New observations of microscopic vortices confirm the existence of a paradoxical phase of matter that may also arise inside neutron stars.


The discovery of pyrene in this far-off cloud, which is similar to the collection of dust…
A team led by researchers at MIT has discovered that a distant interstellar cloud contains an abundance of pyrene, a type of large, carbon-containing molecule known as a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH).
The discovery of pyrene in this far-off cloud, which is similar to the collection of dust and gas that eventually became our own solar system, suggests that pyrene may have been the source of much of the carbon in our solar system. That hypothesis is also supported by a recent finding that samples returned from the near-Earth asteroid Ryugu contain large quantities of pyrene.
“One of the big questions in star and planet formation is: How much of the chemical inventory from that early molecular cloud is inherited and forms the base components of the solar system? What we’re looking at is the start and the end, and they’re showing the same thing. That’s pretty strong evidence that this material from the early molecular cloud finds its way into the ice, dust, and rocky bodies that make up our solar system,” says Brett McGuire, an assistant professor of chemistry at MIT.


British startup plans to supply solar power from space to Icelanders by 2030, in what could be the world’s first demonstration of this novel renewable energy source.
The space solar power project, announced on Monday (Oct. 21), is a partnership between U.K.-based Space Solar, Reykjavik Energy and Icelandic sustainability initiative Transition Labs.
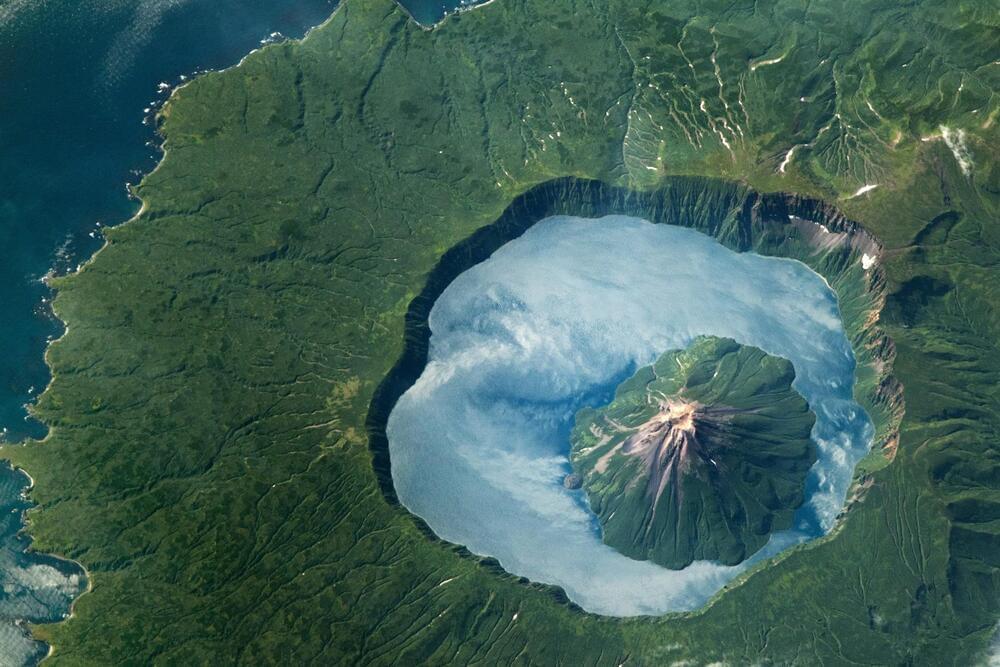
An astronaut captured an enthralling image of Onekotan Island from the International Space Station, showcasing the Krenitsyna Volcano of the Kuril Islands chain.
This remarkable photo highlights geographical features like the Tsar-Rusyr caldera and its deep, reflective Kol’tsevoye Lake, which is among Russia’s deepest. The volcano’s last eruption in 1952 adds a historical layer to the viewing experience, juxtaposing the rugged terrain against the caldera’s lush, vegetated landscape.
Capturing onekotan: a stunning image from space.
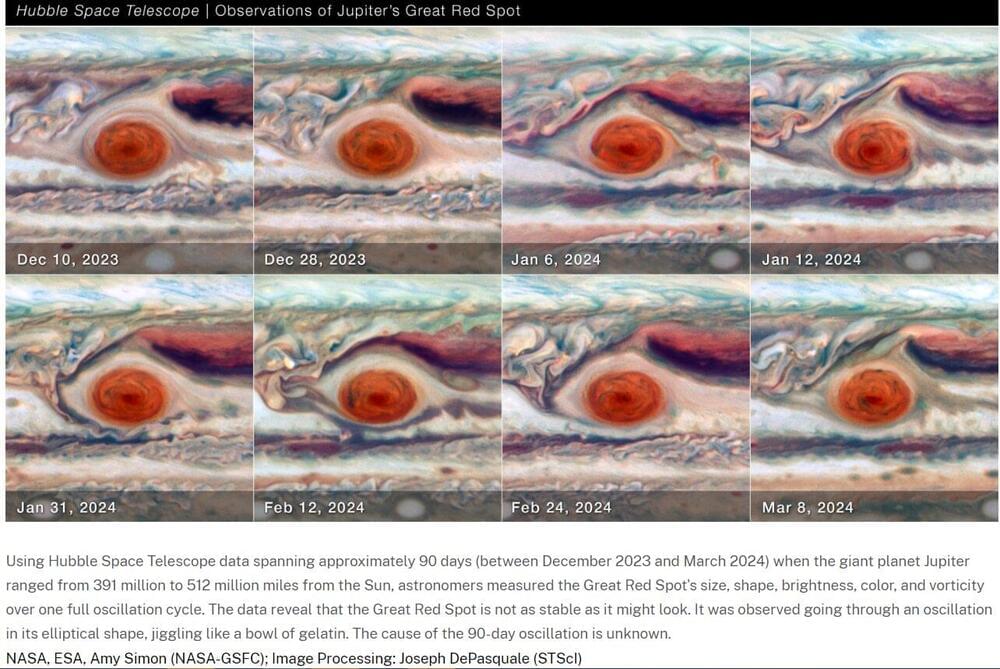
Astronomers have observed Jupiter’s legendary Great Red Spot (GRS), an anticyclone large enough to swallow Earth, for at least 150 years. But there are always new surprises — especially when NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope takes a close-up look at it.
Hubble’s new observations of the famous red storm, collected 90 days between December 2023 to March 2024, reveal that the GRS is not as stable as it might look. The recent data show the GRS jiggling like a bowl of gelatin. The combined Hubble images allowed astronomers to assemble a time-lapse movie of the squiggly behavior of the GRS.
