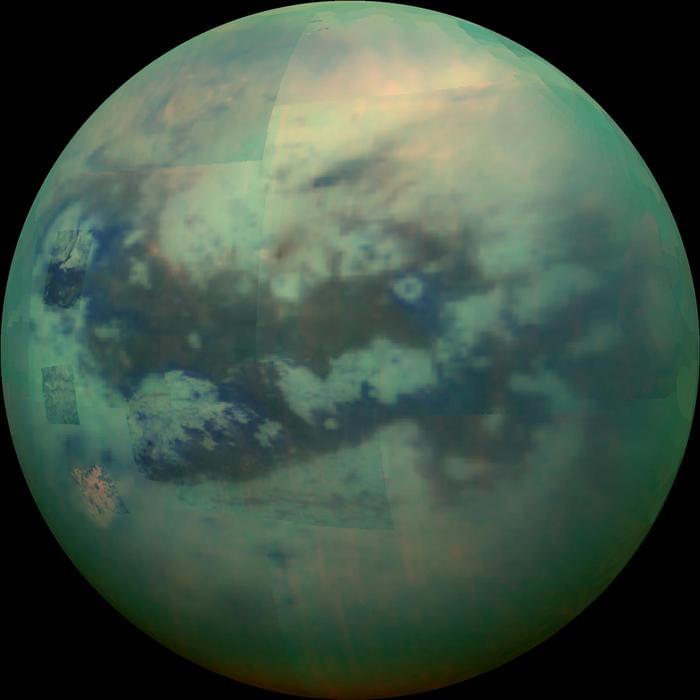
What can a moon’s tidal friction teach us about its formation and evolution? This is what a recent study published in Science Advances hopes to address as a team of researchers at the University of California Santa Cruz investigated a connection between the spin rate and tidal energy on Saturn’s moon, Titan, to determine more about Titan’s interior. This study has the potential to help researchers better understand the internal processes of Titan, leading to better constraints on the existence of a subsurface ocean.
For the study, the researchers used a combination of data obtained by NASA’s now-retired Cassini spacecraft and a series of mathematical calculations to determine Titan’s tidal dissipation, which is the amount of tidal energy lost in an object from friction and other processes, and for which the only moons in the solar system this has been successfully been accomplished being the Earth’s Moon and Jupiter’s volcanic moon, Io. Better understanding a moon’s tidal dissipation helps researchers better understand its formation and evolution, which the researchers successfully estimated for Titan.
“Tidal dissipation in satellites affects their orbital and rotational evolution and their ability to maintain subsurface oceans,” said Dr. Brynna Downey, who is a postdoctoral researcher at the Southwest Research Institute in Colorado and lead author of the study. “Now that we have an estimate for the strength of tides on Titan, what does it tell us about how quickly the orbit is changing? What we discovered is that it’s changing very quickly on a geologic timescale.”