The Salt American foulbrood is an infectious disease that devastates honeybee hives. Scientists say they’ve created a vaccine for it, despite a big hurdle: Bees don’t have antibodies.


A 68-year-old Seattle woman who died after contracting a rare brain-eating amoeba used regular tap water to rinse her sinuses, according to new research.
As noted in a new International Journal of Infectious Diseases case study, the infection was initially misdiagnosed as a brain tumor. During surgery to remove the suspected tumor, the lead neurosurgeon, Charles Cobbs from Seattle’s Swedish Medical Center, was taken aback by the extent of the brain damage. So he extracted a sample for further testing.
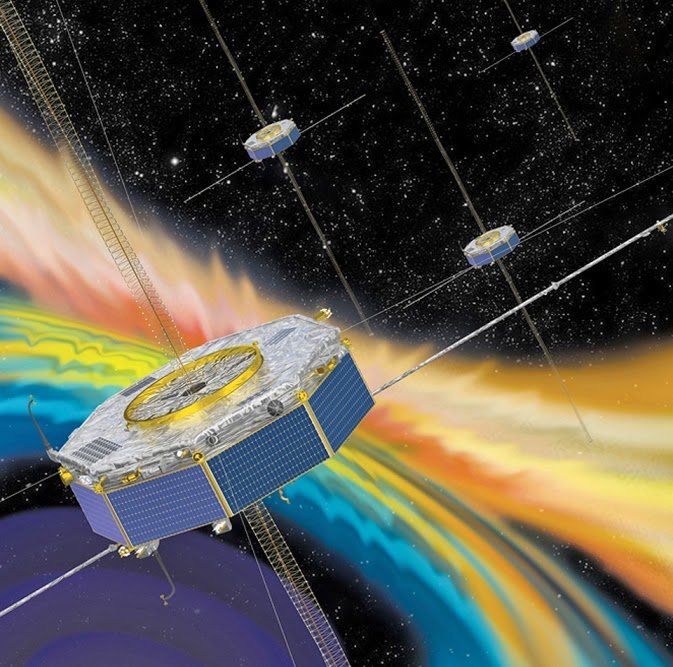

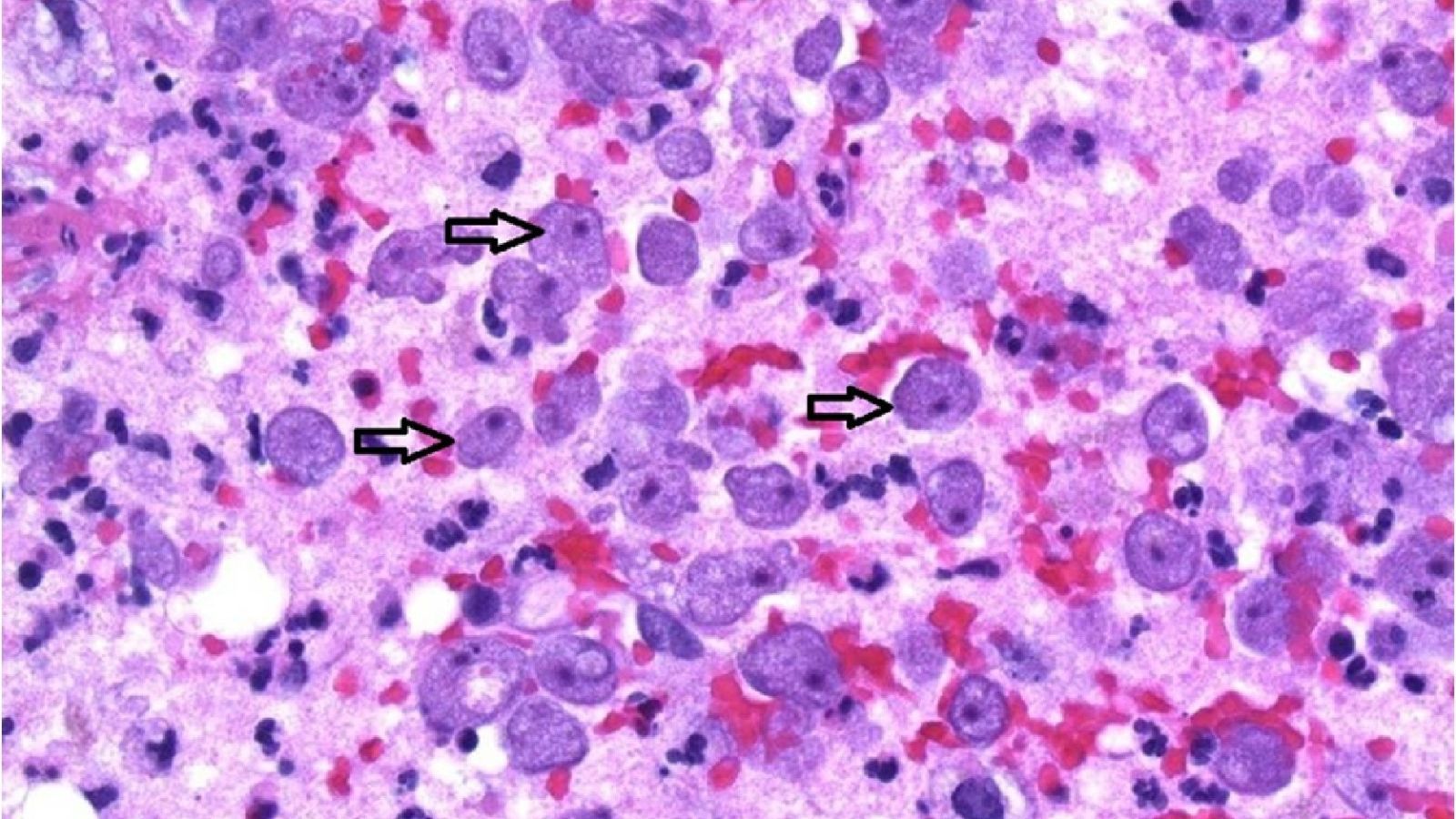
As on Earth, so in space. A four-satellite mission that is studying magnetic reconnection—the breaking apart and explosive reconnection of the magnetic field lines in plasma that occurs throughout the universe—has found key aspects of the process in space to be strikingly similar to those found in experiments at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL). The similarities show how the studies complement each other: The laboratory captures important global features of reconnection and the spacecraft documents local key properties as they occur.
The observations made by the Magnetospheric Multiscale Satellite (MMS) mission, which NASA launched in 2015 to study reconnection in the magnetic field that surrounds the Earth, correspond quite well with past and present laboratory findings of the Magnetic Reconnection Experiment (MRX) at PPPL. Previous MRX research uncovered the process by which rapid reconnection occurs and identified the amount of magnetic energy that is converted to particle energy during the process, which gives rise to northern lights, solar flares and geomagnetic storms that can disrupt cell phone service, black out power grids and damage orbiting satellites.
