Technology paves way for intelligent solar cells, other highly efficient devices programmed at the macro and nano scale.
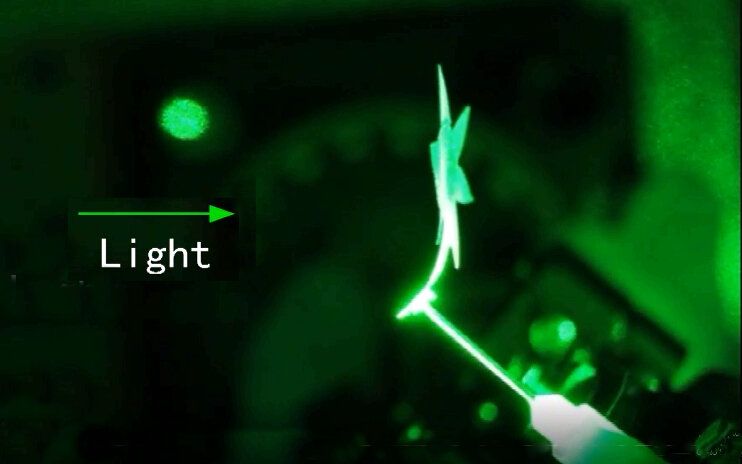
Researchers at Tufts University School of Engineering have created light-activated composite devices able to execute precise, visible movements and form complex three-dimensional shapes without the need for wires or other actuating materials or energy sources. The design combines programmable photonic crystals with an elastomeric composite that can be engineered at the macro and nano scale to respond to illumination.
The research provides new avenues for the development of smart light-driven systems such as high-efficiency, self-aligning solar cells that automatically follow the sun’s direction and angle of light, light-actuated microfluidic valves or soft robots that move with light on demand. A “photonic sunflower,” whose petals curl towards and away from illumination and which tracks the path and angle of the light, demonstrates the technology in a paper that appears today (March 12th, 2021) in Nature Communications.