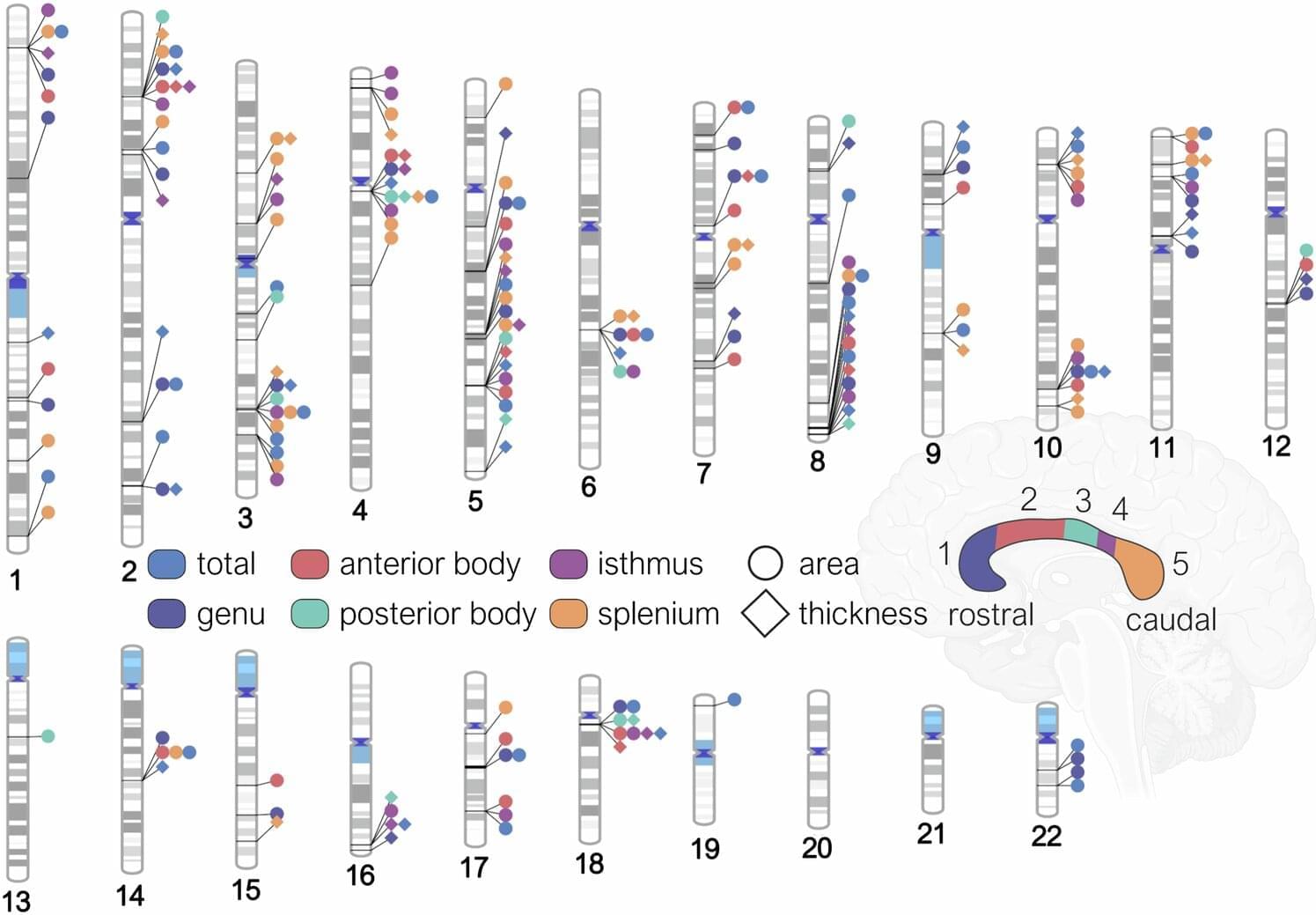
For the first time, a research team led by the Mark and Mary Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute (Stevens INI) at the Keck School of Medicine of USC has mapped the genetic architecture of a crucial part of the human brain known as the corpus callosum—the thick band of nerve fibers that connects the brain’s left and right hemispheres. The findings open new pathways for discoveries about mental illness, neurological disorders and other diseases related to defects in this part of the brain.
The corpus callosum is critical for nearly everything the brain does, from coordinating the movement of our limbs in sync to integrating sights and sounds, to higher-order thinking and decision-making. Abnormalities in its shape and size have long been linked to disorders such as ADHD, bipolar disorder, and Parkinson’s disease. Until now, the genetic underpinnings of this vital structure had remained largely unknown.
In the new study, published in Nature Communications, the team analyzed brain scans and genetic data from over 50,000 people, ranging from childhood to late adulthood, with the help of a new tool the team created that leverages artificial intelligence.