Some community members rallied against the proposed center Thursday night before a rezoning ordinance was approved by council members.



For 2,500 years, Western thought has treated contradiction as catastrophic.
From Aristotle’s law of non-contradiction to modern formal systems, logic has operated under one sacred assumption: a statement cannot be both true and false.
But what if that assumption is wrong?
In my latest Singularity. FM conversation, I sit down with Graham Priest — one of the world’s leading philosophers of logic and the foremost defender of *dialetheism* — the view that some contradictions are true.
We explore:
• Why the liar paradox still unsettles logicians • How paraconsistent logic blocks “explosion” • Whether classical logic is incomplete rather than universal • What Buddhist philosophy understood about contradiction centuries ago • And whether AI systems may require non-classical logics to model human reasoning.

Two recent studies from the University of California, Riverside, published in the same issue of Gut Microbes highlight the role of a gene called PTPN2 in protecting the gut from harmful bacteria linked to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Led by Declan McCole, a professor of biomedical sciences in the School of Medicine, the studies show that when PTPN2 does not function properly, the gut becomes more vulnerable to infection and inflammation.
People with IBD often have higher levels of AIEC, a harmful type of E. coli bacteria. AIEC can attach to the gut lining, invade gut cells, damage the gut’s protective barrier, and worsen inflammation.
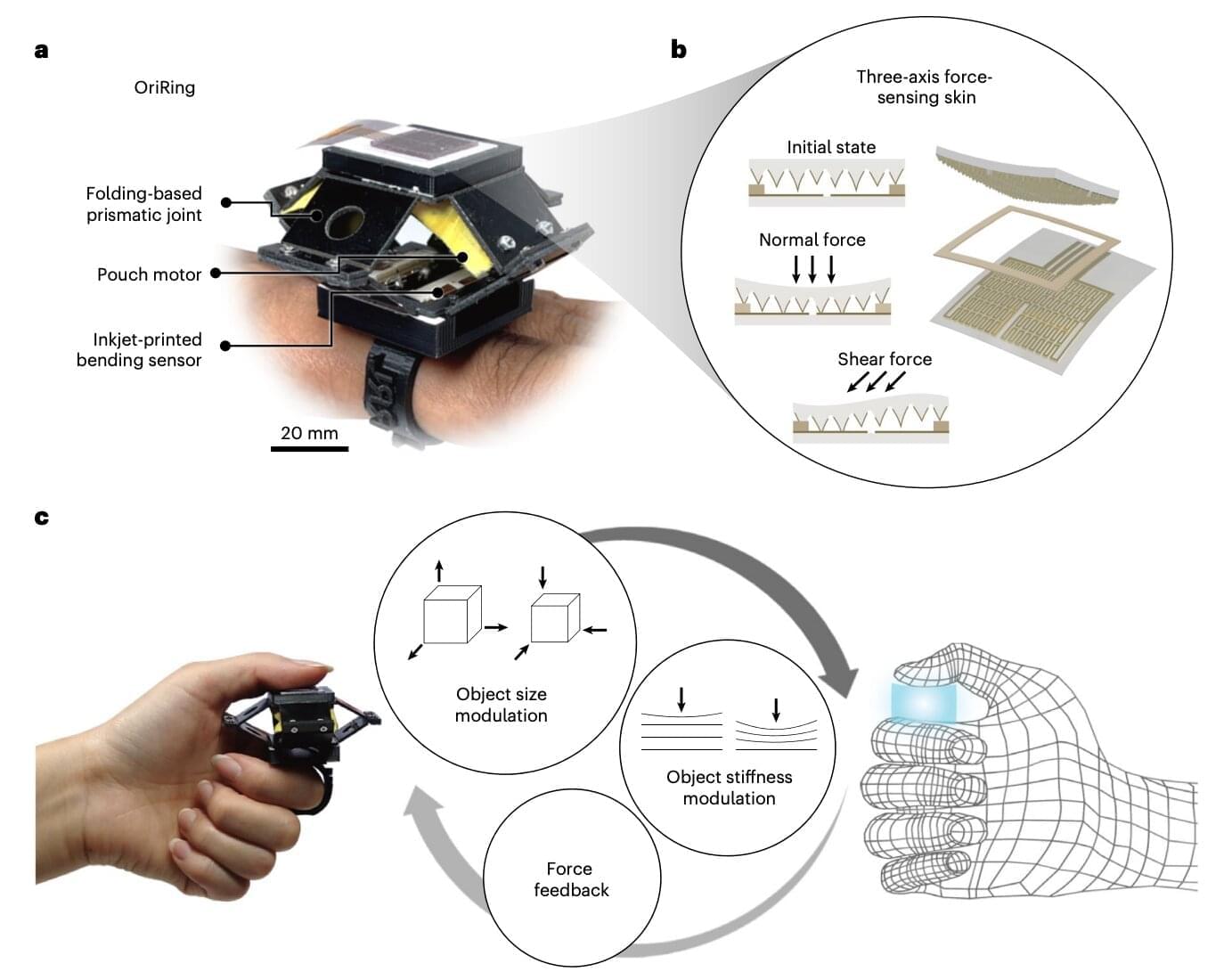
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are technologies that allow users to immerse themselves in digital worlds or enhance their surroundings with computer-generated filters or images, respectively. Both these technologies are now widely used worldwide, whether to experience video games and media content in more engaging ways or improve specific training and assist professionals in their daily tasks.