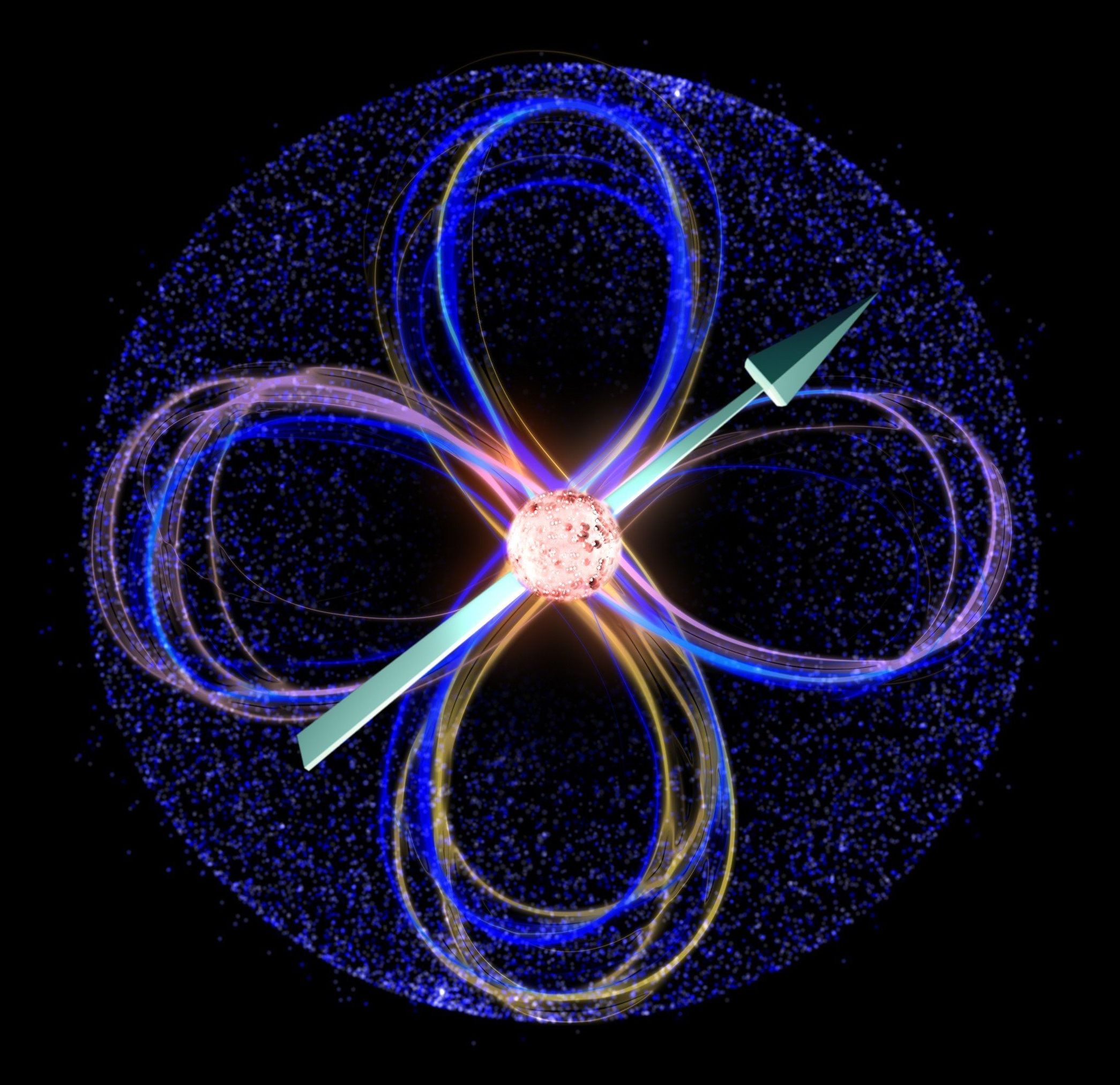
Australian scientists have investigated new directions to scale up qubits—utilising the spin-orbit coupling of atom qubits—adding a new suite of tools to the armory.
Spin-orbit coupling, the coupling of the qubits’ orbital and spin degree of freedom, allows the manipulation of the qubit via electric, rather than magnetic-fields. Using the electric dipole coupling between qubits means they can be placed further apart, thereby providing flexibility in the chip fabrication process.
In one of these approaches, published in Science Advances, a team of scientists led by UNSW Professor Sven Rogge investigated the spin-orbit coupling of a boron atom in silicon.
