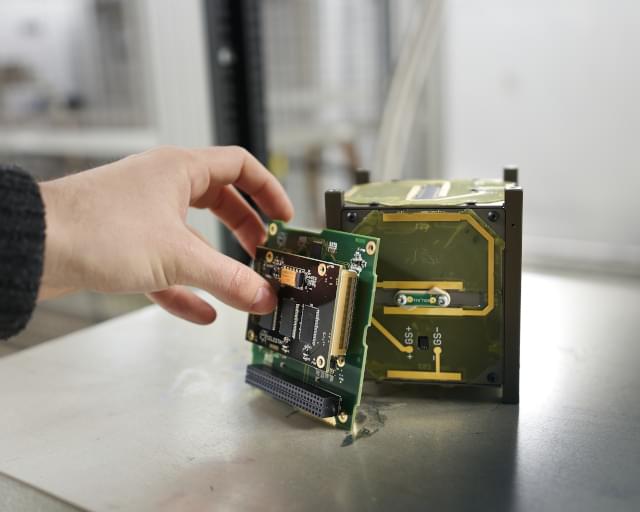
CELESTA, the first CERN-driven satellite, successfully entered orbit during the maiden flight of Europe’s Vega-C launch vehicle. Launched by the European Space Agency from the French Guiana Space Centre (CSG) at 13.13 UTC on 13 July 2022, the satellite deployed smoothly and transmitted its first signals in the afternoon. Weighing one kilogram and measuring 10 centimetres on each of its sides, CELESTA (CERN latchup and radmon experiment student satellite) is a 1U CubeSat designed to study the effects of cosmic radiation on electronics. The satellite carries a Space RadMon, a miniature version of a well-proven radiation monitoring device deployed in CERN’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC). CELESTA has been sent into an Earth orbit of almost 6,000 kilometres. “Right in the middle of the inner Van Allen belt, CELESTA will survey an unusual orbit where radiation levels are at their highest,” explains Markus Brugger, Head of the CERN Experimental Areas group and initiator of both the CHARM and CELESTA projects in the context of the R2E (Radiation to Electronics) initiative. The Space RadMon is a flagship example of how CERN technologies can have applications beyond particle physics experiments. “Based entirely on standardised, ultra-sensitive components selected and calibrated by CERN, and mostly in CERN facilities, the Space RadMon is a lightweight and low-power instrument, ideal for future risk-tolerant space missions,” says Ruben Garcia Alia, R2E project leader. “If CELESTA is successful, the Space RadMon could even be adapted to satellite constellations as a predictive maintenance tool – to anticipate the necessary renewal of satellites.” A radiation model of the CELESTA satellite was also tested in CHARM, a CERN mixed-field facility capable of reproducing, to a large extent, the radiation environment of low Earth orbit. The mission will be an important validation of this capability at the facility. “Capable of testing satellites all at once, rather than component by component, CHARM is a unique installation worldwide, remarkably different from other irradiation test facilities. It offers a simple, low-cost alternative and the possibility to assess system-level effects,” says Salvatore Danzeca, CHARM facility coordinator. The success of this satellite is the result of a fruitful partnership between CERN and the University of Montpellier, which involved many students from both institutions and radiation effect specialists from CERN. CELESTA is based on the CSUM radiation tolerant platform. It will be operated from the CSUM control centre. The European Space Agency provided the launch slot in the framework of its small satellite programme. “On a mission to make space more accessible, CELESTA is an exciting example of how CERN expertise can have a positive impact on the aerospace industry. With this mission, CERN displays its low-cost solutions for measuring radiation and testing satellites against it – thus providing universities, companies and startups with the means to realise their space ambitions,” concludes Enrico Chesta, CERN’s Aerospace and Environmental Applications Coordinator in the Knowledge Transfer group. Further information: Video of the launch More about the aerospace applications.