Stem cells for teeth repair.
Teeth exhibit limited repair in response to damage, and dental pulp stem cells probably provide a source of cells to replace those damaged and to facilitate repair. Stem cells in other parts of the tooth, such as the periodontal ligament and growing roots, play more dynamic roles in tooth function and development. Dental stem cells can be obtained with ease, making them an attractive source of autologous stem cells for use in restoring vital pulp tissue removed because of infection, in regeneration of periodontal ligament lost in periodontal disease, and for generation of complete or partial tooth structures to form biological implants. As dental stem cells share properties with mesenchymal stem cells, there is also considerable interest in their wider potential to treat disorders involving mesenchymal (or indeed non-mesenchymal) cell derivatives, such as in Parkinson’s disease.
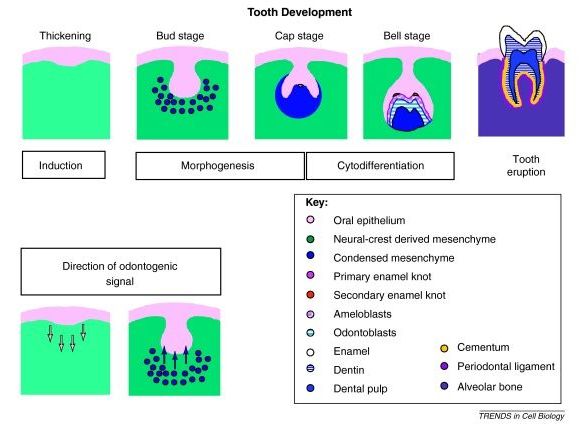
Teeth are complex organs containing two separate specialized hard tissues, dentine and enamel, which form an integrated attachment complex with bone via a specialized (periodontal) ligament. Embryologically, teeth are ectodermal organs that form from sequential reciprocal interactions between oral epithelial cells (ectoderm) and cranial neural crest derived mesenchymal cells. The epithelial cells give rise to enamel forming ameloblasts, and the mesenchymal cells form all other differentiated cells (e.g., dentine forming odontoblasts, pulp, periodontal ligament) (Box 1). Teeth continue developing postnatally; the outer covering of enamel gradually becomes harder, and root formation, which is essential for tooth function, only starts to occur as part of tooth eruption in children.
Tooth development is traditionally considered a series of stages that reflect key processes ( Figure I ). The first step is induction, in which signals from the epithelium to the mesenchyme initiate the developmental process. As localized proliferation of the dental epithelial cells takes place, the cells form a bud around which the mesenchymal cells condense. Differentiation and localized proliferation of the epithelial cells in the bud leads to the cap stage. It is at this stage that crown morphogenesis is initiated by the epithelial signalling centre, an enamel knot regulating the folding of the epithelium. By the bell stage, the precursors of the specialized tooth cells, ameloblasts, coordinate enamel deposition, and odontoblasts, which produce dentine, are formed. Tooth eruption involves the coordination of bone resorption and root development, and occurs postnatally.