Control this humanoid robot in VR.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 2,434
Robot VR Experience
Robots help extend VR into the real-world.

Is Artificial Intelligence Dangerous? 6 AI Risks Everyone Should Know About
Misalignment between our goals and the machine’s
Part of what humans value in AI-powered machines is their efficiency and effectiveness. But, if we aren’t clear with the goals we set for AI machines, it could be dangerous if a machine isn’t armed with the same goals we have. For example, a command to “Get me to the airport as quickly as possible” might have dire consequences. Without specifying that the rules of the road must be respected because we value human life, a machine could quite effectively accomplish its goal of getting you to the airport as quickly as possible and do literally what you asked, but leave behind a trail of accidents.
Discrimination.
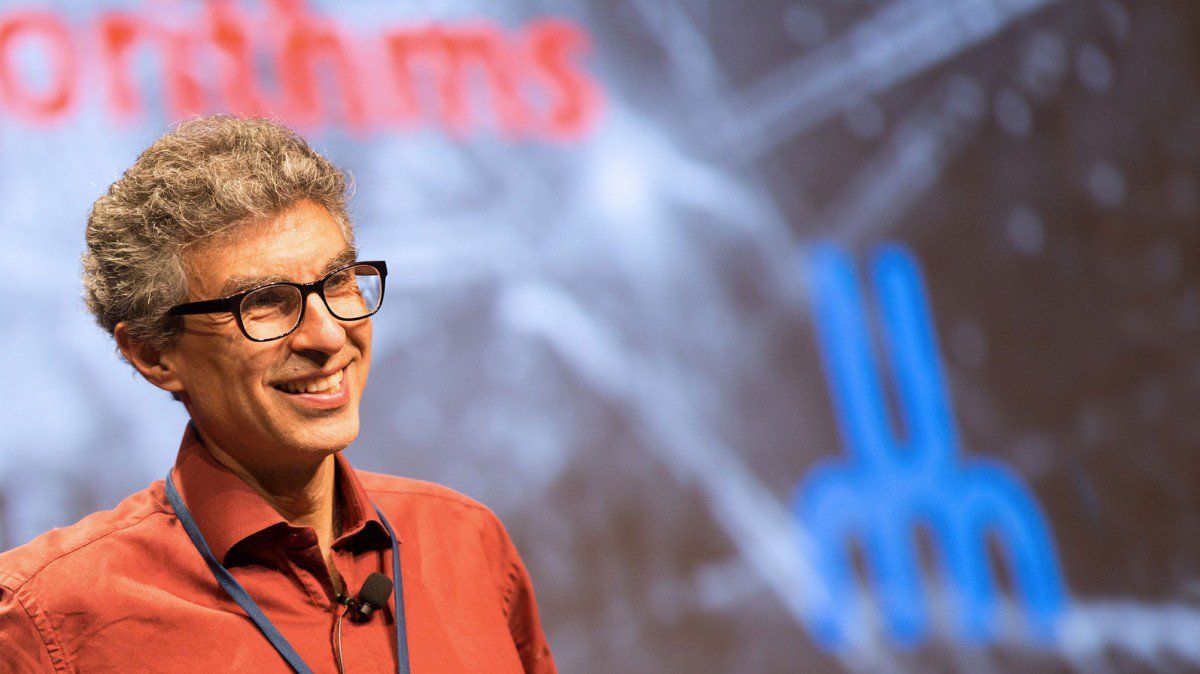

One of the fathers of AI is worried about its future
AI research by itself will tend to lead to concentrations of power, money, and researchers … this is not healthy. Even in a democracy, it’s dangerous to have too much power concentrated in a few hands.
Yoshua Bengio wants to stop talk of an AI arms race, and make the technology more accessible to the developing world.
