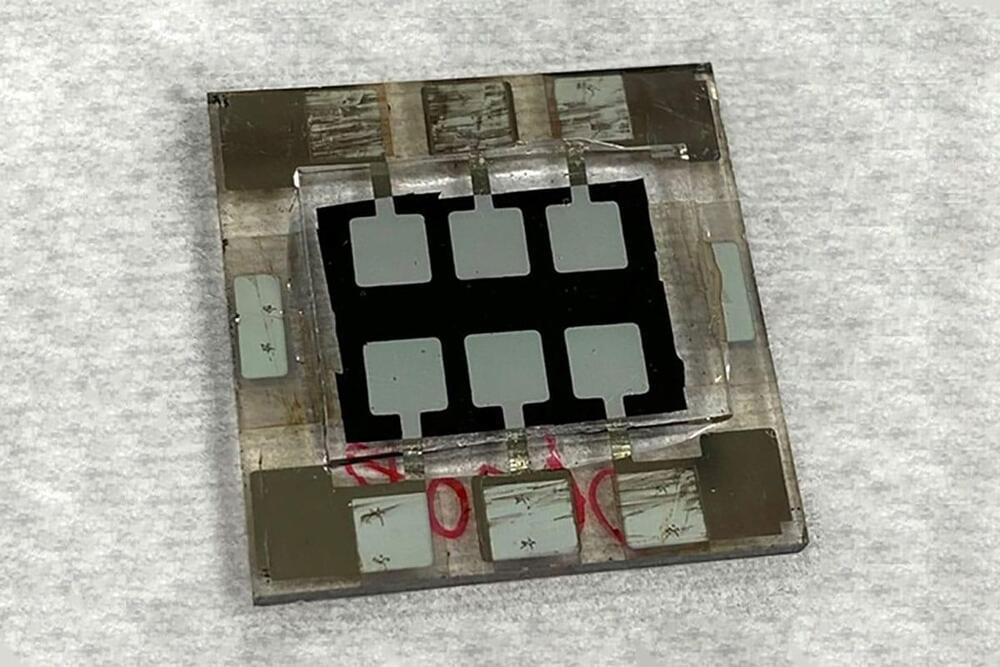
Now, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) have demonstrated a tin-lead perovskite cell that overcomes problems with stability and improves efficiency.
To improve cell stability, NREL researchers used a hole-transporting material made of phenethylammonium iodide and guanidinium thiocyanate. Researchers noted that the formation of quasi-two-dimensional (quasi-2D) structures from additives based on mixed bulky organic cations phenethylammonium and guanidinium provides critical defect control to substantially improve the structural and optoelectronic properties of lead-perovskite thin films with a narrow-bandgap of 1.25 eV.
The new tandem solar cell design with two layers of perovskites measured a 25.5% efficiency. It retained 80% of its maximum efficiency after 1,500 hours of continuous operation or more than 62 days.