A male fruit fly in a laboratory chamber extends his wings and vibrates them to produce his species’ version of a love song. A female fly stays nearby listening. Suddenly, a green light flashes across the chamber for a fraction of a second. The male’s song cuts off mid-note and his wings fold. The female, not impressed by the interrupted serenade, walks away. The culprit? An AI system that watched the male begin his courtship dance and shut down his song-producing brain cells.
Developed by scientists at Nagoya University and their collaborators from Osaka University and Tohoku University, the AI can watch and recognize animal behaviors and control the specific brain circuits that drive them.
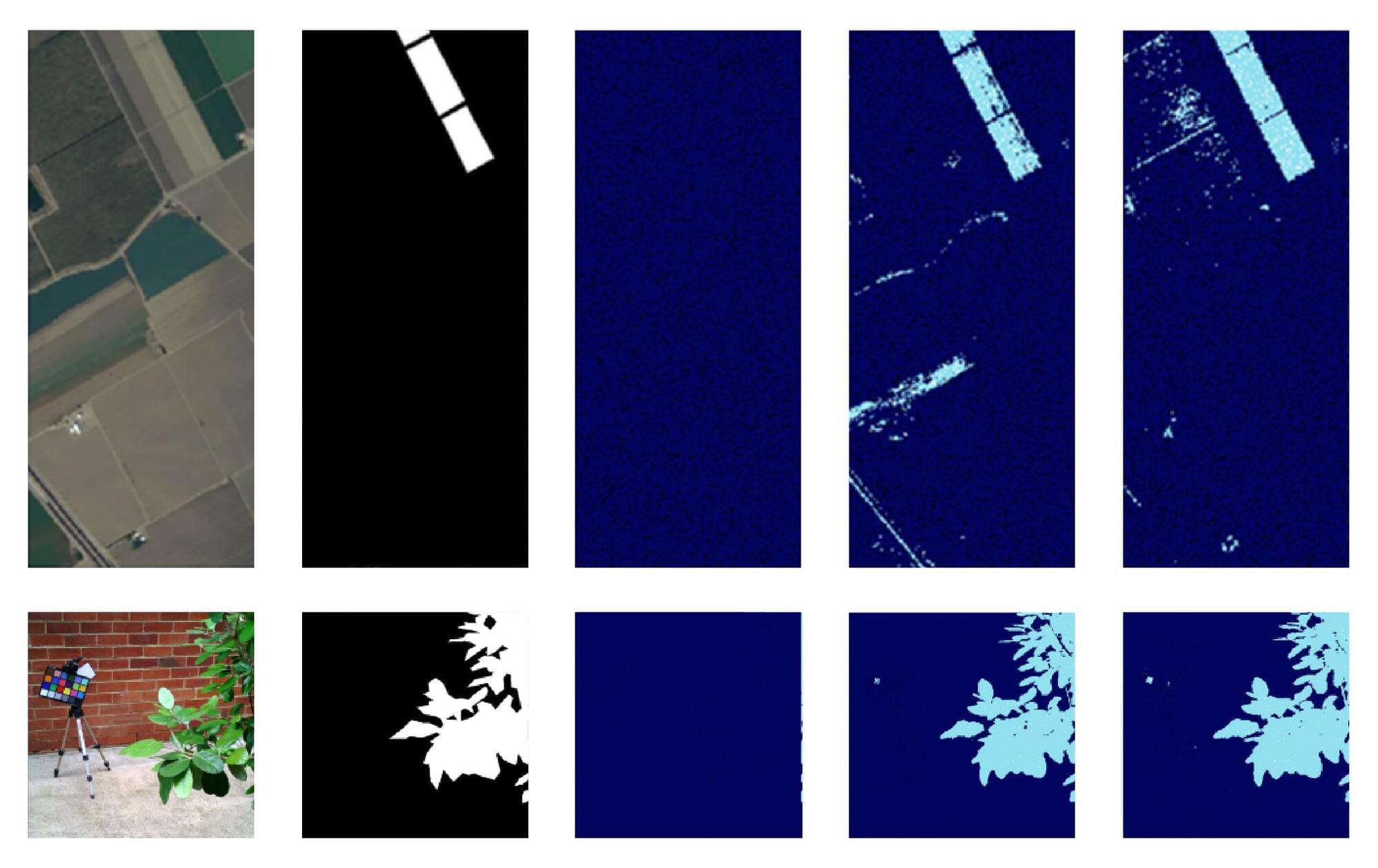
Published in Science Advances, the study presents an advanced AI system that can identify which animal performs a behavior in a group and selectively target only that animal’s brain cells during social interactions.