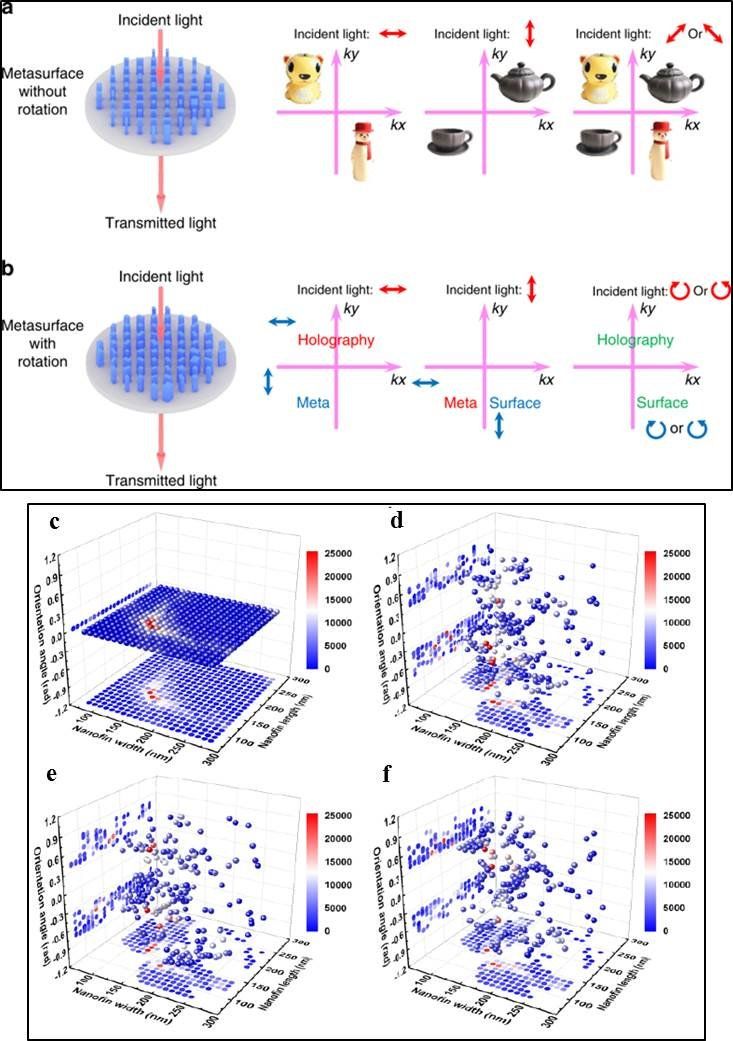
Holography is a powerful tool that can reconstruct wavefronts of light and combine the fundamental wave properties of amplitude, phase, polarization, wave vector and frequency. Smart multiplexing techniques (multiple signal integration) together with metasurface designs are currently in high demand to explore the capacity to engineer information storage systems and enhance optical encryption security using such metasurface holograms.
Holography based on metasurfaces is a promising candidate for applications in optical displays/storage with enormous information bearing capacity alongside a large field of view compared to traditional methods. To practically realize metasurface holograms, holographic profiles should be encoded on ultrathin nanostructures that possess strong light-matter interactions (plasmonic interactions) in an ultrashort distance. Metasurfaces can control light and acoustic waves in a manner not seen in nature to provide a flexible and compact platform and realize a variety of vectorial holograms, with high dimensional information that surpass the limits of liquid crystals or optical photoresists.
Among the existing techniques employed to achieve highly desired optical properties, polarization multiplexing (multiple signal integration) is an attractive method. The strong cross-talk associated with such platforms can, however, be prevented with birefringent metasurfaces (two-dimensional surfaces with two different refractive indices) composed of a single meta-atom per unit-cell for optimized polarization multiplexing.