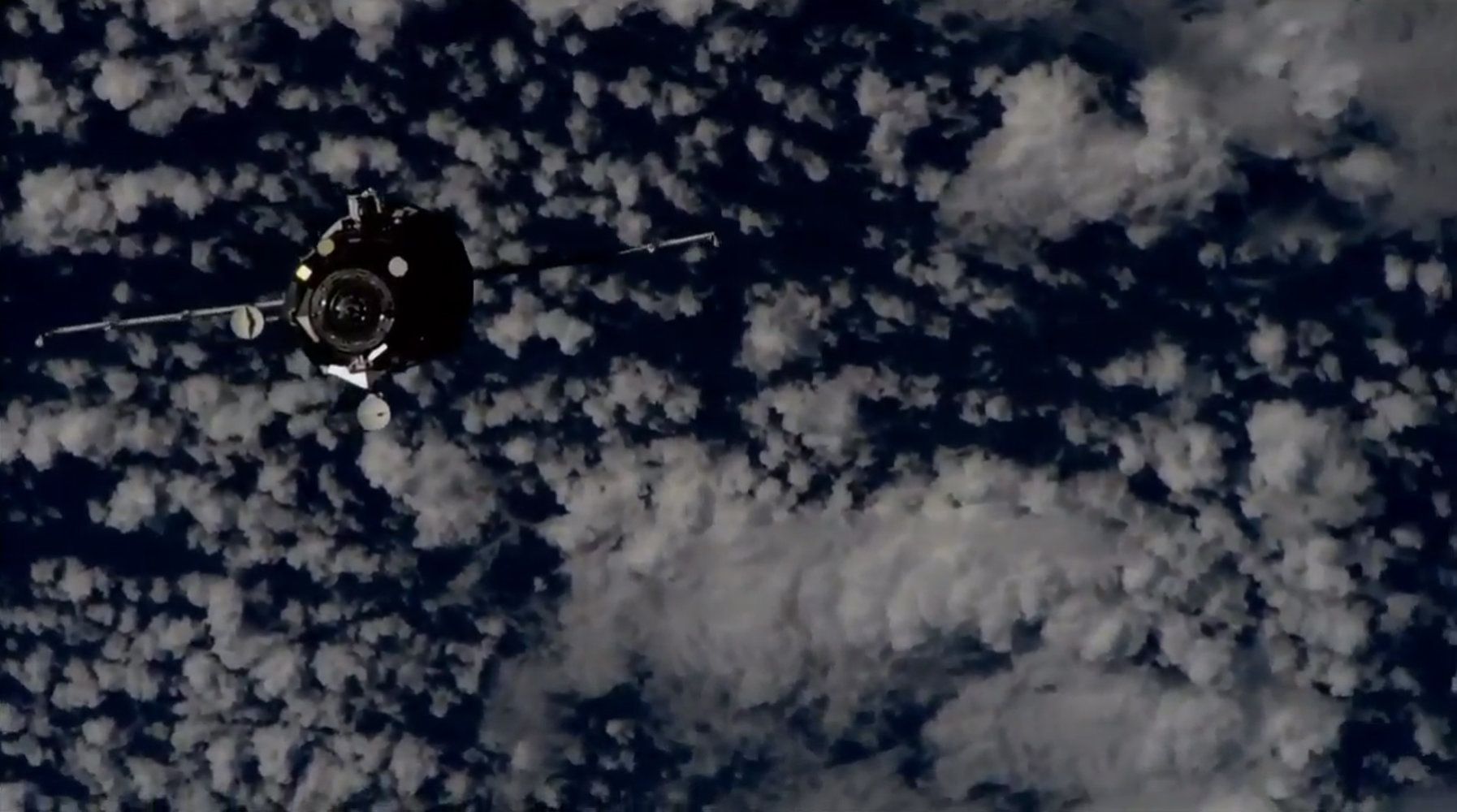

Robotic Russian Cargo Ship Delivers Tons of Supplies to Space Station
An uncrewed Russian cargo ship linked up with the International Space Station Sunday (Nov. 18) to deliver nearly 3 tons of supplies for the orbiting lab.
The resupply ship, called Progress 71, docked at the space station at 2:28 p.m. EST (1928 GMT) as both spacecraft sailed 252 miles (405 kilometers) over Algeria. Progress 71 launched into orbit Friday (Nov. 16) from Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
“A textbook journey for the Progress,” NASA spokesperson Rob Navias said during live commentary. [The Space Station’s Robotic Cargo Ship Fleet in Pictures].