To date, VR and AR have primarily focused on what users see and hear, primarily improving the quality of digital experiences from a visual and auditory standpoint. The sense of touch, on the other hand, has been in great part overlooked.
Researchers at Sungkyunkwan University, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne and Istanbul Technical University recently developed a new wearable device that could allow users to also realistically “feel” tactile sensations aligned with what they are experiencing in a virtual world. This device, introduced in a paper published in Nature Electronics, is an origami-inspired ring that measures forces on a user’s skin, pushing back onto the finger to produce specific sensations.
We experience time as something that flows. Seconds pass. Moments disappear. The future becomes the present and then turns into the past.
But modern physics does not describe time this way.
In this video, we explore why time — as we intuitively understand it — may not exist at the fundamental level of reality.
Drawing on ideas associated with Leonard Susskind, this documentary examines how relativity and quantum physics challenge the idea of a flowing temporal river. Einstein’s theory removes the notion of a universal present. There is no global “now” that sweeps across the universe.
Without a universal present, the idea of time flowing becomes difficult to define physically.
In the relativistic picture, spacetime is a four-dimensional structure. Events are not created moment by moment. They are embedded in geometry. The equations of physics do not contain a moving present. They describe relations between events.

Activation of endothelial cells causes a monocyte recruitment cascade involving rolling, adhesion, activation and transendothelial migration (Figure 1). Selectins, especially P-selectin, mediate the initial rolling interaction of monocytes with the endothelium (32). Monocyte adherence is then promoted by endothelial cell immunoglobulin-G proteins including VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 (32). Potent chemoattractant factors such as MCP-1 and IL-8 then induce migration of monocytes into the subendothelial space (33-35). Ly6hi monocytes, versus Ly6lo, preferentially migrate into the subendothelial space to convert to proinflammatory macrophages in mice (36-38). The enhanced migration of Ly6hi versus Ly6lo monocytes likely results from increased expression of functional P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (39). In addition, the number of blood monocytes originating from the bone marrow and spleen, especially Ly6hi cells, increases in response to hypercholesterolemia (36). Furthermore, hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis increase monocytosis in humans (40,41). Importantly, increased numbers of inflammatory CD14++ CD16+ monocytes independently predicted cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and stroke in patients undergoing elective coronary angiography (42). Intimal macrophages also result from proliferation of monocyte/macrophages, especially in more advanced lesions (43). During the initial fatty streak phase of atherosclerosis (Figure 1), the monocyte-derived macrophages internalize the retained apoB-containing lipoproteins, which are degraded in lysosomes, where excess free cholesterol is trafficked to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to be esterified by acyl CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT), and the resulting cholesteryl ester (CE) is packaged into cytoplasmic lipid droplets, which are characteristic of foam cells (42) (Figure 2) (44,45). Modification of apoB lipoproteins via oxidation and glycation enhances their uptake through a number of receptors not down-regulated by cholesterol including CD36, scavenger receptor A, and lectin-like receptor family (see details below) (Figure 2) (46,47). Enzyme-mediated aggregation of apoB lipoproteins enhances uptake via phagocytosis (Figure 2) (48,49). In addition, native remnant lipoproteins can induce foam cell formation via a number of apoE receptors (LRP1 and VLDLR) (Figure 2) (50,51). Uptake of native LDL by fluid phase pinocytosis may also contribute to foam cell formation (Figure 2) (52,53).