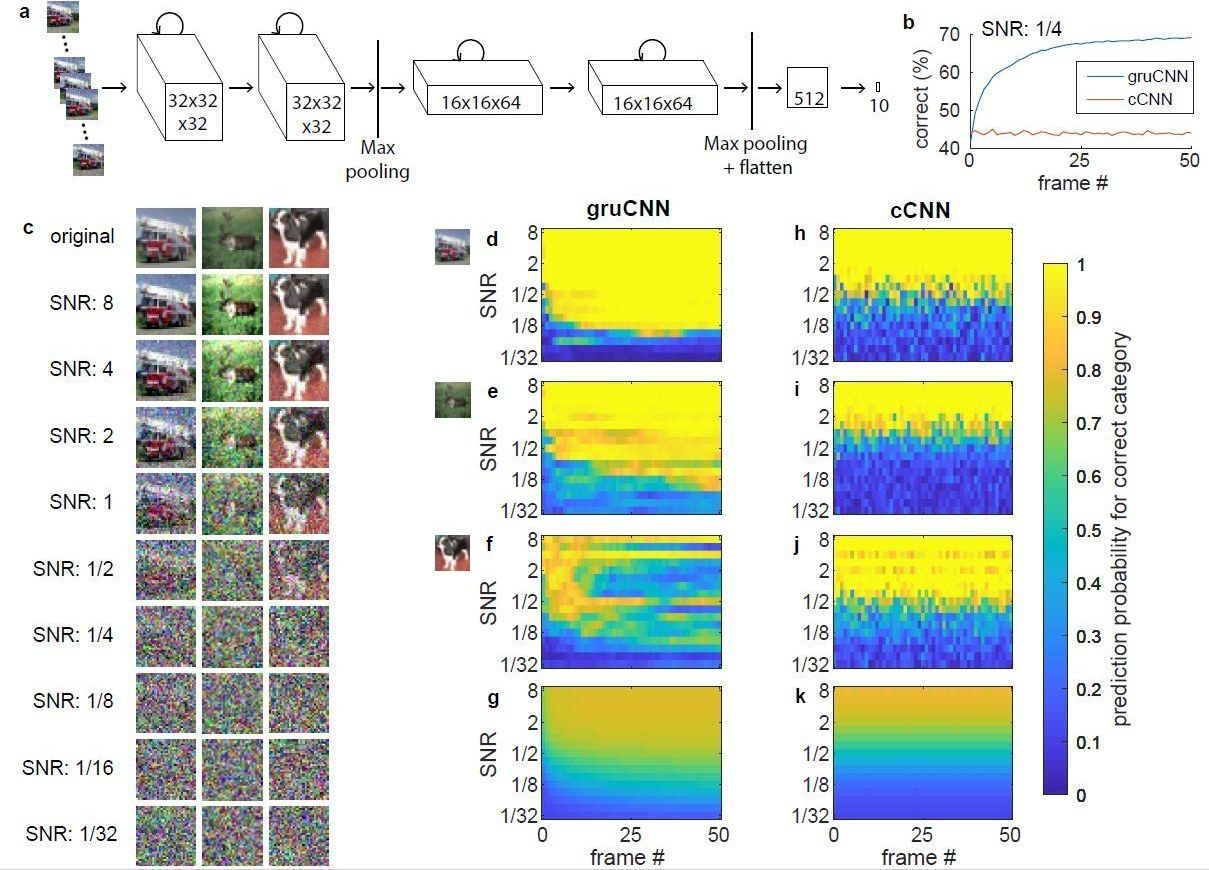
Over the past few years, classical convolutional neural networks (cCNNs) have led to remarkable advances in computer vision. Many of these algorithms can now categorize objects in good quality images with high accuracy.
However, in real-world applications, such as autonomous driving or robotics, imaging data rarely includes pictures taken under ideal lighting conditions. Often, the images that CNNs would need to process feature occluded objects, motion distortion, or low signal to noise ratios (SNRs), either as a result of poor image quality or low light levels.
Although cCNNs have also been successfully used to de-noise images and enhance their quality, these networks cannot combine information from multiple frames or video sequences and are hence easily outperformed by humans on low quality images. Till S. Hartmann, a neuroscience researcher at Harvard Medical School, has recently carried out a study that addresses these limitations, introducing a new CNN approach for analyzing noisy images.

Are we about to see Apple reaching an even newer gold standard in ear buds? Apple has a patent for AirPods with built in biometrics. It’s being called “universal” because the idea calls for ear pods that can be worn in either ear. That would mean no more left-right business.
Much of the tech news coverage is focusing on the “interchangeable” aspect of the patent concept. 9to5Mac’s Alex Allegro said interchangeable earbuds “equipped with ‘at least one’ biometric sensor, which could detect left/right ear placement and accordingly adjust audio.” He assessed the potential advantages as “evolving AirPods from a separate left / right unit to a single component,” which could lower costs and simplify getting a replacement AirPod.
If the ear buds are interchangeable, then it is a big deal in terms of user satisfaction. OK, the product is popular now but The Verge reminds us that the AirPod is not a perfect fit for everyone. Nick Statt: “Due to the shape of some people’s inner ear, the headphones simply don’t fit every possible ear shape well.”


