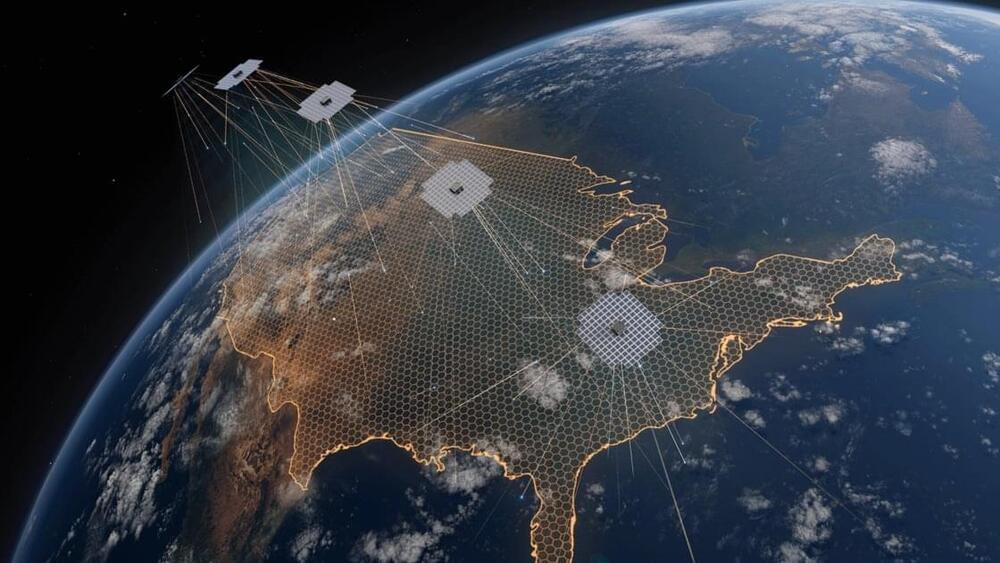
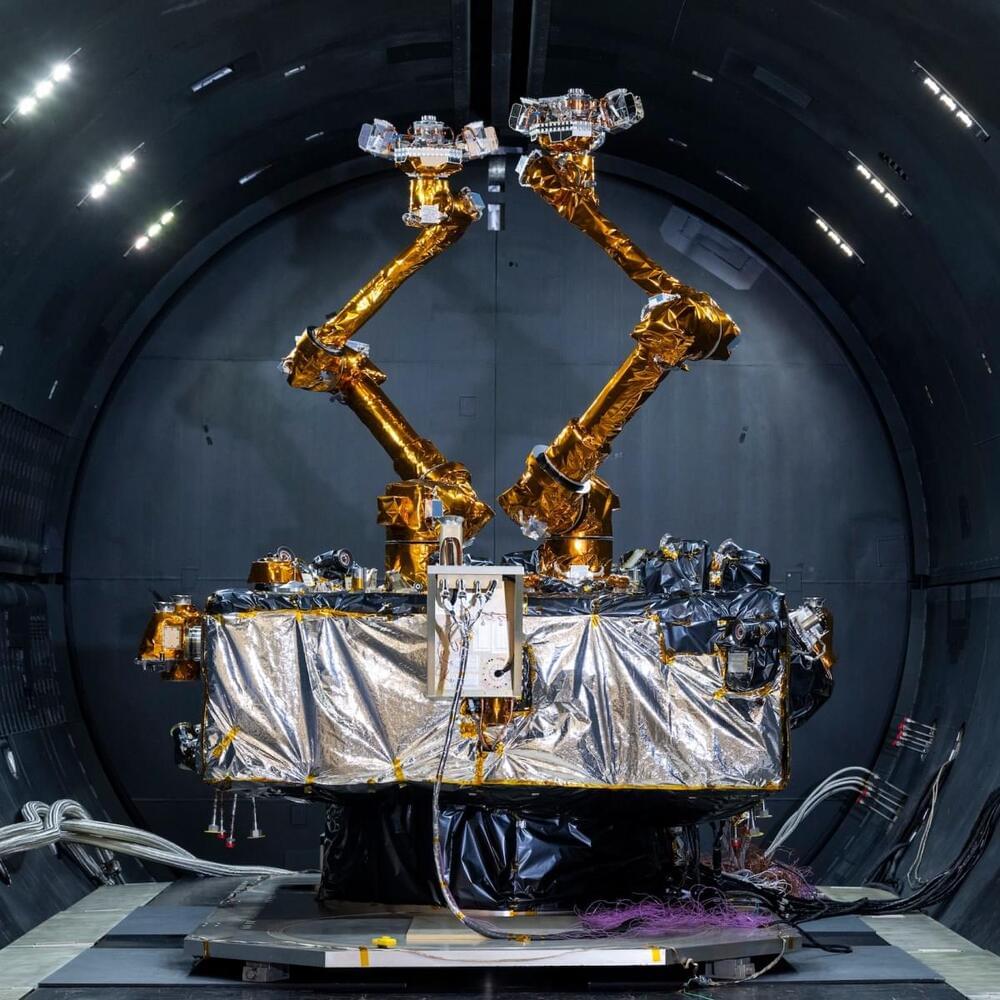
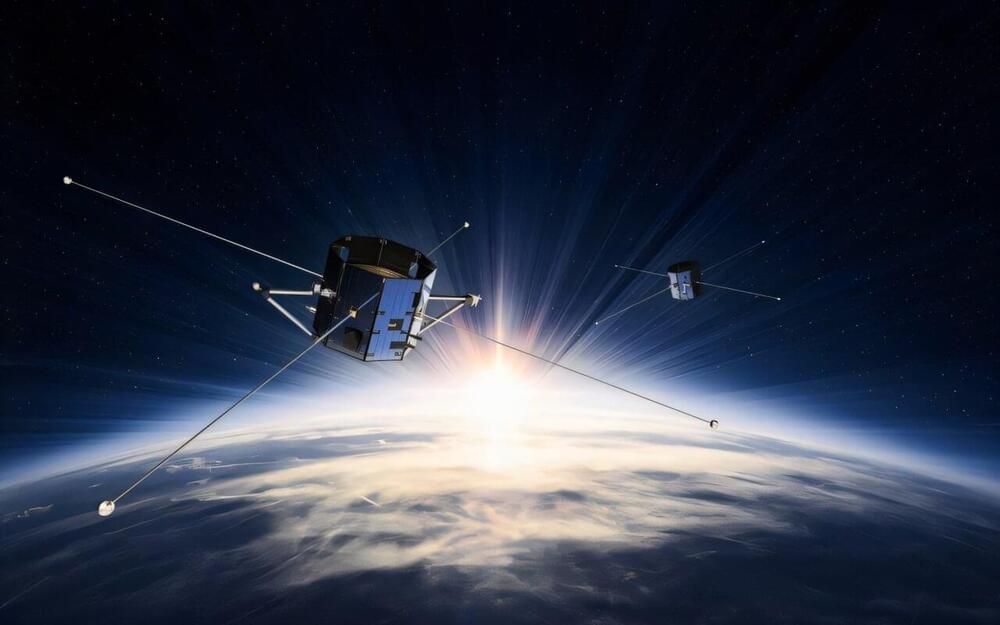
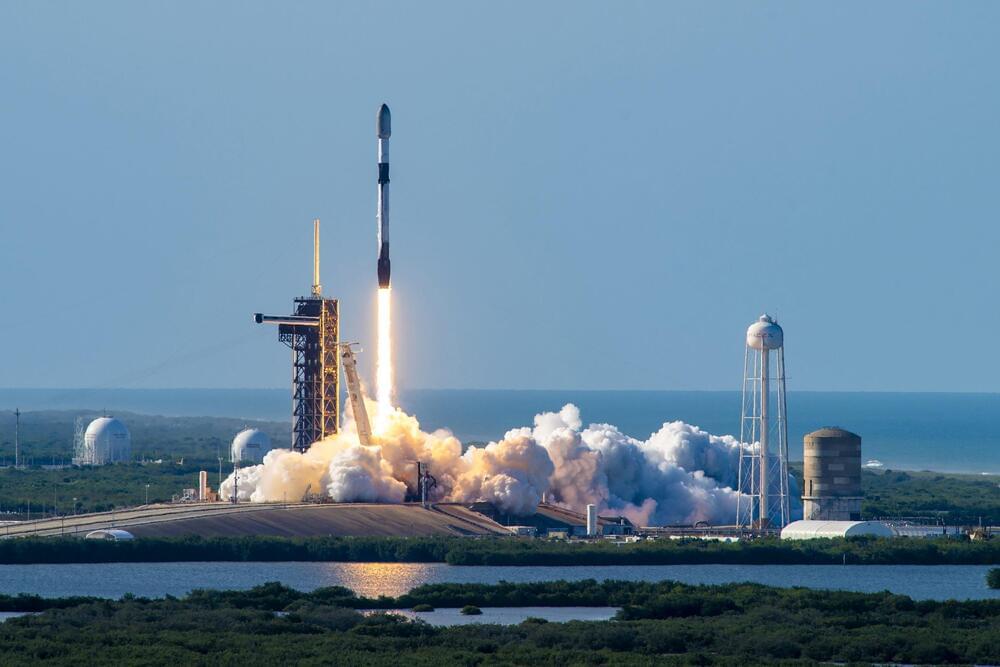
In 2025 and 2026, the company also plans to launch up to 60 next-generation BlueBird satellites with an even larger communications array. The satellites will enable AST SpaceMobile to offer “full continuous service” for potentially hundreds of millions of cellphone customers.
However, satellite industry analyst Tim Farrar notes that AST SpaceMobile still needs FCC approval before it can launch and operate more BlueBird satellites. In August, the US regulator tabled the company’s request to deploy 243 more satellites.