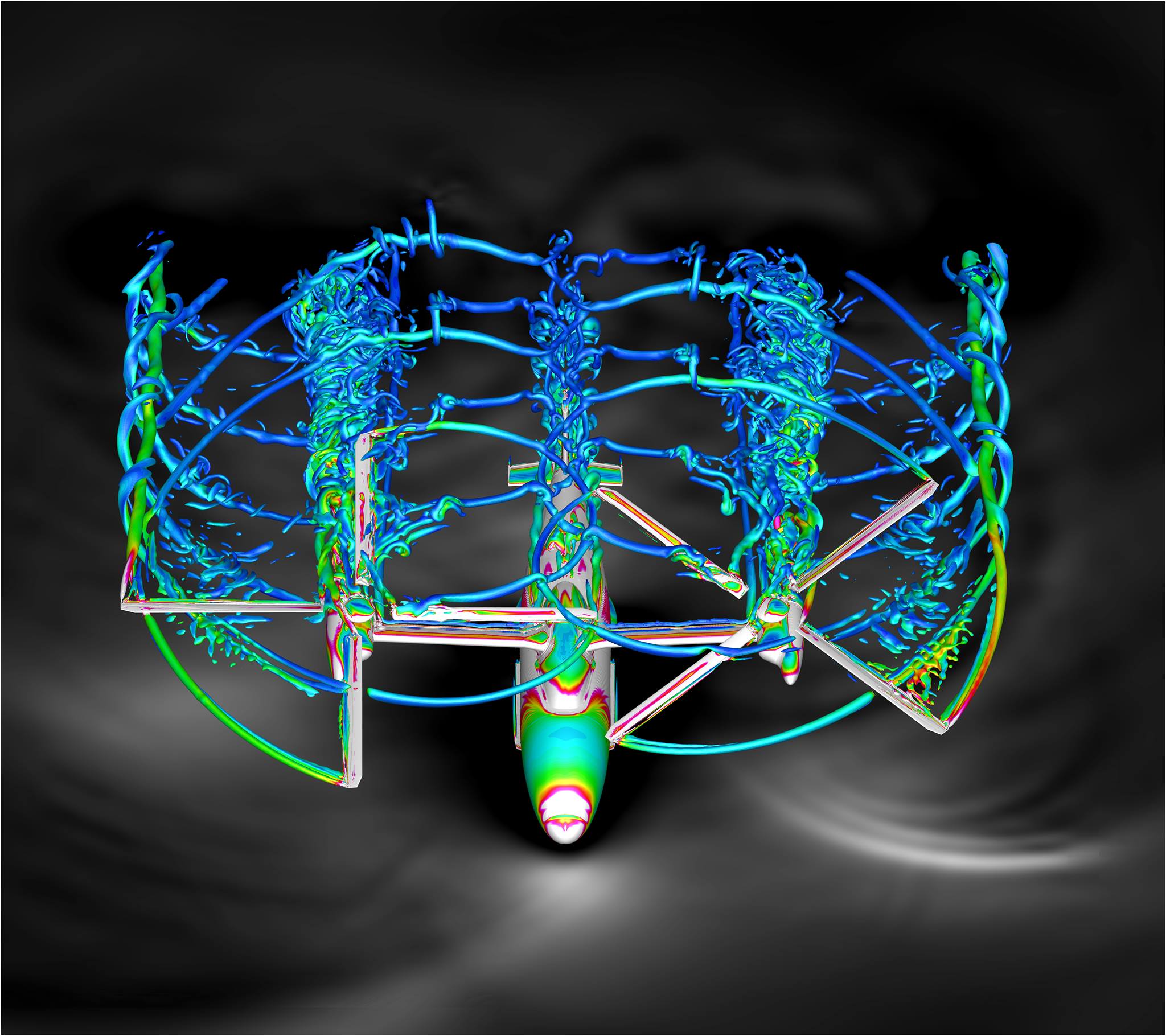
Imagine avoiding ground traffic and riding in one of these air taxis
NASA engineers are using some of the most powerful supercomputers in the world to design rotary wing vehicles that combine both piloted and autonomous operations. Urban Air Mobility is a safe and efficient system that can transport a small number of passengers and cargo, without the need for long runways. Check it out: https://go.nasa.gov/2FvGPfH

Five Functions of the Brain that are Inspiring AI Research
The brain has always been considered the main inspiration for the field of artificial intelligence(AI). For many AI researchers, the ultimate goal of AI is to emulate the capabilities of the brain. That seems like a nice statement but its an incredibly daunting task considering that neuroscientist are still struggling trying to understand the cognitive mechanism that power the magic of our brains. Despite the challenges, more regularly we are seeing AI research and implementation algorithms that are inspired by specific cognition mechanisms in the human brain and that have been producing incredibly promising results. Recently, the DeepMind team published a paper about neuroscience-inspired AI that summarizes the circle of influence between AI and neuroscience research.