Macrophage Cholesterol Metabolism. Native LDL is recognized by the LDL receptor (LDLR). The LDL is endocytosed and trafficked to lysosomes, where the cholesteryl ester (CE) is hydrolyzed to free cholesterol (FC) by the acid lipase. The FC is transported to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to be esterified by acyl CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT). Increased FC in an ER regulatory pool initiates a signaling cascade resulting in down-regulation of the LDL receptor. Cholesterol regulation of the LDLR prevents foam cell formation via this receptor in the setting of hypercholesterolemia. ApoB containing lipoproteins that also contain apoE (apoE remnants, VLDL) can cause cholesterol accumulation via interaction of apoE with apoE receptors including the LRP1 and the VLDL receptor, which are not regulated by cellular cholesterol. Uptake of native LDL by fluid phase pinocytosis may also contribute to foam cell formation.
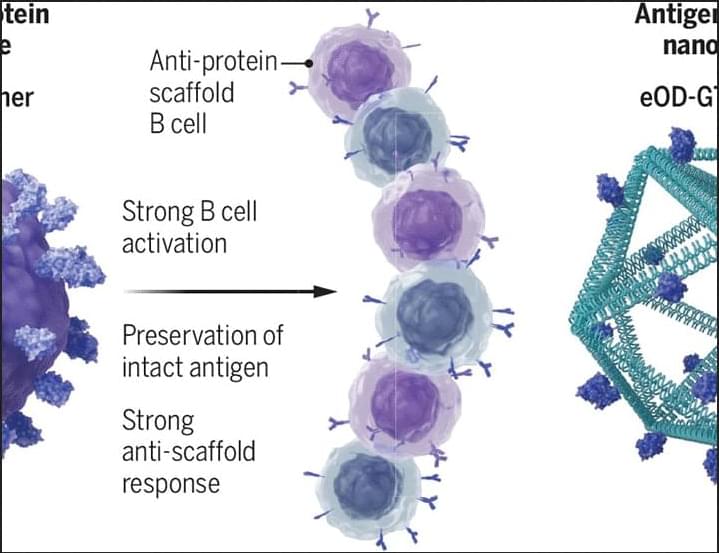
In a new Science study, researchers demonstrate that DNA origami can be used to display HIV protein antigens. When given to mice, these nanoparticles elicited antibody responses that may pave the way for broadly protective immunity against infection.
This approach could lead to more effective HIV vaccines. Learn more in a new Science Perspective.
DNA origami scaffolds displaying HIV antigens stimulate focused antibody responses in mice.
Oliver Bannard and Mark R. Howarth Authors Info & Affiliations
Science
Vol 391, Issue 6785
🔥 New and HOT in Chemical Science!
“” by Kai Mundsinger (Queensland University of Technology, Australia), Christopher Barner-Kowollik (Queensland University of Technology, Australia and Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Germany), et al.
Read it for free.
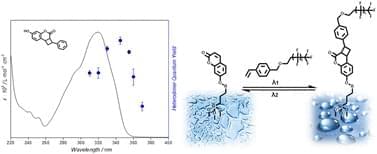
We report the first wavelength-dependent quantum yields of a [2 + 2] photocycloaddition generating the heterodimers of 7-hydroxycoumarin (7HCou) and styrene via a photochemical action plot. The wavelength-dependent heterodimer quantum yields are quantified at a constant number of photons at each wavelength between 310 and 370 nm. The resulting wavelength-dependent quantum yields demonstrate that the heterodimer is most efficiently generated at 345 nm, red-shifted by close to 25 nm compared to the absorption maximum of 7HCou at 320 nm. We subsequently translate these findings to photochemical surface functionalization by exploiting heterodimer formation between a surface bound coumarin derivative and para-styrene perfluoroalkyl ether (StyPFA) on surfaces under 345 nm irradiation to reversibly modulate surface hydrophobicity. The reversibility of the surface heterodimerization is demonstrated by removing StyPFA under UVC irradiation, and re-functionalization on the same surface. Functional heterodimer formation and the reversibility of the reaction on surface are followed via surface-sensitive X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and contact angle measurements. We subsequently apply our photochemical surface functionalization strategy to a dual cure photoresin based on a polyurethane-acrylate interpenetrating network, without deterioration of its mechanical properties, thereby confirming the feasibility of a photocycloaddition-based functionalization strategy for photoresins.

