Amazon is planning a satellite internet constellation that could rival SpaceX Starlink, touted by CEO Elon Musk as a means of getting more people online.
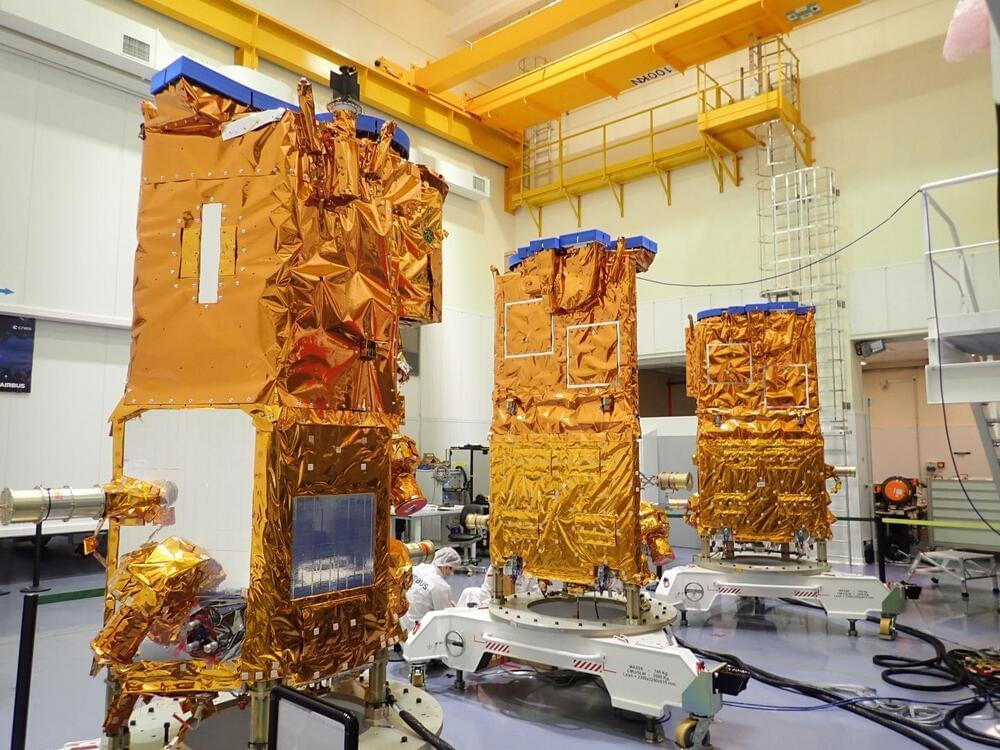




The French Armament General Directorate’s (DGA) ‘Capacité de Renseignement Electromagnétique Spatiale/Space-based Signal Intelligence Capability’ satellites have been successfully launched.
An Arianespace Vega rocket lifted off with the satellites from the European spaceport in French Guiana.
Known by the French acronym CERES, the satellites were designed and built by Airbus Defence and Space, and Thales.

For the satellites spinning around Earth, using electricity to ionize and push particles of xenon gets them to go where they need to go. While xenon atoms ionize easily and are heavy enough to build thrust, the gas is rare and expensive, not to mention difficult to store.
Thanks to new research, we could soon have an alternative. Enter iodine.
Full in-orbit operation of a satellite powered by iodine gas has now been carried out by space tech company ThrustMe, and the technology promises to lead to satellite propulsion systems that are more efficient and affordable than ever before.
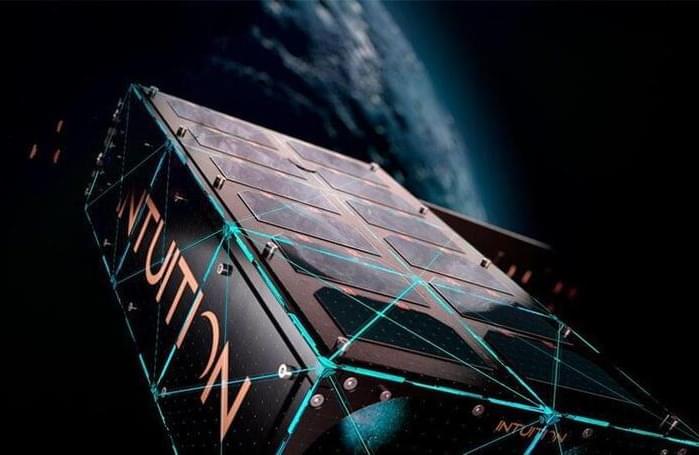

