MANILA, Philippines — A dengue case forecasting system using space data made by Philippine developers won the 2019 National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s International Space Apps Challenge. Over 29,000 participating globally in 71 countries, this solution made it as one of the six winners in the best use of data, the solution that best makes space data accessible, or leverages it to a unique application.
Dengue fever is a viral, infectious tropical disease spread primarily by Aedes aegypti female mosquitoes. With 271,480 cases resulting in 1,107 deaths reported from January 1 to August 31, 2019 by the World Health Organization, Dominic Vincent D. Ligot, Mark Toledo, Frances Claire Tayco, and Jansen Dumaliang Lopez from CirroLytix developed a forecasting model of dengue cases using climate and digital data, and pinpointing possible hotspots from satellite data.
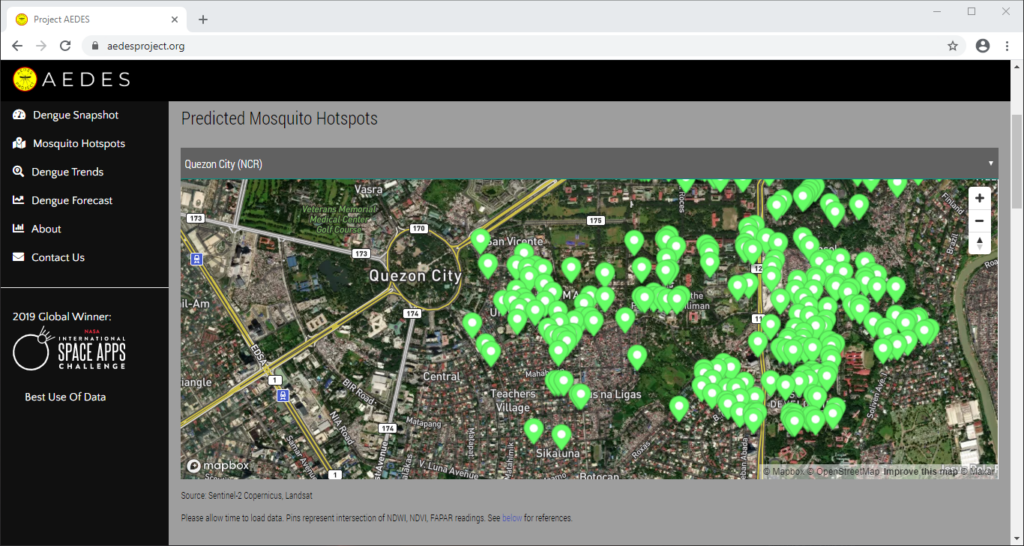
Correlating information from Sentinel-2 Copernicus and Landsat 8 satellites, climate data from the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration of the Department of Science and Technology (DOST-PAGASA) and trends from Google search engines, potential dengue hotspots will be shown in a web interface.