You might be wondering what’s so new about this topic? Everyone knows that most foundational concepts in AI such as neural networks have been inspired by the architecture of the human brain. However, beyond that high level statement, the relationship between the popular AI/deep learning models we used everyday and neuroscience research is not so obvious. Let’s quickly review some of the brain processes that have a footprint in the newest generation of deep learning methods.
Attention is one of those magical capabilities of the human brain that we don’t understand very well. What brain mechanisms allow us to focus on a specific task and ignore the rest of the environment? Attentional mechanisms have become a recent source of inspiration in deep learning models such as convolutional neural networks(CNNs) or deep generative models. For instance, modern CNN models have been able to get a schematic representation of the input and ignore irrelevant information improving their ability of classifying objects in a picture.

Elon Musk says a ‘radical change’ is coming to SpaceX’s monster Mars rocket design
- In a tweet, Musk revealed that “radical change” was coming to the design of the Big Falcon Rocket (BFR), which is meant to go to Mars.
- The tweet appeared to indicate that the second stage of the Falcon 9 will now be used for component tests for the BFR, and that the company is abandoning plans to make the second stage of Falcon 9 reusable.
- Musk has said that his “aspirational” goal is to launch an unmanned cargo mission to Mars by 2022.
In a tweet, Saturday, SpaceX founder Elon Musk announced that “radical change” was coming to the design of the Big Falcon Rocket (BFR), that is being made in an attempt to go to Mars.
Musk left out any specifics of his plan, simply announcing that “SpaceX is no longer planning to upgrade Falcon 9 second stage for reusability” and would be “Accelerating BFR instead.” Musk called the new design “very exciting” and “delightfully counter-intuitive.”
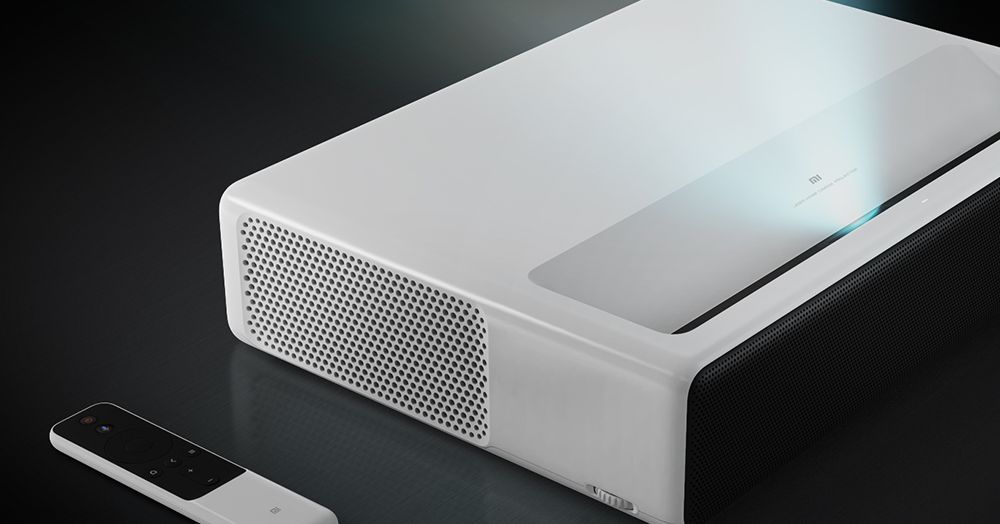

Xiaomi made a 150-inch $2,000 laser projector exclusively available at Walmart
Xiaomi has a couple of new products out in Walmart and gave press the rundown today at an event in New York City. The first is a 150-inch laser projector going for $1,999.99 at Walmart doubles up as a television with Android TV. It may seem overpriced for what it is, but it also marks one of Xiaomi’s infrequent expansions into American offerings.
There are a couple of things to break down here, namely that projector is oddly expensive for a 1920 × 1080p screen. Xiaomi says it has no concrete plans to bring a 4K version to the US, and that this is the same model it’s sold in China. You could have found cheaper 1080p projectors back in 2016.
Still, the laser projector has a number of positives including an ultra-short throw, so it can be placed 20 inches from the wall and still display a bright, colorful image, in contrast with other projectors that might need to be placed at the back of a room and show a more faded image. There’s also a detector on top of the projector so if you get too close to the laser, the projector will shut off its light automatically to prevent you from damaging your eyes. The device also comes with a corresponding remote control with which you can summon Google Assistant.