Plants have a seemingly effortless skill – turning sunlight into energy – and scientists have been working to artificially emulate this photosynthesis process. The ultimate benefits for renewable energy could be huge – and a new approach based on ‘photosheets’ could be the most promising attempt we’ve seen so far.
The new device takes CO2, water, and sunlight as its ingredients, and then produces oxygen and formic acid that can be stored as fuel. The acid can either be used directly or converted into hydrogen – another potentially clean energy fuel.
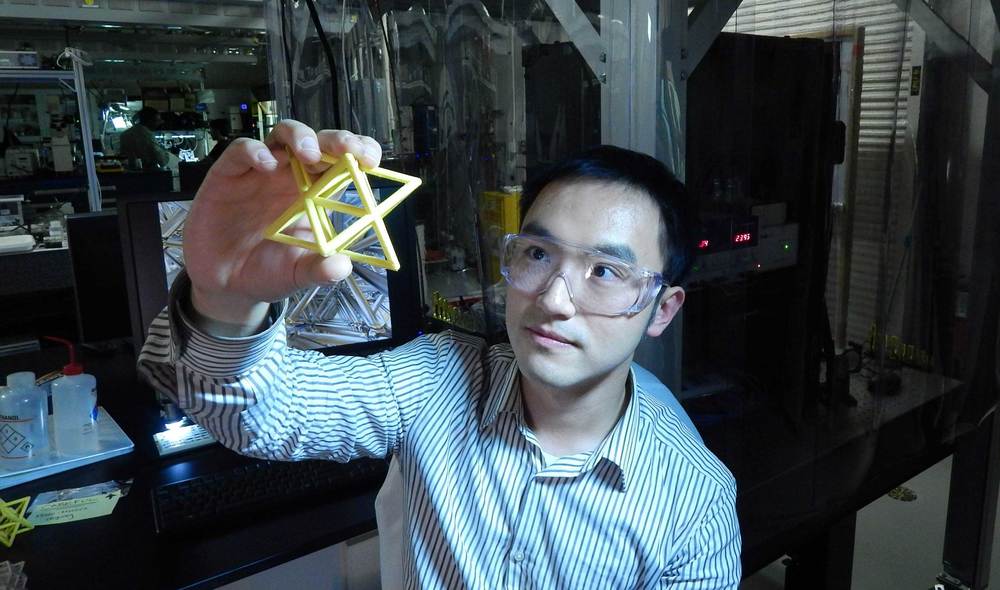
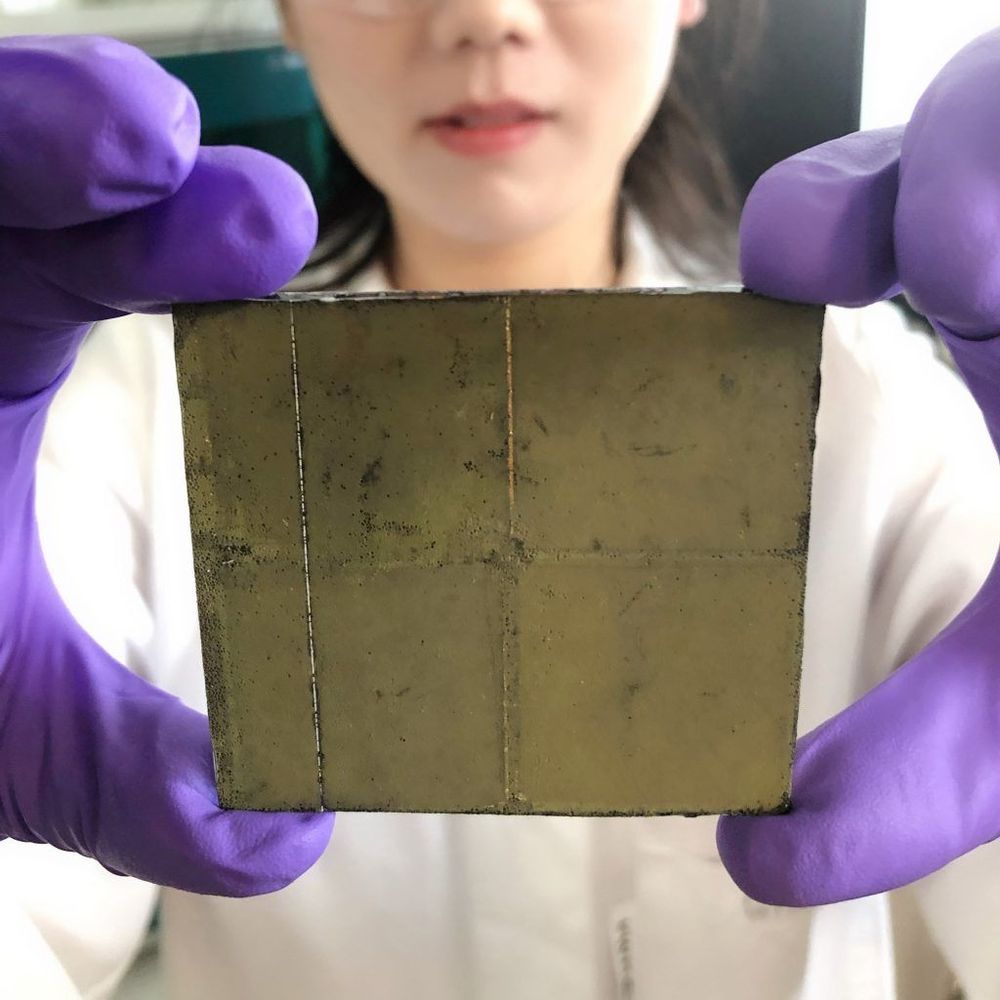
Key to the innovation is the photosheet — or photocatalyst sheet — which uses special semiconductor powders that enable electron interactions and oxidation to occur when sunlight hits the sheet in water, with the help of a cobalt-based catalyst.