The unlikely association of Japan’s Self-Defense Forces with adorable anime characters could reflect a deep-seated discomfort with the nation’s military history.
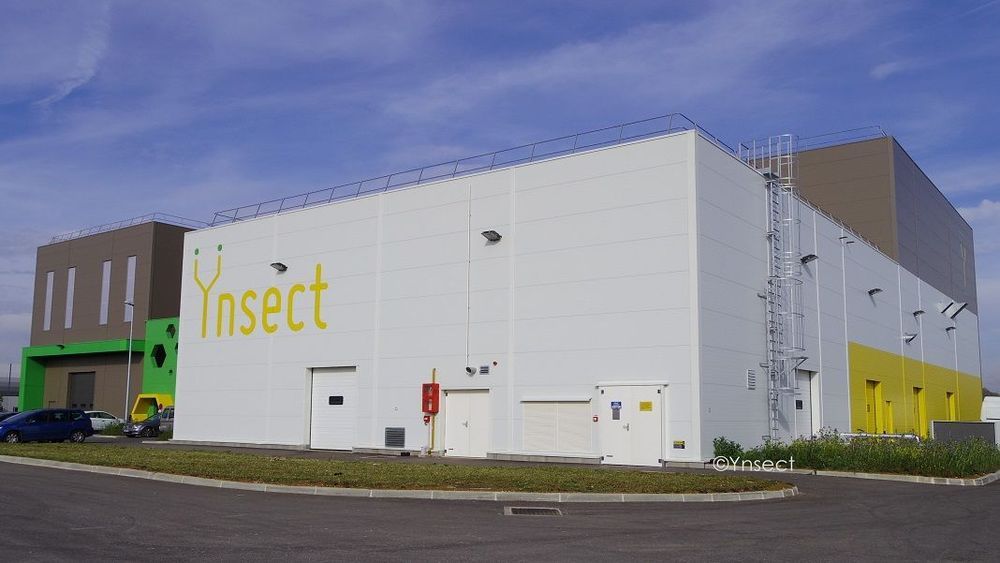



It looks like our food for the future will be bugs. A factory in France will grow bugs as a food source.
in Series C funding in early 2019, and at the time already had $70 million worth of aggregated orders to fill. Now they’re building a bug-farming plant to churn out tiny critters in record numbers.
You’ve probably heard of vertical farms in the context of plants; most existing vertical farms use LED lights and a precise mixture of nutrients and water to grow leafy greens or other produce indoors. They maximize the surface area used for growing by stacking several layers of plants on top of one another; the method may not make for as much space as outdoor fields have, but can yield a lot more than you might think.
Ÿnsect’s new plant will use layered trays too, except they’ll be cultivating beetle larvae instead of plants. The ceilings of the facility are 130 feet high—that’s a lot of vertical space to grow bugs in. Those of us who are grossed out by the thought will be glad to know that the whole operation will be highly automated; robots will tend to and harvest the beetles, and AI will be employed to keep tabs on important growing conditions like temperature and humidity.



