Researchers working on machine learning have discovered a problem that no one, anywhere in the universe, will ever be able to solve.



By giving $1,000 per month to a family.
Presidential candidate Andrew Yang, a 43-year-old entrepreneur-turned-politician, is focusing his campaign on helping Americans who are losing jobs to automation.
Yang wants all Americans to benefit from a universal basic income, which would provide regular cash payments to people regardless of their employment status. Although he is a long-shot candidate, the Democrat said he believes so strongly in the need for a basic income that he is dedicated to running.
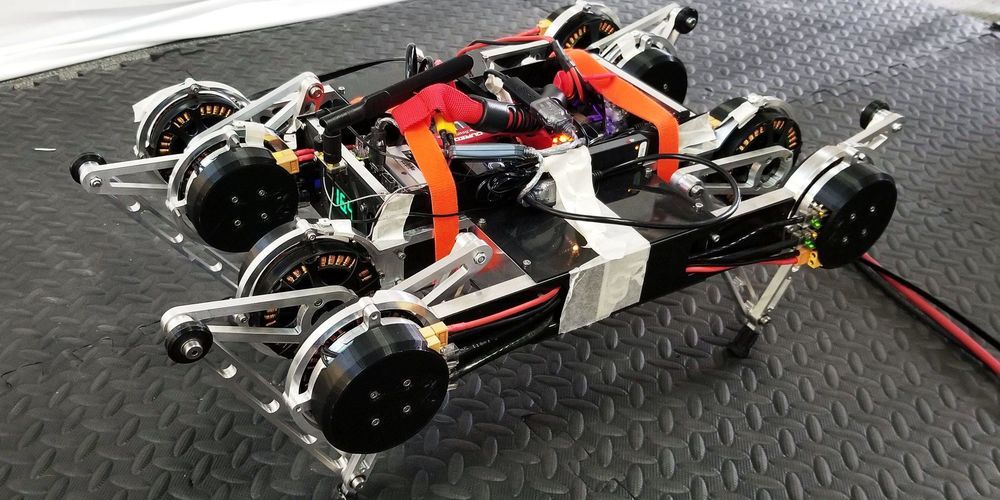
The bike can now hug turns and deftly switch directions.

As the new year begins, we approach one of the most awaited life extension events of 2019: the Undoing Aging conference.
Starting off with a success
The Undoing Aging conference series started off in 2018, with the first being held in Berlin, Germany, in mid-March. Especially when you consider that UA2018 was the inaugural event of the series, it was extremely successful; the three-day conference organized by SENS Research Foundation (SRF) and Forever Healthy Foundation (FHF) brought together many of the most illustrious experts in the fields of aging research, biotechnology, regenerative medicine, AI for drug discovery, advocacy and policy, and business and investment.
Isaac Asimov was one the world’s most celebrated and prolific science fiction writers, having written or edited more than 500 books over his four-decade career. The Russian-born writer was famous for penning hard science fiction in his books, such as that in I, Robot, Foundation and Nightfall. Naturally, his work contained many predictions about the future of society and technology.
We’re not living in space, but the Russian science-fiction author foresaw the rise of intelligent machines and the disruption of the digital age.

These dated interfaces are not equipped to handle today’s exponential rise in data, which has been ushered in by the rapid dematerialization of many physical products into computers and software.
Breakthroughs in perceptual and cognitive computing, especially machine learning algorithms, are enabling technology to process vast volumes of data, and in doing so, they are dramatically amplifying our brain’s abilities. Yet even with these powerful technologies that at times make us feel superhuman, the interfaces are still crippled with poor ergonomics.
Many interfaces are still designed around the concept that human interaction with technology is secondary, not instantaneous. This means that any time someone uses technology, they are inevitably multitasking, because they must simultaneously perform a task and operate the technology.
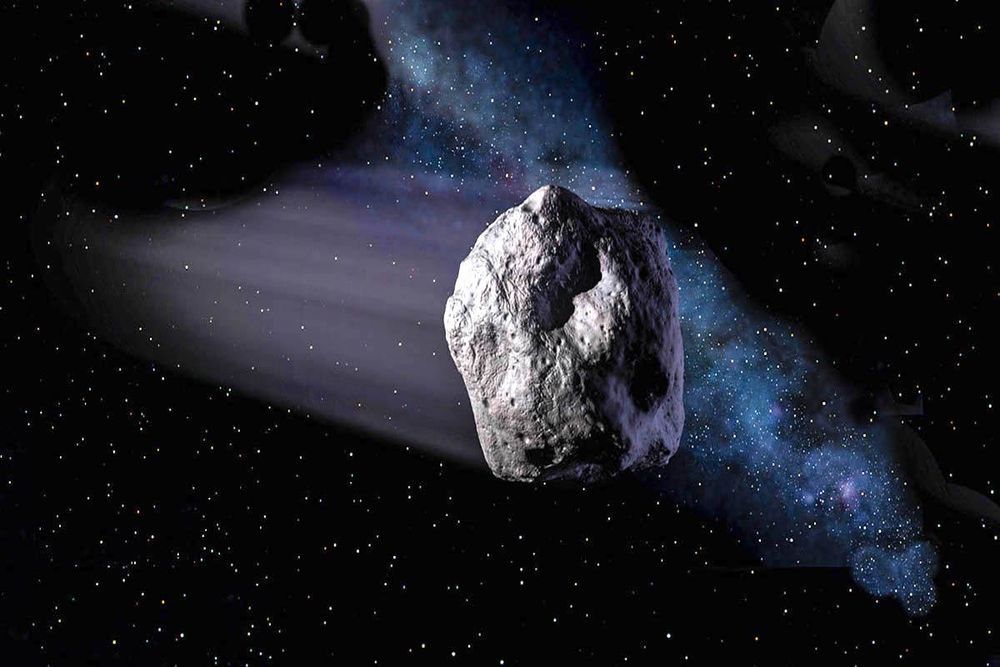


Using steam to propel a spacecraft from asteroid to asteroid is now possible, thanks to a collaboration between a private space company and the University of Central Florida.
UCF planetary research scientist Phil Metzger worked with Honeybee Robotics of Pasadena, California, which developed the World Is Not Enough spacecraft prototype that extracts water from asteroids or other planetary bodies to generate steam and propel itself to its next mining target.
UCF provided the simulated asteroid material and Metzger did the computer modeling and simulation necessary before Honeybee created the prototype and tried out the idea in its facility Dec. 31. The team also partnered with Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University in Daytona Beach, Florida, to develop initial prototypes of steam-based rocket thrusters.