“While we knew its motion varies slightly in its longitude, we didn’t expect to see the size oscillate. As far as we know, it’s not been identified before,” said Amy Simon of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, lead author of the science paper published in The Planetary Science Journal. “This is really the first time we’ve had the proper imaging cadence of the GRS. With Hubble’s high resolution we can say that the GRS is definitively squeezing in and out at the same time as it moves faster and slower. That was very unexpected, and at present there are no hydrodynamic explanations.”
As Oumuamua leaves our solar system, we explore the reasons for continuing the chase.🔒Remove your personal information from the web at JoinDeleteMe.com/astrum and use code ASTRUM for 20% off 🙌
DeleteMe international Plans: https://international.joindeleteme.com.
A huge thanks to our Patreons who help make these videos possible. Sign-up here: https://bit.ly/4aiJZNF
Astrum Podcast: https://www.buzzsprout.com/2250635/share.
Displate Posters: https://astrumspace.info/Displates.
Astrum Merch! https://astrum-shop.fourthwall.com/
Join us on the Astrum discord: / discord.
SUBSCRIBE for more videos about space and astronomy.
Subscribe! http://goo.gl/WX4iMN
Facebook! http://goo.gl/uaOlWW
Twitter! http://goo.gl/VCfejs.
Astrum Spanish: / @astrumespanol.
Astrum Portuguese: / @astrumbrasil.
Credits.

Voyager 1 reconnected with Earth using a backup transmitter inactive for over 40 years.
NASA’s Voyager 1 probe, the most distant human-made object, briefly lost contact with Earth between Oct. 19 and Oct. 24 due to an unexpected shutdown of its main radio transmitter. This signal loss occurred after a command sent to power one of Voyager’s heaters unintentionally triggered the probe’s fault protection system. As a safeguard, the fault protection system automatically powers down non-essential functions when the spacecraft detects an overdraw of its power supply or other malfunctions. Engineers have since reestablished contact through Voyager 1’s backup S-band transmitter, which hadn’t been used since 1981.

While scientists know there’s water on the Moon, its exact locations and forms remain largely unknown. A trailblazing NASA mission will get some answers.
NASA’s Lunar Trailblazer mission, designed to map and study water on the Moon, will employ innovative instruments to explore surface water dynamics and support future lunar colonies by providing vital data on potential water sources that could be converted into oxygen or fuel.
Unveiling lunar mysteries: nasa’s trailblazer mission.
