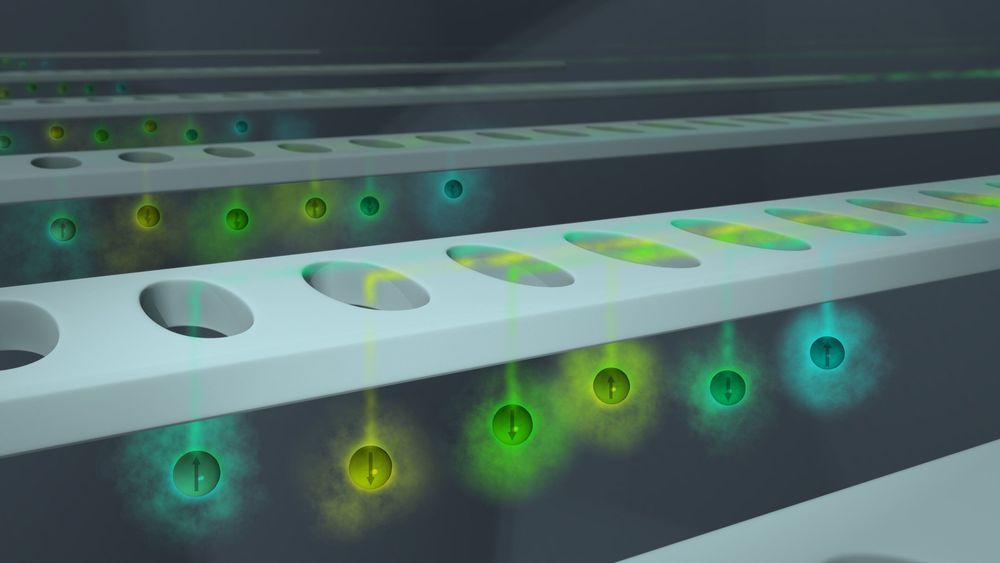
Borrowing a page from high-energy physics and astronomy textbooks, a team of physicists and computer scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has successfully adapted and applied a common error-reduction technique to the field of quantum computing.
In the world of subatomic particles and giant particle detectors, and distant galaxies and giant telescopes, scientists have learned to live, and to work, with uncertainty. They are often trying to tease out ultra-rare particle interactions from a massive tangle of other particle interactions and background “noise” that can complicate their hunt, or trying to filter out the effects of atmospheric distortions and interstellar dust to improve the resolution of astronomical imaging.
Also, inherent problems with detectors, such as with their ability to record all particle interactions or to exactly measure particles’ energies, can result in data getting misread by the electronics they are connected to, so scientists need to design complex filters, in the form of computer algorithms, to reduce the margin of error and return the most accurate results.