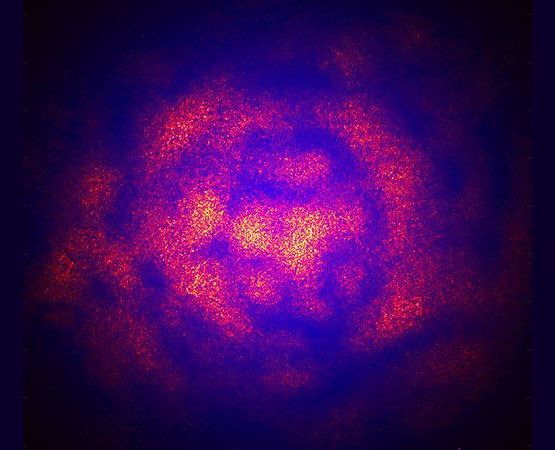
The cosmos was born in a churning fluid 300 million times hotter than the sun. We’ve recreated this hell, and it’s not just hot, it is also very, very strange, says Amanda Gefter (science writer based in London). TO LOOK deep into the fundamental structure of matter is to look billions of years back in time, to the moment when matter first blinked into being. Recreating the conditions of that moment has long been an aim for physicists wanting to understand how the universe evolved from the cosmic fireball that existed a fraction of a second after the big bang. Now researchers at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) at Brookhaven National Laboratory in Upton, New York, have, almost certainly, finally recreated the moments after creation. By colliding nuclei together at enormous speeds, RHIC experimenters were able to break down the structure of nuclear matter. This resulted, most experts agree, in the formation of a long-sought-after plasma that is believed to be the primal stuff of the cosmos, the state of matter at the beginning of time. It turns out, though, that the nature of matter is inextricably tied to the vacuum in which it resides. And the RHIC experiments have thrown up some surprises. They seem to show that the vacuum is a richer and more complicated place than was previously imagined. They suggest the boundary between something and nothing is more blurred than experts had predicted. The stuff made at RHIC is a plasma consisting of quarks and gluons, the most basic building blocks of everything we see around us. Quarks combine in threes to form the protons and neutrons that comprise the nucleus of every atom. But while we can observe a single proton or neutron, we cannot observe a single quark. Quarks are perpetually confined to group living. In fact, the harder you try to pull quarks apart, the stronger the force between them becomes. This is part of the theory of quantum chromodynamics (QCD), which describes how the force between the quarks is carried by the massless gluons.
In QCD, it is the vacuum that imprisons the quarks. While it may sound like a barren place, the vacuum of QCD is a complex, dynamic arena. It writhes with virtual particles that appear in pairs, then annihilate and disappear again. It is haunted by strange creatures of various kinds, too, topologically complex knots and twists that are relatives of wormholes, places where space turns in on itself and seems treacherous. These knots and twists carve out paths for the gluons to travel along, thereby keeping the quarks together. These strange ideas have credence because of the success of QCD in predicting the reactions of fundamental particles. The only way to unglue quarks is to “melt” the vacuum between them. But the vacuum doesn’t give in easily. To raze its jagged terrain requires enormous amounts of concentrated energy, found only in powerful nuclear collisions, or the fireball at the earliest moments of time.