A new European satellite will use machine learning to provide rapid, low-cost information on soil conditions to enable smarter agriculture. The project is a model for what novel sensors and artificial intelligence technology can do in a vehicle no bigger than a shoebox.
Edge computing is a fashionable buzz-phrase for the technique of shifting the processing power away from the server farms of the internet and out to where the data is being collected. According to some, edge computing is the next great tech revolution, and in the case of satellites, where communications bandwidth is severely limited, it could be transformational.
The Intuition-1 satellite program will provide soil data to drive European precision agriculture projects, which involve applying fertilizer only when and where needed rather than treating an entire field. Precision agriculture is both more economical and easier on the environment — the catch is that it requires detailed information about soil conditions on a small scale. At present, establishing levels of soil nutrients in sufficient detail involves taking samples from multiple locations and sending them to a laboratory for analysis. This typically takes about three weeks.
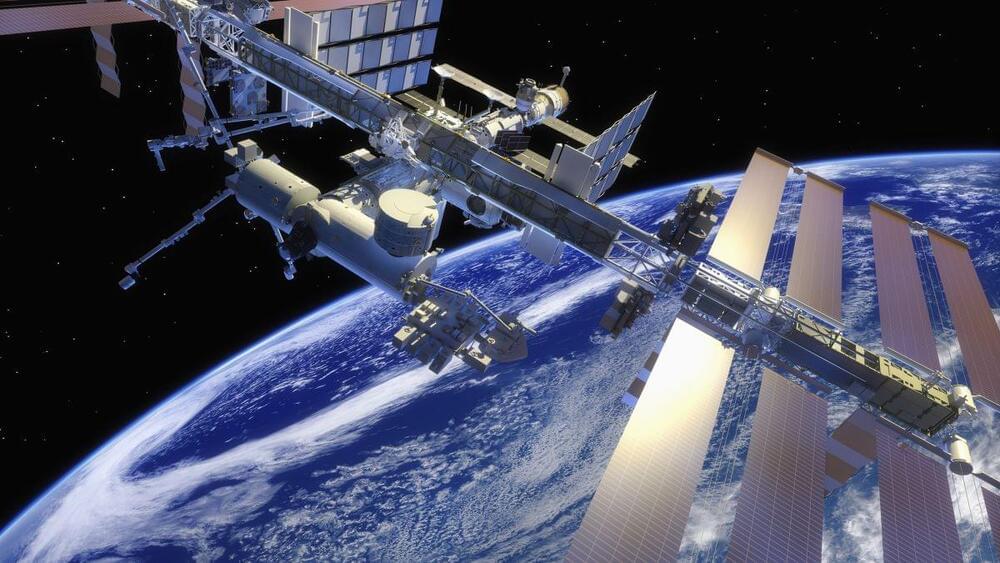

In the wee morning hours of Tuesday (Nov. 16), the seven-person crew of the International Space Station (ISS) awoke in alarm. A Russian missile test had just blasted a decommissioned Kosmos spy satellite into more than 1,500 pieces of space debris — some of which were close enough to the ISS to warrant emergency collision preparations.
The four Americans, one German and two Russian cosmonauts aboard the station were told to shelter in the transport capsules that brought them to the ISS, while the station passed by the debris cloud several times over the following hours, according to NASA.
Ultimately, Tuesday ended without any reported damage or injury aboard the ISS, but the crew’s precautions — and the NASA administrator’s stern response to Russia — were far from an overreaction. Space debris like the kind created in the Kosmos break-up can travel at more than 17,500 mph (28,000 km/h), NASA says — and even a scrap of metal the size of a pea can become a potentially deadly missile in low-Earth orbit. (For comparison, a typical bullet discharged from an AR-15 rifle travels at just over 2,200 mph, or 3,500 km/h).
A Russian missile test blasted a Kosmos spy satellite into more than 1,500 pieces of space debris.
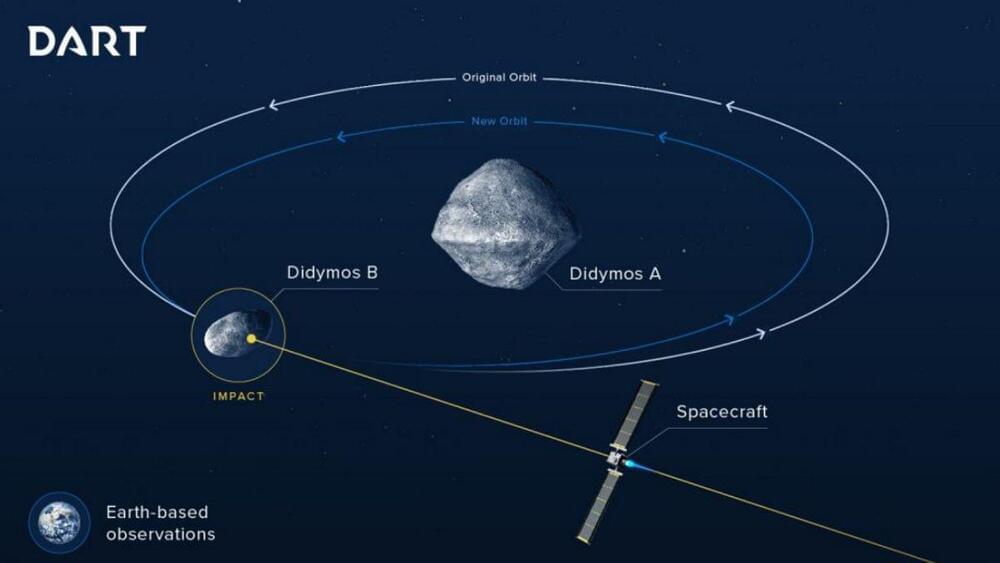
“We know of no asteroids that are coming in to hit the Earth,” Rivkin emphasizes. DART, he says, is part of a multi-pronged effort to examine the asteroid collision problem. “Asteroid impacts are really the only natural disaster that humanity can see coming years or decades in advance and do anything about.”
NASA calls DART its “First Planetary Defense Test Mission.” Rivkin is the DART investigation team lead at Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory, which is running the experiment for NASA.
Full Story:
Andy Rivkin remembers going to the arcade in the early 1980s to play the iconic video game “Asteroids.” Later this month, the team he leads is scheduled to launch a satellite aimed at an asteroid 7 million miles away to prove that Earthlings can save themselves from an asteroid impact by shooting first, Atari-style.
The launch window for NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission opens next week. DART is an experiment to see if by crashing a spacecraft directly into an asteroid, the asteroid can be nudged off its trajectory. If intercepted and struck far enough away, even a slight alteration in the path of an asteroid could cause it to miss Earth, avoiding a potentially catastrophic impact.

