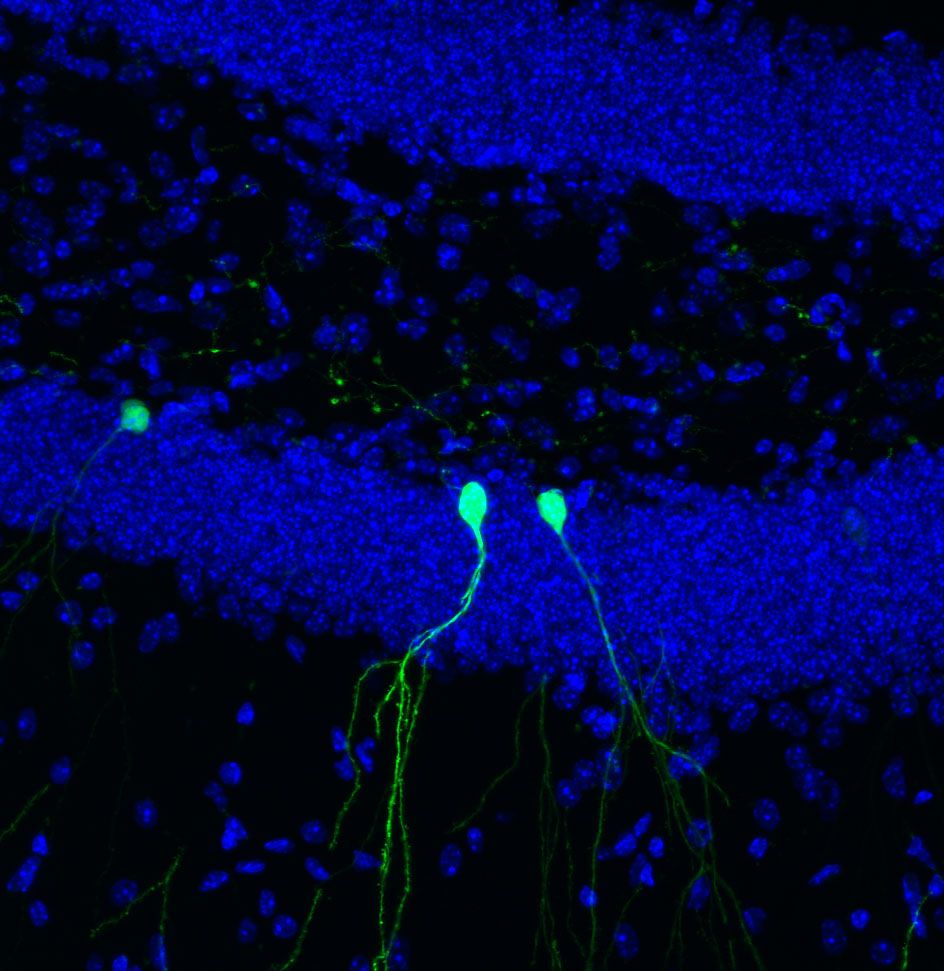
When tweaking its architecture, the adult brain works like a sculptor—starting with more than it needs so it can carve away the excess to achieve the perfect design. That’s the conclusion of a new study that tracked developing cells in an adult mouse brain in real time.
New brain cells began with a period of overgrowth, sending out a plethora of neuronal branches, before the brain pruned back the connections. The observation, described May 2, 2016 in Nature Neuroscience, suggests that new cells in the adult brain have more in common with those in the embryonic brain than scientists previously thought and could have implications for understanding diseases including autism, intellectual disabilities and schizophrenia.
“We were surprised by the extent of the pruning we saw,” says senior author Rusty Gage, a professor in Salk’s Laboratory of Genetics and holder of the Vi and John Adler Chair for Research on Age-Related Neurodegenerative Disease.