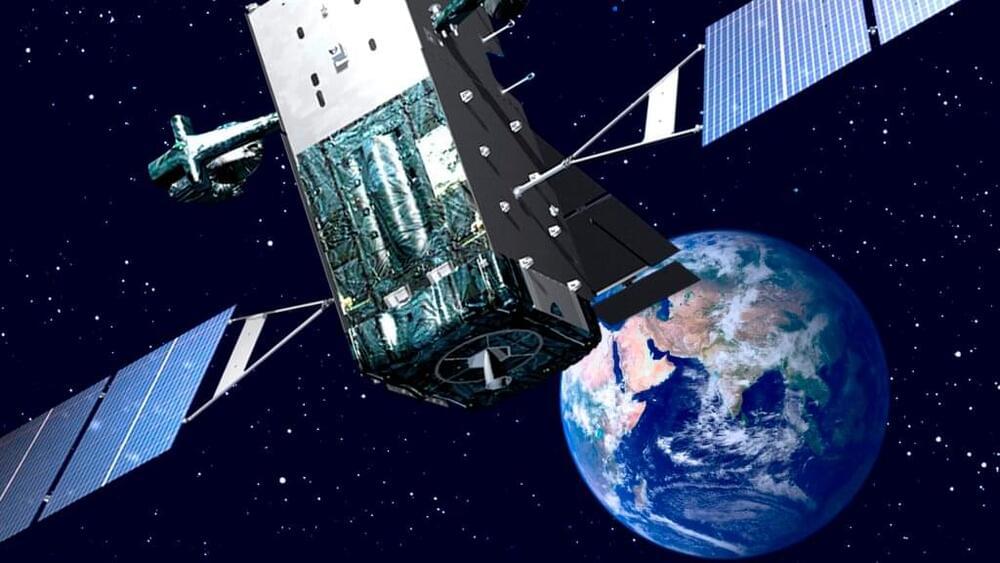
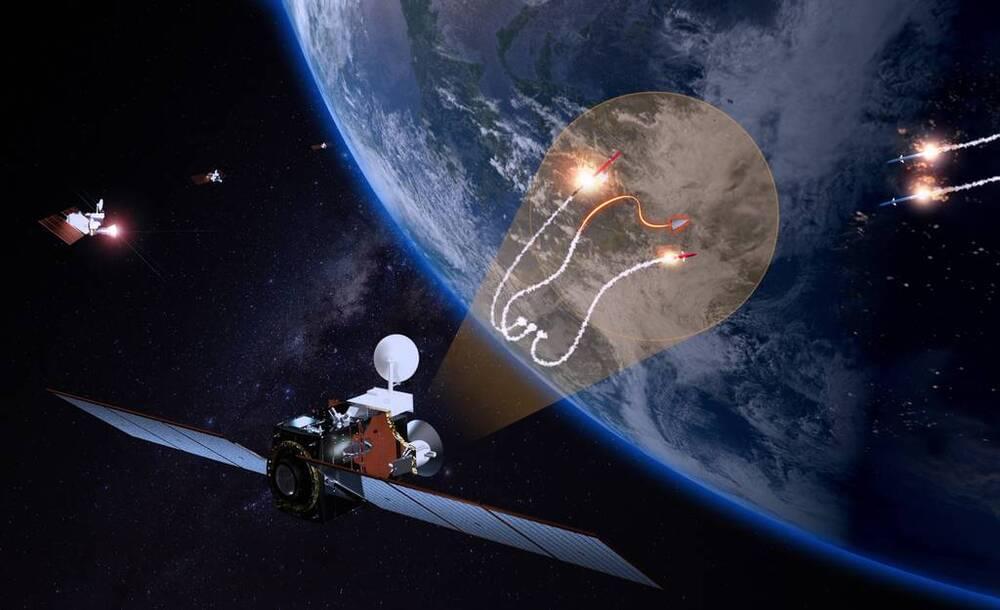
“This launch represents the conclusion of the production and launch phase, and the commencement of the satellites’ critical missile detection and early warning mission,” Maj. Matt Blystone, program manager at the Space Force’s Space Systems Command (SSC), told reporters today at a pre-launch briefing.
SBIRS, conceived in 1996, was designed to replace the elderly Defense Support Program (DSP) satellites, the first of which was launched in 1970. The operational constellation comprises three satellites in Geosynchronous Orbit (GEO) and two hosted payloads on classified satellites in Highly Elliptical Orbits over the poles. Lockheed Martin is the SBIRS prime contractor and Northrop Grumman the payload integrator.
Assuming the Thursday launch goes as planned, the last of the satellites, SBIRS GEO-6, is expected to be up and running by “late spring, early summer” next year, Blystone said. The time between now and then will be filled with various tests of the satellite and its subsystems.