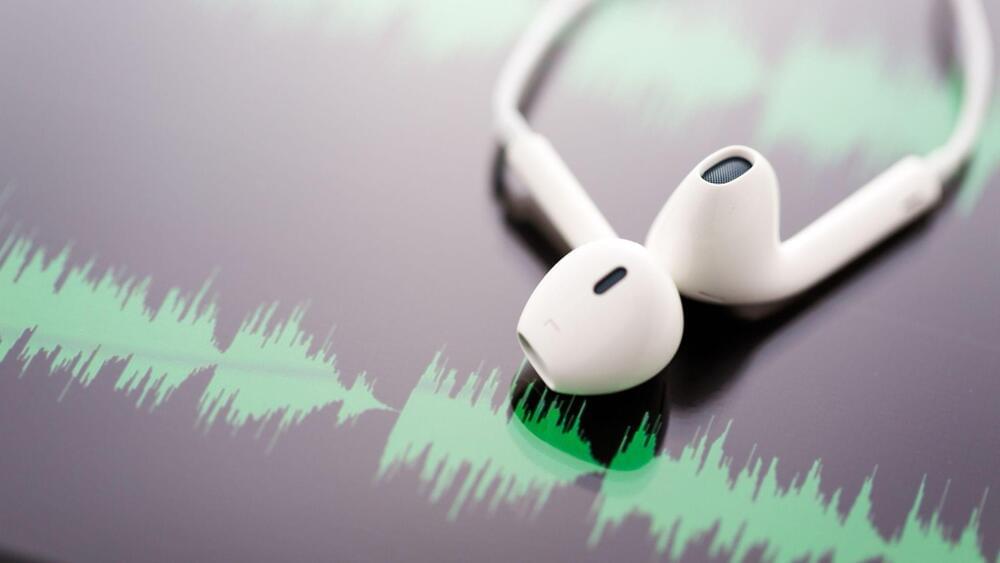
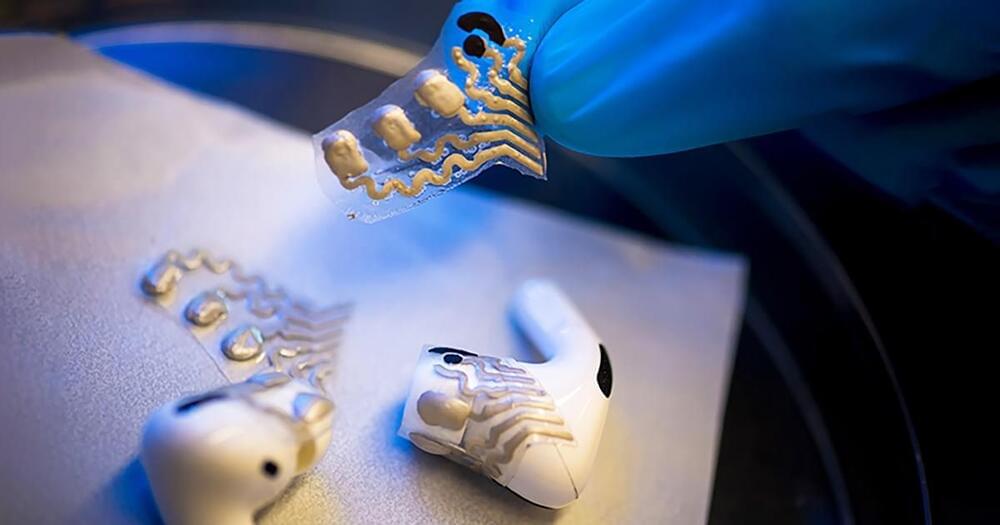
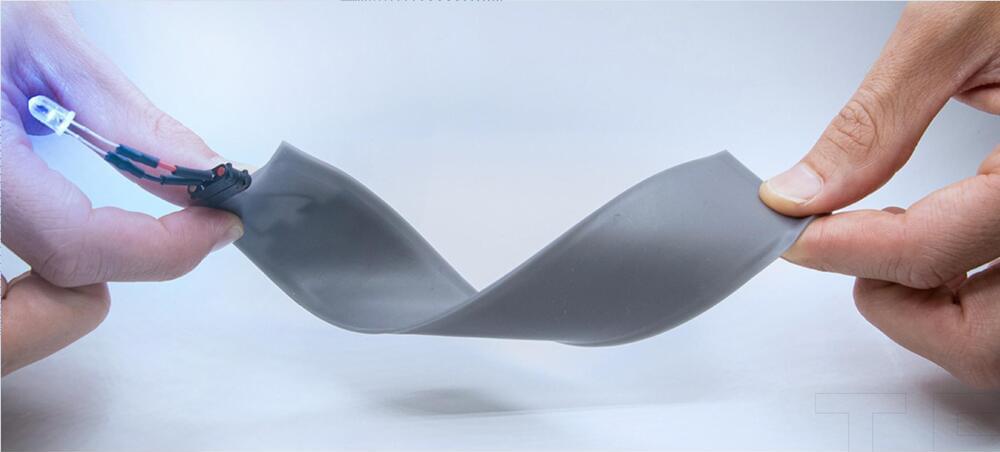
A first-of-its-kind flexible sensor turns a pair of earbuds into a device capable of recording brain activity and analyzing sweat, making them useful for diagnosing diseases and health monitoring.
The background: Health monitoring wearables can measure our blood pressure, track our heart rates, and even detect infections before we start to feel sick, helping us take better care of ourselves and potentially even giving us a way to prevent the spread of diseases.
The devices are useless if no one wants to wear them, though, so finding designs that are comfortable and easy to integrate into daily life is key. Because earbuds are already popular, researchers have used them as the basis for health monitoring devices that record brain activity to predict strokes, epileptic seizures, or Parkinson’s disease.