A new method to create light while retaining the energy using Q-Dot technology.
All light sources work by absorbing energy – for example, from an electric current – and emit energy as light. But the energy can also be lost as heat and it is therefore important that the light sources emit the light as quickly as possible, before the energy is lost as heat. Superfast light sources can be used, for example, in laser lights, LED lights and in single-photon light sources for quantum technology. New research results from the Niels Bohr Institute show that light sources can be made much faster by using a principle that was predicted theoretically in 1954. The results are published in the scientific journal, Physical Review Letters.
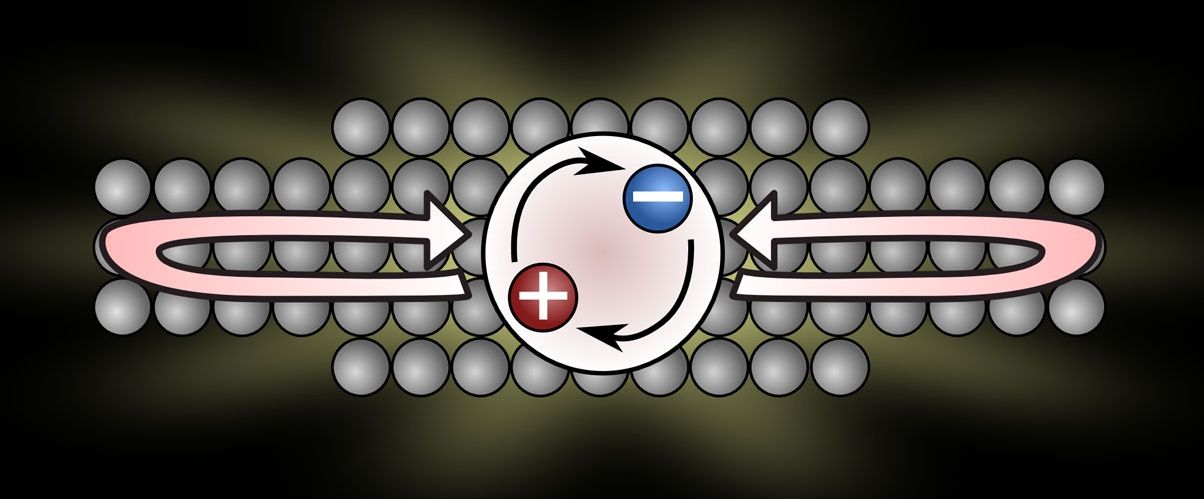
Researchers at the Niels Bohr Institute are working with quantum dots, which are a kind of artificial atom that can be incorporated into optical chips. In a quantum dot, an electron can be excited (i.e. jump up), for example, by shining a light on it with a laser and the electron leaves a ‘hole’. The stronger the interaction between light and matter, the faster the electron decays back into the hole and the faster the light is emitted.
But the interaction between light and matter is naturally very weak and it makes the light sources very slow to emit light and this can reduce energy efficiency. Already in 1954, the physicist Robert Dicke predicted that the interaction between light and matter could be increased by having a number of atoms that ‘share’ the excited state in a quantum superposition.