Renewable energy is now richer than the Oil industry.
In yet another sign of the pace of the global energy transition – and the massive switch taking place in the investment community – the market value of company that describes itself as the world’s biggest producer of wind and solar power, US utility NextEra, has overtaken that of what used to be the world’s most valuable company, oil major ExxonMobil.
The flip occurred last last week, when NextEra overtook ExxonMobil to become the largest energy company in the US by market value. As Forbes reported, an investment in NextEra a decade ago would have delivered to return of 600 per cent, while an investment in ExxonMobil would have returned minus 25 per cent.
The shift is as significant as the one the world has seen in the auto industry, with electric vehicle maker Tesla overtaking the biggest car companies in the world in the last year, to the point where it is now valued at more than the next five biggest global car makers combined, despite producing just a fraction of the number of cars.
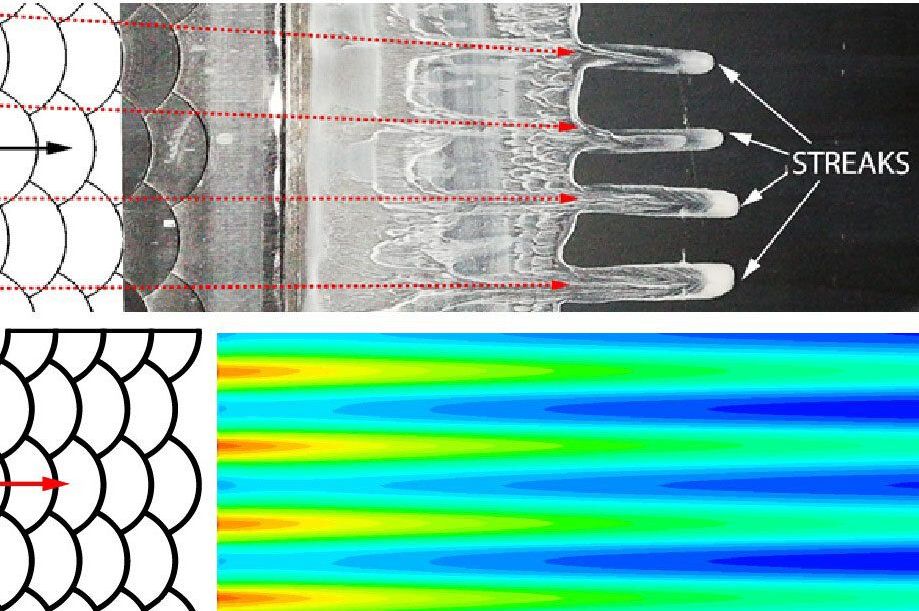
The team’s findings have been published in Nature: Scientific Reports: “Transition delay using biomimetic fish scale arrays,” and in the Journal of Experimental Biology: “Streak formation in flow over biomimetic fish scale arrays.”
Reducing drag means faster aircraft speeds and less fuel consumption—an important area of study for aerodynamicists such as Professor Bruecker, City’s Royal Academy of Engineering Research Chair in Nature-Inspired Sensing and Flow Control for Sustainable Transport, and City’s Sir Richard Oliver BAE Systems Chair for Aeronautical Engineering.
Through their biomimetic study, Professor Bruecker’s team has discovered that the fish-scale array produces a zig-zag motion of fluid in overlapping regions of the surface of the fish, which in turn causes periodic velocity modulation and a streaky flow that can eliminate Tollmien-Schlichting wave induced transition to reduce skin friction drag by more than 25 percent.
Yes, it is True! A Tesla car is cruising space! The founder of SpaceX Elon Musk wanted to launch a ‘silly’ payload for SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket debut flight because a rocket’s first flight has potential to fail. Typically, aerospace companies launch massive concrete blocks as mass simulators during risky rocket flights. As the dreamer that Musk is, he opted to launch something that would inspire the public to dream big and look at the stars — his flashy midnight cherry Tesla Roadster. The electric vehicle became the crazy payload for the rocket’s launch.
On February 6, 2018, SpaceX conducted Falcon Heavy’s debut flight; It lifted-off from historic launch Pad 39A at NASA Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida. The successful test turned Falcon Heavy into the most powerful rocket in operation, it produced about five million pounds of thrust (22MN). During the mission, SpaceX shared Live footage as the Tesla Roadster was placed into orbit. It was a very inspiring to watch an actual car orbiting around Earth with, a mannequin dressed as an astronaut, positioned in the Tesla driver’s seat; while the radio played “Life on Mars” by David Bowie (video below). After the awe-inspiring launch, Musk wholeheartedly said — “Life cannot just be about solving one sad problem after another. There need to be things that inspire you, that make you glad to wake up in the morning and be part of humanity. That is why we did it. We did for you.”

Ramping Up
Johnson announced that the U.K. would invest about £160 million ($207 million) that will go toward factories that would develop new turbines as well as floating offshore turbines themselves. In order to power every home in the U.K., those turbines would need to generate about 40 GW of power, Engadget reports. That’s four times the nation’s current wind energy output.
“Your kettle, your washing machine, your cooker, your heating, your plug-in electric vehicle, the whole lot of them will get their juice cleanly and without guilt from the breezes that blow around these islands,” Johnson announced at the U.K. Conservative party conference.


Circa 2016
Scientists from a Belgian university have built a solar-powered machine that can turn urine into drinkable water. They deployed it at a 10-day music and theater festival in central Ghent, Belgium. The experiment was a success as the scientists were able to recover a 1,000 litres of unconsumed water, which will be used to make Belgian beer, from the urine of several partygoers.