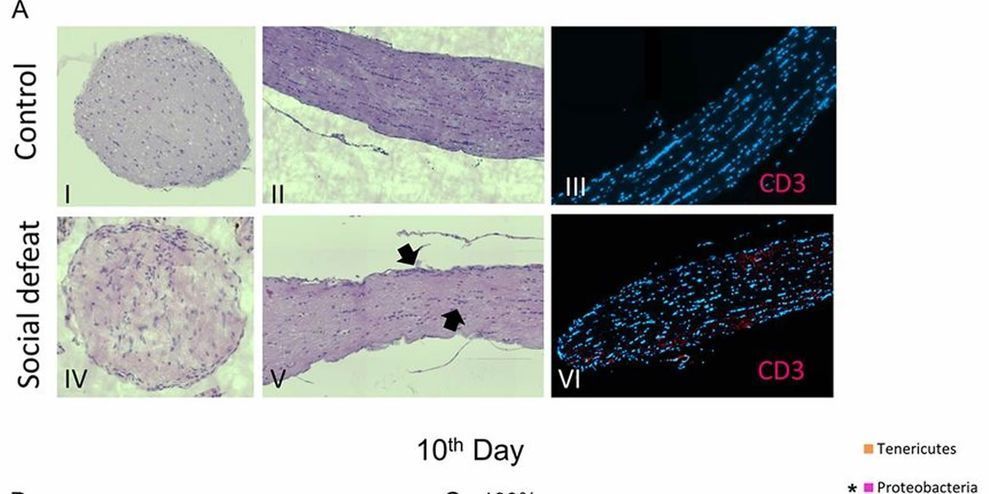
Stressful life events most likely contribute to autoimmune diseases, but scientists don’t have a deep understanding of the underlying chain of events. A study on mice published this week in mSystems suggests that the gut microbiota may play a significant role in that connection. Researchers found that the onset of stress caused changes in the intestinal bacteria that, in turn, stimulated the activity of immune cells in a way that increased the likelihood that the body would a…
Chronic social stress in mice induces the expression of virulent genes in the gut microbiota. The altered microbiota increases the presence of effector T helper cells in the lymph nodes and induces myelin autoreactive cells. Exposure to chronic stress, therefore, may increase the risk of developing autoimmune diseases for some individuals with a susceptibility.