The United States said Monday it was investigating a “debris-generating event in outer space” after astronauts on the International Space Station were forced to prepare for a possible evacuation. It came amid unconfirmed reports that Russia had carried out an anti-satellite weapon (ASAT) test…
“US Space Command is aware of a debris-generating event in outer space. We are actively working to characterize the debris field and will continue to ensure all space-faring nations have the information necessary to maneuver satellites if impacted,” the agency said.
“We are also in the process of working with… the State Department and NASA, concerning these reports and will provide an update in the near future.”
NASA has not yet commented, but its Russian counterpart Roscomos, downplayed the incident.
SpaceX shot 53 Starlink internet satellites into orbit on top of a Falcon 9 rocket Saturday from foggy Cape Canaveral, commencing a new phase of deploying the global broadband network with the first launch into a new “shell” some 335 miles above Earth.
The mission was the 31st Falcon 9 launch in two-and-a-half years dedicated to carrying satellites for the Starlink internet network, bringing the total number of Starlink spacecraft launched to 1,844.
Veiled in fog, the Falcon 9 lifted off from pad 40 at Cape Canaveral at 7:19:30 a.m. EST (1219:30 GMT) Saturday. Nine Merlin main engines throttled up to produce 1.7 million pounds of thrust, powering the launcher off the pad and quickly through the ground-hugging fog layer.
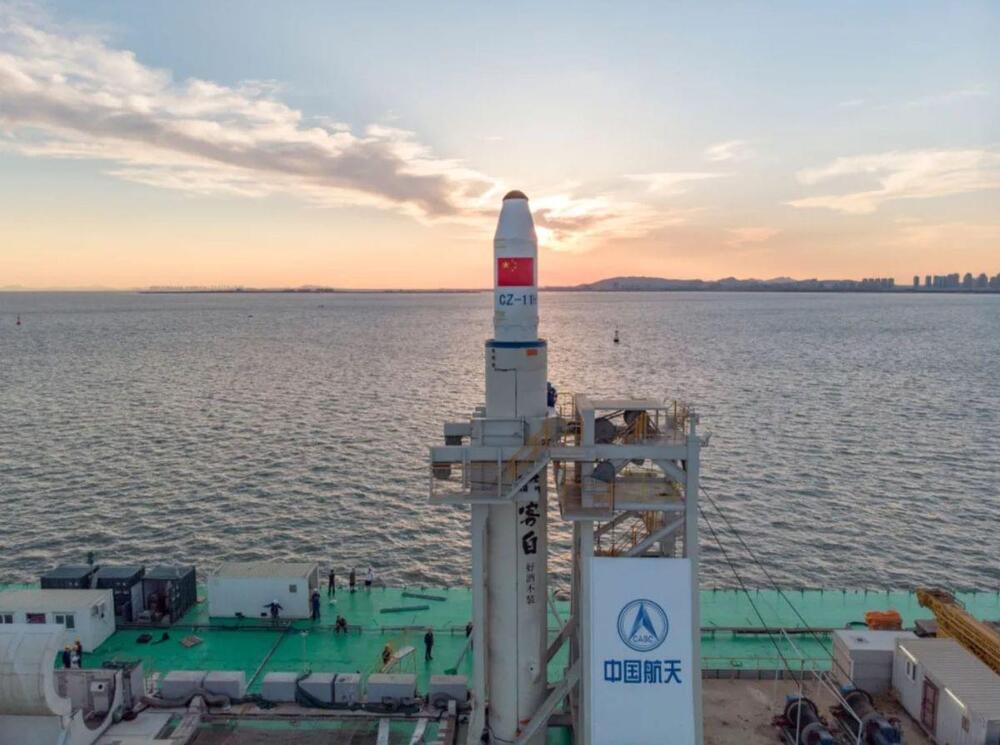

China is building a specially designed ship for launching rockets into space from the seas in an effort to boost its capacity to launch satellites and recover rocket stages.
The 533 feet (162.5 meters) long, 131 feet (40 meters) wide “New-type rocket launching vessel” is being constructed for use with the new China Oriental Spaceport at Haiyang, Shandong province on the Eastern coast.