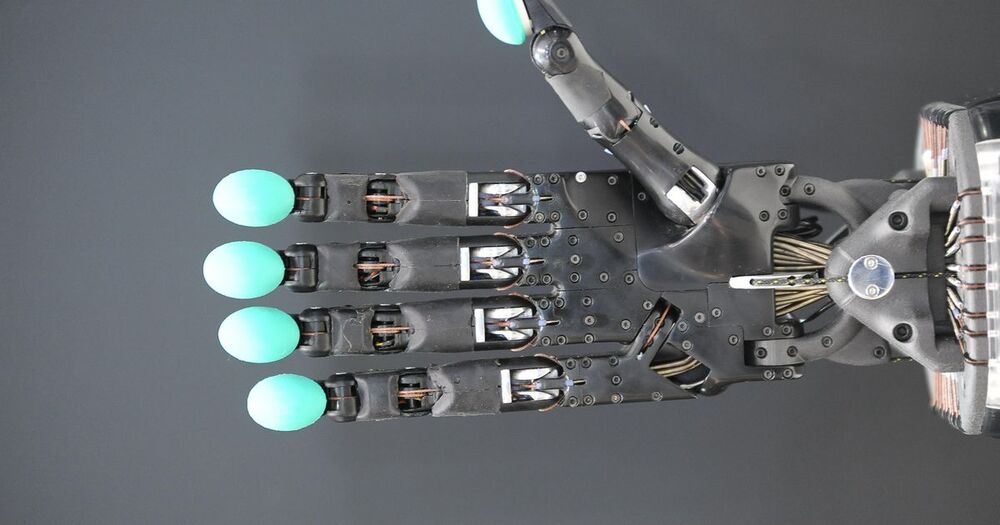
“I can feel touching my daughter’s hand or touching my wife’s hand, or picking up a hollow eggshell without crushing it,” Anderson says of his work with Psyonic, a startup operating out of the University of Illinois’ Research Park, in Urbana-Champaign. Psyonic expects to provide commercial prostheses with pressure sensing next year, and ones with sensory feedback sometime after that.
Technology is on the threshold of turning the unthinkable into reality. Awkward, unfeeling prostheses are morphing into mind-controlled extensions of the human body that give their wearers a sense of touch and a greater range of motion.
Along with sensory feedback, Psyonic’s rubber and silicone prosthesis uses machine learning to give its wearers intuitive control. The Modular Prosthetic Limb from Johns Hopkins University promises to deliver “humanlike” strength, thought-controlled dexterity and sensation. It’s currently in the research phase. And Icelandic company Ossur is conducting preclinical trials on mind-controlled leg and foot prostheses. These and other advances could make it dramatically easier for amputees to perform the sorts of tasks most people take for granted.