Our trusted and proven sources were correct once again, as just hours after we broke the news that a Gattaca series is in development at Showtime, The Hollywood Reporter confirmed our exclusive. One of our writers here at Giant Freakin Robot wrote just two weeks ago that the 1997 dystopian sci-fi classic would be perfect as a television series, and it’s amazing how quickly we went from hoping it would happen to confirming that it is. The new series will be coming from the creators of Homeland, Howard Gordan and Alex Gansa.
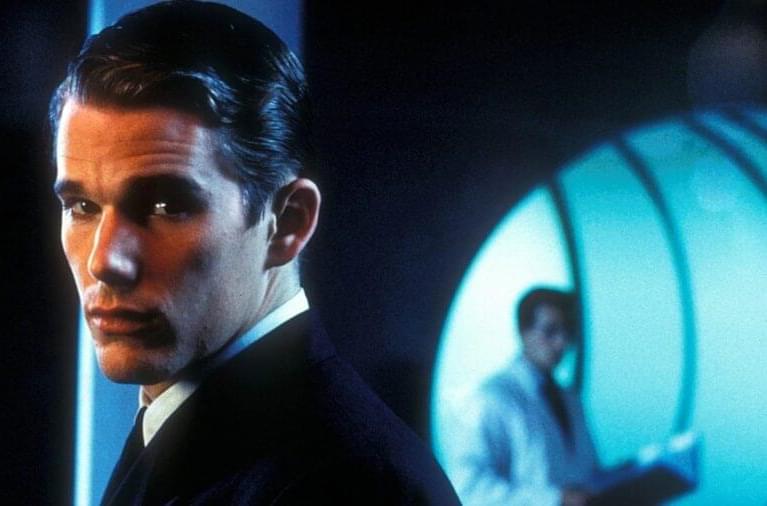
As noted in our initial report, this is not the first time the film, starring Ethan Hawke, Uma Thurman, and Jude Law, has been optioned as a series. Back in 2009, Sony attempted to turn the movie into a procedural from Gil Grant, a writer on 24 and NCIS. The underrated cult-classic movie is ideal for transforming into a prestige series on a premium network as its themes on transhumanism, genetic manipulation, and a stratified society have become more relevant as technology leaps forwards every year.
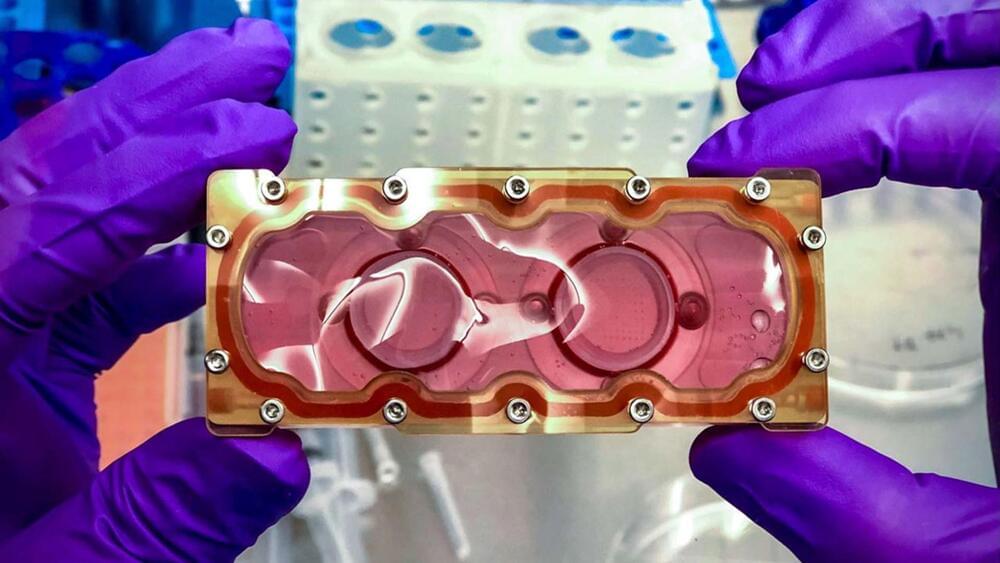
In Gattaca, eugenics separates society into “valids” and “in-valids,” even if genetic discrimination is illegal; that hasn’t stopped businesses from profiling, giving the best jobs to the former and only menial labor opportunities to the latter. Ethan Hawke plays Vincent, an in-valid with a heart defect that uses samples from Jude Law’s Jerome Morrow, a paralyzed Olympic champion swimmer that’s also a valid. Using the purloined DNA, Vincent cons his way into a job at Gattaca Aerospace Corporation, eventually being selected as a navigator for a trip to Saturn’s moon, Titan.