Pure lithium metal is a promising replacement for the graphite-based anodes currently used in electric vehicle batteries. It could tremendously reduce battery weights and dramatically extend the driving range of electric vehicles relative to existing technologies. But before lithium metal batteries can be used in cars, scientists must first figure out how to extend their lifetimes.
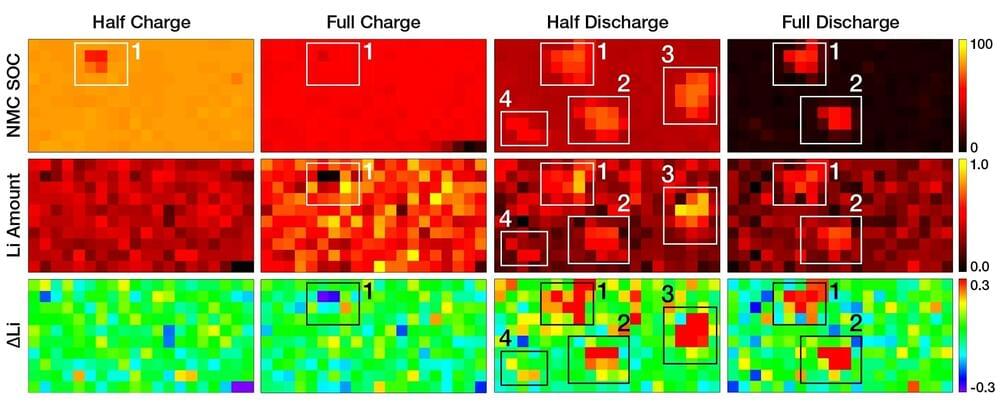
A new study led by Peter Khalifah—a chemist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and Stony Brook University—tracked lithium metal deposition and removal from a battery anode while it was cycling to find clues as to how failure occurs. The work is published in a special issue of the Journal of the Electrochemical Society honoring the contributions of Nobel Prize-winning battery researcher John Goodenough, who like Khalifah is a member of the Battery 500 Consortium research team.
“In a good battery, the rate of lithium plating (deposition) and stripping (removal) will be the same at all positions on the surface of electrodes,” Khalifah said. “Our results show that it’s harder to remove lithium at certain places, which means there are problems there. By identifying the cause of the problems, we can figure out how to get rid of them and make better batteries with higher capacities and longer lifetimes.”