Search results for 'Nicholi': Page 27
Apr 12, 2021
Famed Neurobiologist Slams Neuralink’s Monkey Demo
Posted by Nicholi Avery in category: neuroscience
Inverse spoke to Andrew Schwartz, a University of Pittsburgh neurobiologist who helped pioneer BCI technology — and he says that Neuralink seems to be bragging about things that scientists, himself included, could do decades ago.
Neuralink made a huge production out of something researchers have been able to do for decades.
Apr 1, 2021
Social Determinants of Health Impact Fetal Brain Development
Posted by Nicholi Avery in categories: biotech/medical, education, employment, health, neuroscience
New data from Children’s National Hospital shows parental experience with a number of social determinants of health can ultimately impact brain development in utero, something researchers said should suggest future community health intervention among pregnant people. The data, published in JAMA Network Open, specifically found poorer brain development in fetuses among pregnant people with low socioeconomic status (SES), low educational attainment, and limited employment opportunity.
New data from Children’s National Hospital has found that social determinants of health like income, education, and occupation can impact fetal brain development, following that child into life.
Mar 7, 2021
Scientists Create ‘Clock’ That Measures Biological Age
Posted by Nicholi Avery in categories: biological, life extension
This enables scientists to determine an organism’s biological age with high precision. Get the details here.
Feb 11, 2021
CRISPR Treatment Offers The Potential To Live Forever
Posted by Nicholi Avery in categories: biotech/medical, life extension
CRISPR/Cas9 treatment allowed mice to live 25% longer and be physically stronger. Biologists see these results being relatively easy to reproduce on humans in a clinical setting.
Feb 8, 2021
How Scientists Reversed Aging, And What It Means For You
Posted by Nicholi Avery in categories: biotech/medical, life extension
By blocking a receptor in macrophages, researchers were able to reverse aging in mice.
There are many suggested causes of old age. Telomere shortening, DNA damage, and depletion of stem cells are just a few of the proposed sources.
Recently, researchers found that a type of cell called a macrophage also plays a crucial role in aging. Macrophages are phagocytotic immune cells; they consume cells and other pathogens flagged by the immune system as dangerous. When macrophages need to consume a pathogen, their energy needs drastically go up.
Continue reading “How Scientists Reversed Aging, And What It Means For You” »
Dec 4, 2020
Scientists Invent a Microscope That Can Safely Look Straight Through Your Skull
Posted by Nicholi Avery in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
A team of scientists has now found a way to create a clear image from scattered infrared light emitted from a laser, even after it’s passed through a thick layer of bone.
‘Our microscope allows us to investigate fine internal structures deep within living tissues that cannot be resolved by any other means,’ said physicists Seokchan Yoon and Hojun Lee from Korea University.
Seeing what the heck is going on inside of us is useful for many aspects of modern medicine. But how to do this without slicing and dicing through barriers like flesh and bone to observe living intact tissues, like our brains, is a tricky thing to do.
Continue reading “Scientists Invent a Microscope That Can Safely Look Straight Through Your Skull” »
Dec 2, 2020
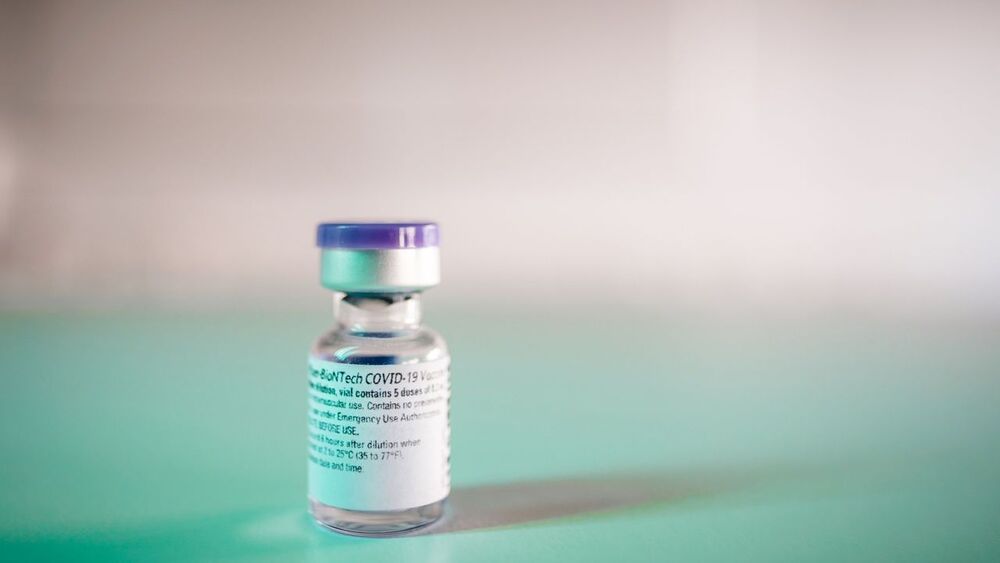
‘Wonderful news to wake up to’: U.K. greenlights Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine
Posted by Nicholi Avery in categories: biotech/medical, health
MHRA will only become fully independent on 1 January 2021, following Brexit, but U.K. regulations allow it to grant authorizations on an emergency basis. The United Kingdom has bought 40 million doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine—enough for 20 million people—and health secretary Matt Hancock today announced the first 800,000 doses will be available next week. The rollout will prioritize health workers as well as the elderly and other vulnerable populations, but the Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation has yet to offer its final guidance on the exact priorities.
Russia on 11 August allowed its COVID-19 vaccine, developed by the Gamaleya Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology, to be used on certain groups of people, and China has granted emergency use authorizations (EUAs) for several vaccines and has already vaccinated hundreds of thousands of people with them. A few other countries, including the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain, have issued an EUA for one of the Chinese vaccines, produced by Sinopharm.
The Pfizer vaccine, whose key ingredient is messenger RNA that encodes the spike protein of the pandemic coronavirus, was found to have 95% efficacy, a clinical trial measurement of effectiveness, in a phase III trial in 43,000 people. But it presents logistical challenges for a widescale and rapid rollout, as it requires storage at −70°C. The lesser demands of other vaccines—including a candidate developed by the University of Oxford and AstraZeneca—mean they will likely still play an important role in providing vaccinations for the whole U.K. population—and for global coverage, according to Michael Head, a global health researcher at the University of Southampton, “but, for now, this is wonderful news to wake up to.”
Nov 23, 2020
New insights from study of people age 90 and above
Posted by Nicholi Avery in category: futurism
Six years after our initial report, Lesley Stahl visits surviving members of the 90+ Study and finds out what scientists have learned from following the study’s participants.
Nov 18, 2020
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: First Human Study Shows Reversal in Biology of Aging
Posted by Nicholi Avery in categories: biotech/medical, life extension

TEL AVIV — November 18, 2020: In a scientifically verified approach, signalling an important breakthrough in the study of aging, Tel Aviv University and The Sagol Center for Hyperbaric Medicine and Research at Shamir Medical Center announced today that, for the first time in humans, two key biological hallmarks of aging, telomere length shortening, and accumulation of senescent cells, can be reversed. The prospective clinical trial, published in peer-reviewed Journal Aging, utilizes Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy protocols to demonstrate cellular level improvement in healthy aging adults.
For the first-time a human study shows the reversal in the biology of aging including telomere shortening with Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy.
Continue reading “Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: First Human Study Shows Reversal in Biology of Aging” »